SuperPro Designer: Modeling a Reactor and Separator
Summary
TLDRThis video provides a step-by-step guide to simulating the biodiesel production process from soybean oil using SuperPro Designer. It covers key stages including registering components (methanol, soybean oil, sodium methoxide), configuring a continuous stirred-tank reactor (CSTR) for the transesterification reaction, and using a centrifuge for separation. The process also involves setting up material and energy balances, adjusting operational parameters, and optimizing equipment for efficient production. The simulation aims for an 83% conversion of soybean oil, with detailed attention to reactor power consumption, separation efficiency, and potential system recycling for higher yields.
Takeaways
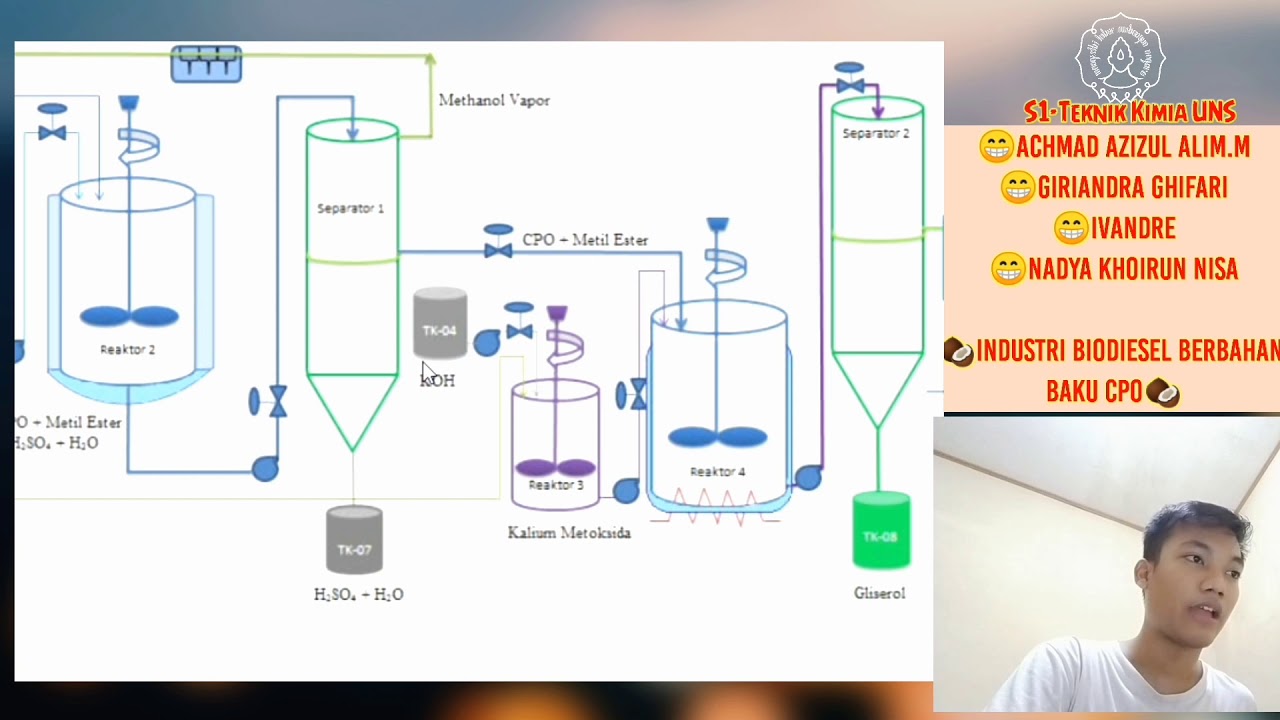
- 😀 The process involves designing a reactor and a separation unit to obtain biodiesel from soybean oil through a transesterification reaction with methanol.
- 😀 The reaction produces biodiesel and glycerol, with 83% conversion of soybean oil as per the given parameters.
- 😀 SuperPro Designer software is used to simulate the process, where components like methanol, soybean oil, sodium methoxide, biodiesel, and glycerol are registered.
- 😀 Key properties, such as molecular weight, density, boiling point, and critical pressure, are entered for each component used in the simulation.
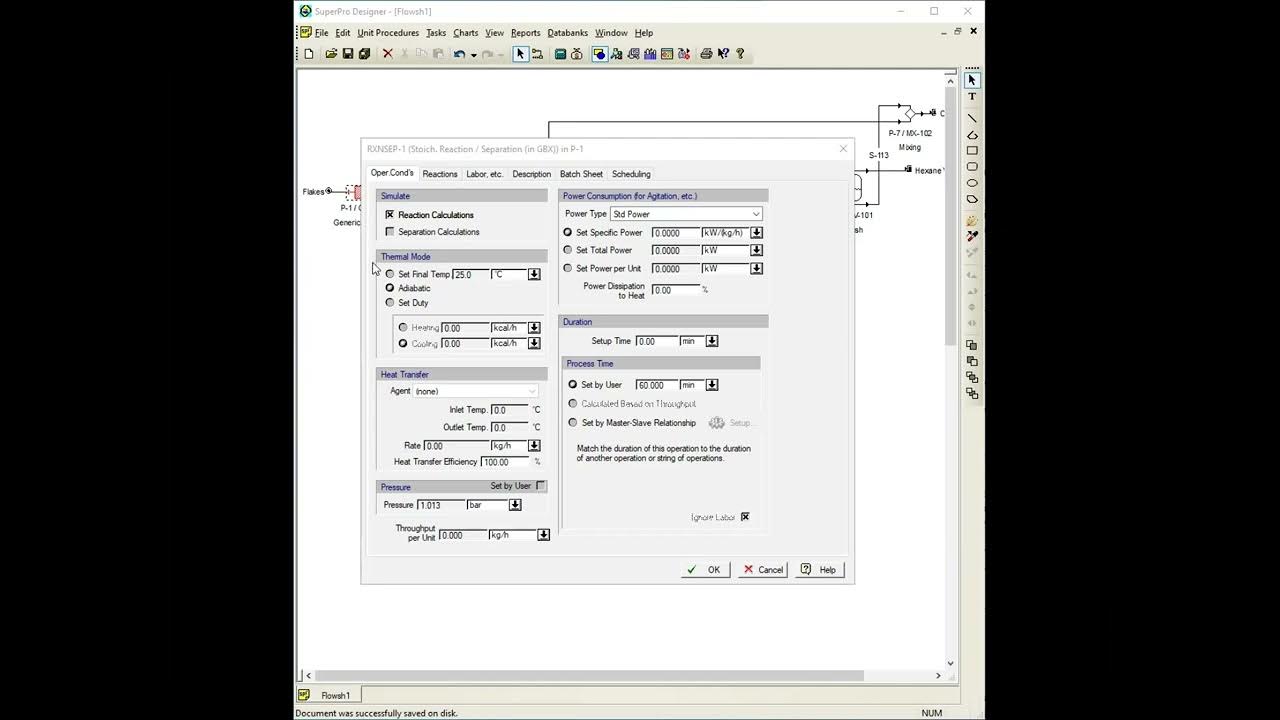
- 😀 The process uses a Continuous Stirred Tank Reactor (CSTR) with specific power consumption for agitation and a centrifuge for separation of biodiesel from the products.
- 😀 The reactor's operation is set based on the given power for agitation, and stoichiometry is entered for the reaction between methanol and soybean oil.
- 😀 In the CSTR, the stoichiometry is defined as 3 moles of methanol per mole of soybean oil, producing 3 moles of biodiesel and 1 mole of glycerol.
- 😀 The centrifuge is set to remove 99.99% of biodiesel and soybean oil, with specified power consumption for the separation process.
- 😀 After the separation, additional steps, like splitting glycerol and methanol from impurities, and recycling unreacted soybean oil, are suggested to improve overall conversion.
- 😀 The batch time for the entire process is 4 hours, and scheduling using a Gantt chart is recommended to optimize equipment operation and timing in batch or continuous modes.
Q & A
What is the main objective of the process described in the video?
-The main objective is to design a reactor and a separation unit to produce biodiesel from soybean oil through a transesterification reaction.
What are the key components involved in the biodiesel production process?
-The key components are soybean oil, methanol, sodium methoxide (as a catalyst), biodiesel, and glycerol.
What is the role of sodium methoxide in the process?
-Sodium methoxide is used as a catalyst to facilitate the transesterification reaction between soybean oil and methanol to produce biodiesel and glycerol.
What is the significance of the 83% conversion rate mentioned in the video?
-The 83% conversion rate refers to the efficiency of the transesterification reaction, indicating that 83% of the soybean oil is converted into biodiesel and glycerol.
What is the function of the centrifuge in the process?
-The centrifuge is used to separate the biodiesel and soybean oil from the other products, primarily glycerol and methanol, based on their density differences.
What is the importance of selecting the correct operating conditions for the reactor?
-Selecting the correct operating conditions, such as temperature, pressure, and power for agitation, ensures optimal performance and conversion rates for the reaction in the reactor.
How are the components registered in the simulation software?
-Components are registered in the SuperPro Designer software by selecting 'Tasks', then 'Pure Components', and adding components like methanol, soybean oil, sodium methoxide, and glycerol. Specific properties such as molecular weight and pressure are also inputted.
What is the purpose of defining the stoichiometry in the reactor?
-Defining the stoichiometry in the reactor ensures that the correct molar ratios are used for the reactants (methanol and soybean oil) and products (biodiesel and glycerol), which is critical for accurate simulations and material balance calculations.
What does the power consumption of 1.4 kW per cubic meter in the reactor indicate?
-The power consumption of 1.4 kW per cubic meter indicates the amount of energy required for agitation within the reactor, ensuring that the reaction occurs effectively.
Why is steam chosen as the heat transfer agent in the reactor?
-Steam is chosen as the heat transfer agent because it is effective at providing the necessary heat to maintain the desired reaction temperature in the reactor, especially at elevated temperatures.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)