#AghamUnite: Relativity and the Big Bang
Summary
TLDRThis video delves into Einstein's theory of relativity, contrasting Newtonian mechanics' absolute space-time with special relativity's relative space-time, where time dilation and length contraction occur. It introduces Einstein's equation E=mc^2, highlighting mass-energy equivalence. The video further explores general relativity, explaining gravity as space-time curvature caused by mass. It concludes with the cosmological redshift and its role in the big bang theory, showcasing Einstein's profound impact on our understanding of the universe.
Takeaways
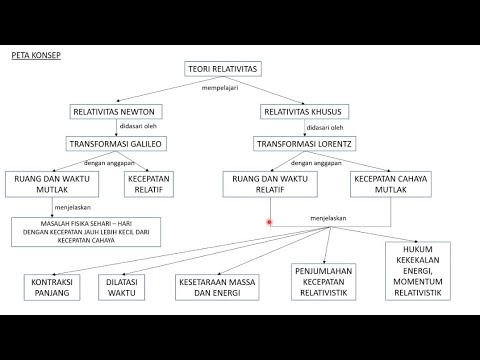
- 📚 Newtonian mechanics is based on absolute space and time, suggesting that physical laws are the same in all inertial frames.
- 🌐 Maxwell's equations, which describe electromagnetic fields, contradict Newtonian mechanics by showing that results can vary with different reference frames.
- 🚀 Einstein's Special Relativity challenges Newtonian mechanics, proposing that space and time are relative and intertwined, forming a single entity called spacetime.
- ⏱️ Time dilation and length contraction are phenomena predicted by Special Relativity, where the experience of time and the measurement of length differ for objects in motion relative to an observer.
- 💡 The principle of invariant light speed is a cornerstone of Special Relativity, stating that the speed of light is constant across all reference frames.
- ⚖️ Energy and mass are equivalent, as expressed by Einstein's famous equation E = mc^2, which has profound implications for understanding the universe's energy dynamics.
- 🌌 General Relativity extends Special Relativity by including gravity, asserting that gravity is not a force but a curvature of spacetime caused by mass.
- 🌍 The curvature of spacetime by massive objects like the sun influences the motion of other objects, such as planets, explaining the structure of the solar system.
- 🌑 Black holes are regions of spacetime where mass is so concentrated that it deforms spacetime significantly, leading to an intense gravitational pull.
- 🌌 Cosmological redshift occurs as light stretches due to the warping of spacetime, resulting in a longer wavelength as it travels through the universe.
Q & A
What is Newtonian mechanics and how does it relate to the concept of absolute space and time?
-Newtonian mechanics is the application of Newton's laws of motion. It states that all inertial frames are retained and space and time are absolute, meaning that physical experiments yield the same results regardless of the motion of the reference frame.
How do Maxwell's equations differ from Newtonian mechanics in terms of space and time?
-Maxwell's equations describe electromagnetic fields and their results are not constant but change depending on the situation. Unlike Newtonian mechanics, which assumes absolute space and time, Maxwell's equations imply that the results can vary with different reference frames.
What is the theory of special relativity and how does it challenge Newtonian mechanics?
-Special relativity, created by Albert Einstein, contradicts Newtonian mechanics by stating that space and time are not independent but can be mixed, forming a single entity called space-time. It also asserts that space and time are relative and depend on reference frames.
What are the two postulates of special relativity?
-The two postulates of special relativity are: 1) The principle of relativity, which states that the laws of physics are the same in all inertial frames, and 2) The principle of invariant light speed, which asserts that the speed of light is constant in a vacuum, regardless of the motion of the light source or observer.
What is time dilation and how is it explained by special relativity?
-Time dilation is the phenomenon where time appears to move slower for an object in motion relative to a stationary observer. Special relativity explains this as a consequence of the relative nature of space and time, where the motion of the object affects the passage of time as experienced by the observer.
What is length contraction and how does it relate to the motion of an object?
-Length contraction is the phenomenon where the length of an object in motion is measured to be shorter than its length at rest, as observed by a stationary observer. This is a consequence of special relativity, indicating that the motion of the object affects its measured length.
What is the famous equation derived from special relativity that relates energy and mass?
-The famous equation derived from special relativity is E = mc^2, where E is energy, m is mass, and c is the speed of light. This equation shows that mass can be converted into energy and vice versa.
Why is the speed of light significant in the context of special relativity?
-The speed of light is significant in special relativity because it is the ultimate speed limit in the universe. Nothing can move faster than light, and it is the constant speed that light travels in a vacuum, which is approximately 3 x 10^8 meters per second.
What is general relativity and how does it differ from special relativity?
-General relativity is Einstein's theory that explains gravity as the curvature of space-time caused by massive bodies. It differs from special relativity in that it includes gravity in its framework, while special relativity does not account for gravitational effects.
How does general relativity explain the force of gravity?
-General relativity explains gravity as the warping of space-time by massive objects. The curvature of space-time influences the path of objects, causing them to move along curved trajectories, which we perceive as the force of gravity.
What is the cosmological redshift and how is it related to general relativity?
-The cosmological redshift is the stretching of light as it travels through the expanding universe, causing the light to shift towards the red end of the spectrum. This phenomenon is related to general relativity as it demonstrates how the stretching of space-time affects the properties of light.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Special Relativity | Speed of Light and Spacetime | Time Dilation and Length Contraction

Theory of relativity explained in 7 mins

Einstein’s relativity simply explained in Quran - There Is No Clash

Teori Relativitas Khusus Kelas 12 Kurikulum Merdeka | Relativitas; Panjang, Massa, Waktu & Kecepatan
Teori Relativitas Khusus: 1. Pendahuluan

Teoria da Relatividade Restrita
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)