11 Human Rights And Bill Of Rights
Summary
TLDRThe video script discusses the fundamental nature of human rights, which are inherent to all individuals regardless of background or beliefs. It highlights the universality and inalienability of these rights, emphasizing their importance in allowing people to live with dignity and freedom from abuse. The script further explains different classes of rights, including natural, constitutional, statutory, and political rights, and outlines specific rights protected by the 1987 Philippine Constitution, such as the right to due process, freedom of expression, and the right against torture. It underscores the role of the Bill of Rights in safeguarding citizens' rights and privileges.
Takeaways
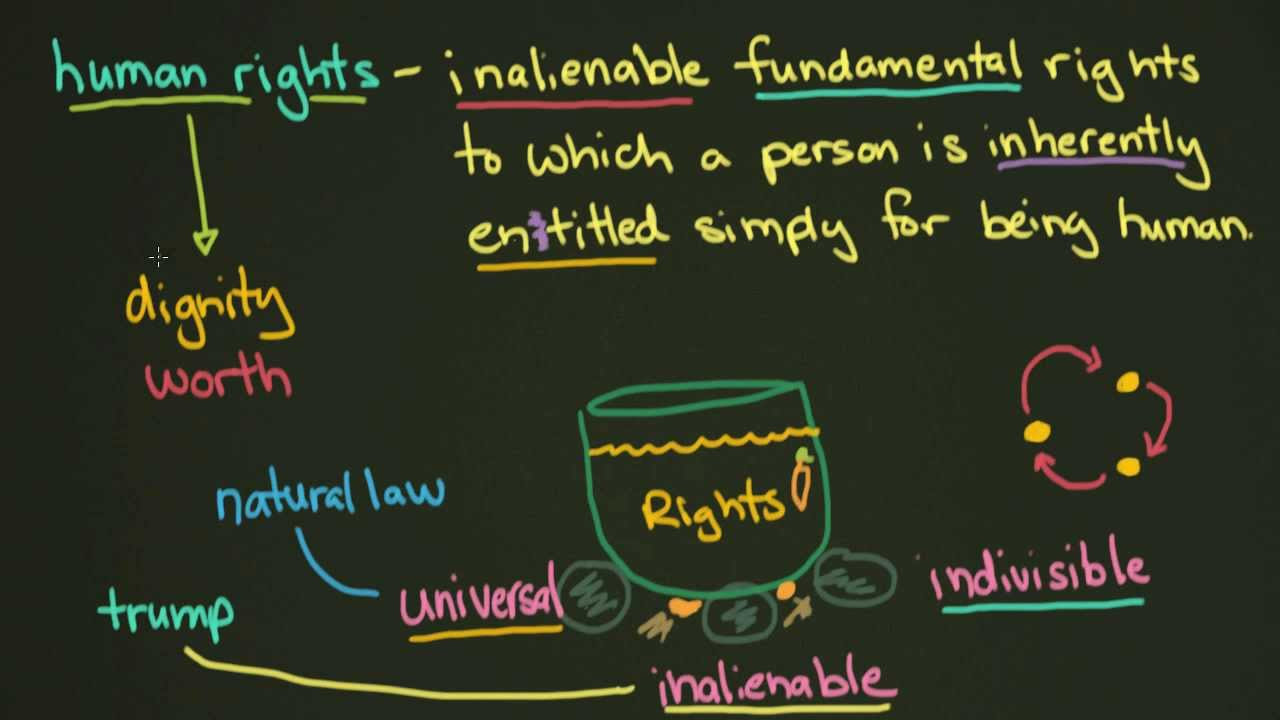
- 🌍 Human rights are universal and inalienable, applying to every person regardless of their origin, beliefs, or lifestyle.
- 🔒 These rights are inherent and cannot be taken away; they are not granted by governments but are fundamental to human dignity and peace.
- 📜 The concept of human rights predates formal law, being 'inscribed in the hearts of people' long before legal documents were drafted.
- 😡 Despite their universality, human rights violations are widespread, highlighting the ongoing struggle for their protection and enforcement.
- 🌐 The United Nations emphasizes the interdependence and indivisibility of human rights, where the state of one right can impact others.
- 🏛 Human rights are categorized into natural rights (from God), constitutional rights (protected by law), statutory rights (provided by legislation), and political and economic rights.
- 📝 The Philippine Constitution of 1987, specifically Article 3, enshrines a comprehensive list of rights and freedoms for its citizens.
- 🚫 The Bill of Rights in the Philippine Constitution includes prohibitions on torture, unreasonable searches, and self-incrimination, among other protections.
- 🏢 Economic rights allow individuals to access resources and engage in professions, contributing to their ability to provide for themselves and their families.
- 🏛️ The right to due process and equality before the law ensures fair treatment and justice for all individuals in legal matters.
- 🗳️ Political rights enable citizens to participate in governance and influence the administration, fostering a democratic society.
- 🏡 The right to abode includes the freedom to immigrate and work in a country without immigration restrictions, exemplifying personal freedom.
Q & A
What are human rights and why are they important?
-Human rights are the basic rights and freedoms that belong to every person from birth until death, regardless of their origin, beliefs, or lifestyle. They are important because they allow individuals to live in dignity and peace, protecting them from abuses by institutions or individuals.
What does the term 'Universal inalienable rights' mean?
-Universal inalienable rights refer to rights that belong to all individuals, no matter who they are or where they are from, and cannot be taken away unless a specific situation calls for it, as defined by the United Nations.
How are human rights described in terms of their impact on each other?
-Human rights are described as interdependent and indivisible, meaning that the fulfillment or violation of one right can directly affect others.
What does the principle of non-discrimination in human rights entail?
-The principle of non-discrimination in human rights means that all people should be protected and respected without prejudice, regardless of race, nationality, gender, religion, or political leaning.
What are the different classes of rights mentioned in the script?
-The different classes of rights mentioned are natural rights, constitutional rights, statutory rights, and political rights, each with specific implications and protections.
What are natural rights and why are they considered a gift from God?
-Natural rights are rights that are considered inherent and inalienable, such as the right to live and the right to be loved. They are seen as a gift from God because they exist independently of any government or legal system.
Can you explain the concept of constitutional rights?
-Constitutional rights are rights that are conferred and protected by a country's constitution, such as the right to due process and the prohibition of torture.
What are statutory rights and how do they differ from constitutional rights?
-Statutory rights are rights provided by laws that are promulgated by the lawmaking body and can be abolished by the same body, such as the right to a minimum wage or the right to preliminary investigation. They differ from constitutional rights in that they are not as deeply entrenched in the legal system.
How do economic rights relate to the concept of democracy?
-Economic rights, in a democratic context, refer to the rights to have access to certain resources like land, labor, and capital, which enable individuals to practice their chosen profession or find work, thus supporting their livelihood.
What does the 1987 Philippine Constitution say about human rights?
-The 1987 Philippine Constitution, specifically Article 3 or the Bill of Rights, declares and protects the rights and privileges of Filipino citizens, including prohibition from torture, the right to due process, and the right to privacy.
Can you provide an example of a right mentioned in the Bill of Rights that protects against unlawful practices?
-An example is the right against unreasonable searches and seizures, which protects individuals from violations of their privacy and property without proper legal justification.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)