Coronary Angioplasty 3d medical animation by Dandelion Team
Summary
TLDRThe script explains coronary artery disease, caused by cholesterol plaques narrowing the arteries. Coronary angioplasty is a procedure to widen these arteries without surgery. A catheter and guidewire are used to navigate to the heart, where a balloon inflates to compress plaques. A stent, often drug-coated, is then deployed to keep the artery open, improving blood flow to the heart. The stent remains permanently to prevent re-narrowing and plaque buildup.
Takeaways
- 💓 The heart, like all organs, requires a constant supply of blood, provided by the coronary arteries.
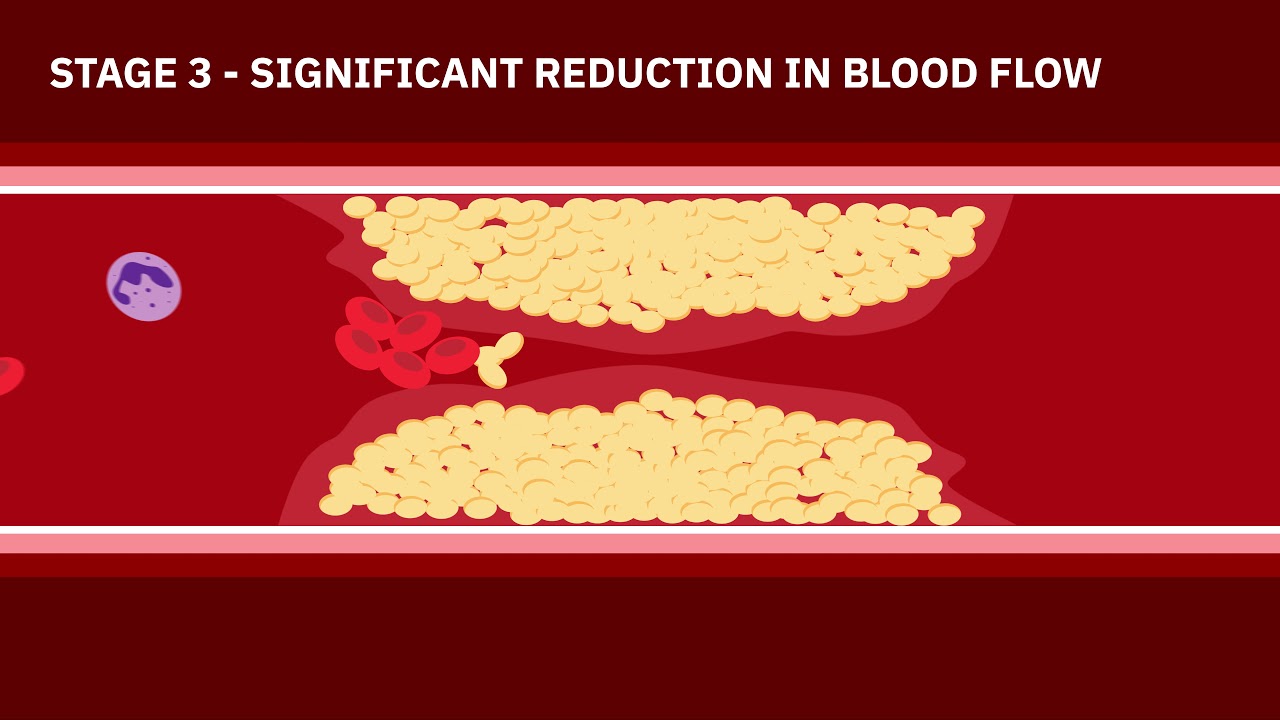
- 🚫 Coronary artery disease is caused by plaque buildup, which is composed of cholesterol deposits that narrow the arteries over time.
- 🩺 Coronary angioplasty is a procedure to widen blocked or narrowed coronary arteries without the need for open-heart surgery.
- 💉 Local anesthesia is used, so patients are awake during the procedure, with a needle inserted through the skin into an artery.
- 🧵 A thin, flexible guide wire is inserted through the needle and navigated to the heart via the arterial system.
- 🌐 A catheter is advanced through the coronary arteries, and a contrast dye is injected to identify arterial blockages via fluoroscopy.
- 🎈 If significant blockages are found, a small balloon is guided to the affected area and inflated to widen the artery and compress fatty deposits.
- 🛠️ A stent, a tiny coil of wire mesh, is used to support the artery walls and prevent re-narrowing after angioplasty.
- 🔄 The stent is collapsed around a balloon, guided through the blockage, and expands when the balloon is inflated, locking into place.
- 💊 Most stents implanted are drug-coated, slowly releasing medication to prevent future plaque buildup and arterial re-narrowing.
- 🔚 After the stent is in place, the balloon and catheter are deflated and removed, completing the angioplasty procedure.
Q & A
What is the primary function of the coronary arteries?
-The coronary arteries are responsible for supplying a constant flow of blood to the heart.
What causes coronary artery disease?
-Coronary artery disease is caused by plaque buildup, which consists of cholesterol deposits, in the walls of the coronary arteries, leading to narrowing over time.
What is a coronary angioplasty and why is it performed?
-A coronary angioplasty is a medical procedure used to widen blocked or narrowed coronary arteries without the need for open-heart surgery.
How is the patient typically prepared for a coronary angioplasty?
-The skin is numbed, and the patient remains awake during the procedure. A needle is inserted through the skin into one of the arteries via an incision in the groin, wrist, or arm.
What is the purpose of the guide wire used in the procedure?
-The guide wire is inserted through the needle into the artery and up to the heart, allowing the catheter to be advanced to the coronary arteries.
What is the role of the contrast dye in the angioplasty procedure?
-The contrast dye is injected through the tube to make the blockages in the artery visible under fluoroscopy, an X-ray imaging technique.
What is the purpose of the small balloon used in the angioplasty?
-The small balloon is used to widen the affected section of the artery by squashing the fatty deposits against the artery wall when inflated.
What is a stent and how does it function in an angioplasty?
-A stent is a tiny coil of wire mesh that supports the walls of the artery and helps prevent it from re-narrowing. It is collapsed around a balloon and guided through the blockage, expanding and locking into place when the balloon is inflated.
Why are most stents implanted during an angioplasty drug-coated?
-Drug-coated stents release medication slowly to help prevent future plaque buildup and the re-narrowing of the blood vessel.
What happens after the stent is successfully placed in the artery?
-Once the stent is in place, the balloon and catheter are deflated and removed, leaving the stent to permanently hold the artery open and improve blood flow to the heart.
What is the significance of fluoroscopy in the angioplasty procedure?
-Fluoroscopy is an X-ray device used to identify blockages in the artery by visualizing the contrast dye, guiding the doctor in the placement of the stent and balloon.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)