Introduction to pH | Biology foundations | High school biology | Khan Academy
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the concept of pH, the pH scale, and its importance in understanding acidity and basicity. It introduces the meaning of pH, the relationship between hydrogen ions and acidity, and explains that the scale ranges from 0 to 14, with 7 being neutral. Substances below 7 are acidic, while those above 7 are basic. The video emphasizes that the pH scale is logarithmic, meaning a one-point change represents a tenfold difference in acidity or basicity. It also highlights the significance of pH in biological and chemical processes and warns against the dangers of extreme pH levels.
Takeaways
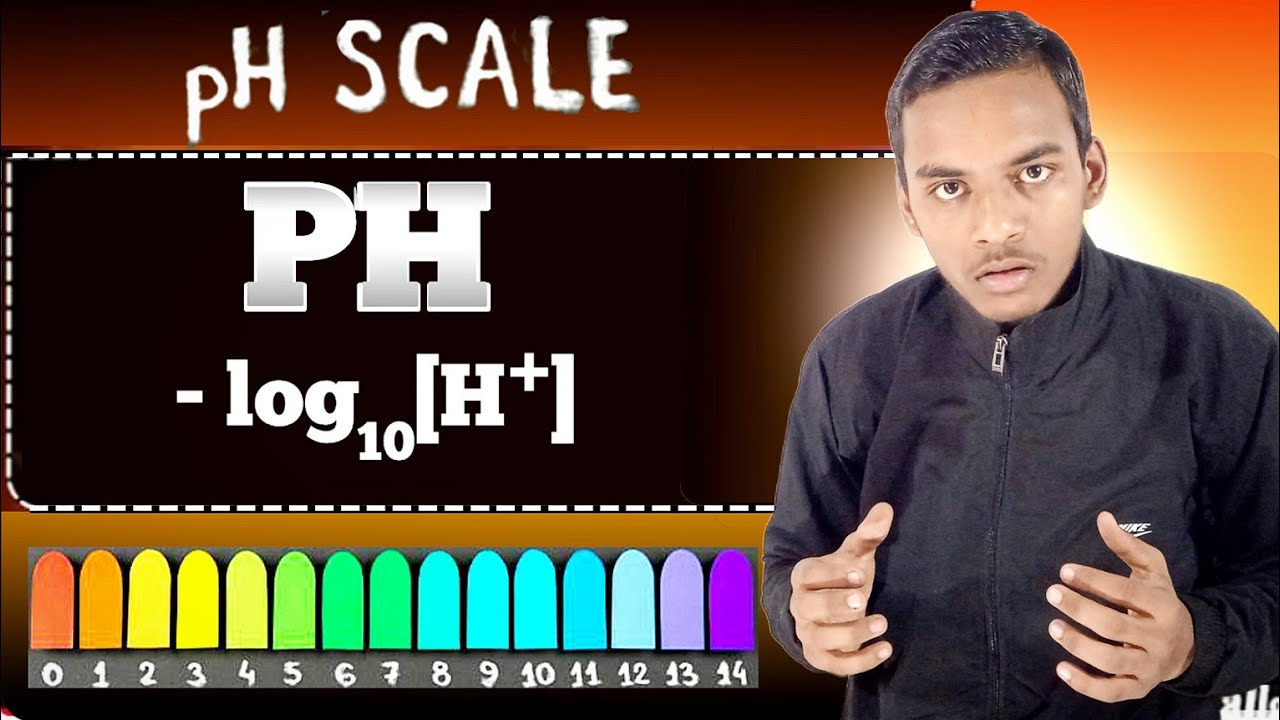
- 😀 pH stands for potential (or power) of hydrogen, and is a measure of acidity or basicity in a substance.
- 😀 The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14, with 7 being neutral, values less than 7 indicating acidity, and values greater than 7 indicating basicity.
- 😀 Acidity is associated with substances that have a high concentration of hydrogen ions (H+).
- 😀 Basicity (or alkalinity) refers to substances that react with hydrogen ions.
- 😀 Common examples of acidic substances include fruits like lemons and grapefruits, as well as orange juice.
- 😀 Basic substances include bleach, ammonia, and liquid drain cleaners. Soap is also considered basic.
- 😀 Strong acids and bases can be harmful to your skin and health, and should not be consumed or tested for taste.
- 😀 pH balance is important in biological systems, such as the blood, and even slight deviations can lead to serious health issues.
- 😀 The pH scale is logarithmic, meaning each step in the scale represents a tenfold change in acidity or basicity.
- 😀 For example, a pH of 4 is 10,000 times more acidic than a pH of 8, showing the significant difference between adjacent pH levels.
- 😀 pH can affect biological reactions and influence chemical reactions, which is important in both biology and chemistry.
Q & A
What does pH stand for?
-pH stands for 'potential of hydrogen' or 'power of hydrogen.' There is some debate about the exact meaning of the 'p,' but it generally refers to how hydrogen ions influence acidity or basicity.
Why is hydrogen important when discussing pH?
-Hydrogen ions (H+) play a major role in determining whether a substance is acidic or basic. Acids tend to have high concentrations of hydrogen ions, while bases tend to react with or neutralize them.
What is the range of the pH scale?
-The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14. A pH of 7 is neutral, below 7 is acidic, and above 7 is basic (or alkaline).
What are some examples of acidic substances?
-Common acidic substances include lemons, grapefruits, and orange juice. These substances typically have a sour taste and are found on the lower end of the pH scale.
What are some examples of basic substances?
-Examples of basic substances include bleach, ammonia solution, and liquid drain cleaner. These substances often have a slippery texture and are found on the higher end of the pH scale.
What does 'alkaline' mean?
-'Alkaline' is another term for basic. It comes from the Arabic word 'alkali,' which referred to compounds that were basic by our modern definition.
Why should we avoid consuming highly acidic or highly basic substances?
-Highly acidic or basic substances are extremely reactive and can cause damage to the skin, cells, and tissues. They can be harmful or even fatal if ingested or improperly handled.
What is the pH of neutral substances?
-Substances that are neutral, such as water or blood, have a pH of 7. These substances are neither acidic nor basic.
Is the pH scale linear?
-No, the pH scale is logarithmic. This means that each step on the scale represents a tenfold increase or decrease in acidity or basicity. For example, a pH of 4 is 10,000 times more acidic than a pH of 8.
How does pH influence biological reactions?
-pH can significantly influence biological reactions, as many enzymes and chemical processes in the body function optimally at specific pH levels. Changes in pH can affect the efficiency or occurrence of these reactions.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Conceito de pH e pOH | Brasil Escola

Pengantar Oseanografi - Acidity, Alkalinity dan Dissolve Gases
What is PH?🤔 PH क्या होता है ll How find it ll Chemistry ll importance in our daily life ll

Why is soil pH important to farmers? | #aumsum #kids #science #education #children

Logarithms and the pH scale

What Is The pH Scale | Acids, Bases & Alkalis | Chemistry | FuseSchool
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)