PROSES TRANSFORMASI BAKTERI (REPRODUKSI BAKTERI)
Summary
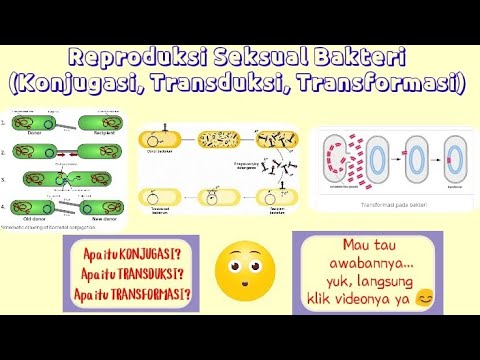
TLDRThis video discusses the process of bacterial transformation, where bacteria acquire DNA from their environment. It explains how bacterial cells recognize and transport DNA into their own cells. The process begins when a donor bacterial cell breaks open, releasing DNA fragments. These fragments can be taken up by a recipient cell, potentially integrating into its DNA if they are similar. This results in recombinant DNA and alters the bacterial characteristics. If the DNA is not compatible, it may be degraded or exist as a plasmid within the recipient cell.
Takeaways
- 😀 Transformation is a process where bacteria acquire DNA from their surroundings.
- 😀 The bacterial cell surface has proteins that recognize DNA from closely related species.
- 😀 These proteins help transport DNA into the bacterial cell.
- 😀 The process of transformation starts when a donor bacterial cell undergoes lysis and releases DNA fragments.
- 😀 Some of the DNA fragments are taken up by a recipient bacterial cell.
- 😀 If the donor DNA is similar to the recipient's DNA, it will integrate into the recipient's genome, forming recombinant DNA.
- 😀 This change in DNA structure causes a change in the bacterial traits.
- 😀 If the donor DNA is not similar to the recipient DNA, it is degraded by nucleases.
- 😀 Occasionally, donor DNA can exist alongside the recipient's DNA as a plasmid.
- 😀 The transformation process involves both the donor and recipient bacteria interacting with their DNA.
Q & A
What is transformation in bacteria?
-Transformation is the process by which bacteria acquire DNA from their surrounding environment.
How does bacterial transformation occur?
-Bacterial transformation occurs when a bacterial cell, called the donor, releases DNA fragments into the environment. These fragments are then taken up by a recipient cell, which may incorporate the DNA into its own structure.
What role do the proteins on the surface of bacterial cells play in transformation?
-Proteins on the surface of bacterial cells help recognize DNA from closely related species and assist in transporting the DNA into the cell.
What happens when the donor cell undergoes lysis?
-When the donor bacterial cell undergoes lysis (breaks apart), its DNA is released in fragments, which may then be taken up by a recipient cell.
What is a recombinant DNA?
-Recombinant DNA is formed when the donor DNA successfully integrates into the recipient's DNA, creating a new combination of genetic material.
What determines whether the donor DNA will integrate into the recipient's DNA?
-If the donor DNA closely resembles the recipient's DNA, it will integrate into the recipient's genome, forming recombinant DNA. If the donor DNA is too different, it may be degraded.
What happens if the donor DNA is incompatible with the recipient DNA?
-If the donor DNA is not similar enough to the recipient DNA, it will be degraded by nucleases, which break down the foreign DNA.
Can donor DNA survive in the recipient cell without integrating?
-Yes, sometimes donor DNA can survive within the recipient cell as a plasmid, a small circular piece of DNA that exists independently of the bacterial chromosome.
What are plasmids, and how do they relate to bacterial transformation?
-Plasmids are small, circular DNA molecules that can exist independently within bacterial cells. During transformation, donor DNA may survive as a plasmid in the recipient cell instead of integrating into the chromosome.
What are the implications of transformation for bacterial traits?
-The incorporation of new DNA into a bacterial cell can lead to changes in the bacteria's traits, including new abilities or characteristics.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)