Introduction to signal flow grsphs
Summary
TLDRIn this session, the instructor discusses signal flow graphs, emphasizing the application of Mason's rule for solving complex systems. The lesson covers identifying forward paths and feedback loops, detailing the necessary formulas and calculations involved. Participants learn to differentiate between various paths and how to convert block diagrams into signal flow graphs for better understanding. The interactive nature of the session allows for clarifying doubts while ensuring that everyone grasps the essential concepts of forward paths and feedback, ultimately enhancing their skills in analyzing signal flow systems.
Takeaways
- 😀 The topic discussed is signal flow graphs and the use of Mason's Rule for analysis.
- 😀 Mason's Rule involves using the formula C/R, where C represents the controlled output and R represents the reference input.
- 😀 The forward path is identified as the path directing to the right in the signal flow graph, with examples of paths given (e.g., G1, G2, G3).
- 😀 Feedback loops are integral to signal flow graphs, and multiple loops can exist simultaneously.
- 😀 The delta (Δ) is calculated by subtracting the contributions of feedback loops from the forward path.
- 😀 In the example, two forward paths are identified, which lead to specific calculations for determining the output.
- 😀 The identification of feedback loops is essential, with specific examples provided for clarity.
- 😀 The graph must be converted into a block diagram for better understanding, ensuring alignment between the two forms.
- 😀 There is a focus on recognizing and converting negative feedbacks within the signal flow.
- 😀 The session encourages engagement and understanding of the concepts through practice and assignments related to the signal flow graphs.
Q & A
What is the main topic discussed in the transcript?
-The main topic discussed is signal flow graphs, specifically how to apply Mason's rule to solve problems related to these graphs.
What is Mason's rule used for in signal flow graphs?
-Mason's rule is used to calculate the overall transfer function of a system represented by a signal flow graph by considering forward paths and feedback loops.
How do you identify forward paths in a signal flow graph?
-Forward paths are identified by tracing the path from the input to the output, counting all unique routes that the signal can take without retracing any steps.
What is the significance of feedback loops in signal flow graphs?
-Feedback loops are significant because they influence the overall output of the system. They need to be counted and evaluated correctly when applying Mason's rule.
What does the delta value represent in Mason's rule?
-The delta value represents the overall contribution of the feedback loops to the transfer function, calculated as 1 minus the sum of the feedback loops affecting a given forward path.
How many forward paths were identified in the transcript, and what were they?
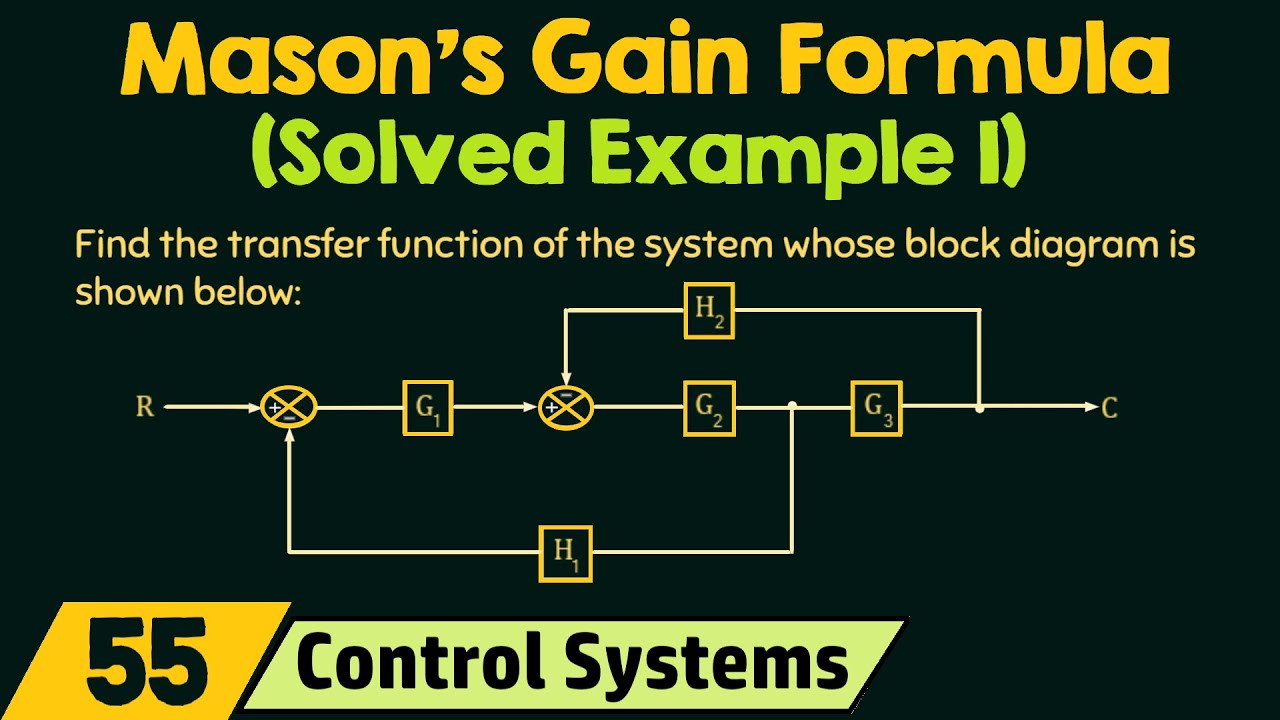
-Two forward paths were identified: one through G1, G2, G3 and another through G1, G4.
What is the first step to applying Mason's rule according to the transcript?
-The first step is to identify all forward paths and feedback loops in the signal flow graph.
What approach does the speaker recommend for converting a block diagram into a signal flow graph?
-The speaker recommends aligning the components of the block diagram with the signal flow graph to simplify the visualization and identification of paths and loops.
What happens to the forward path when feedback loops are involved?
-When feedback loops are involved, the forward path contributions may be affected, and specific calculations need to be made to account for the feedback when applying Mason's rule.
Why does the speaker emphasize understanding each component before using the formulas?
-The speaker emphasizes this understanding to ensure that students can accurately apply the formulas and derive correct results without confusion, enhancing their overall comprehension of the topic.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео
Mason’s Gain Rule (Solved Example 1)

SPLDV (Substitusi, Eliminasi, Campuran)

Plus Two Maths Onam Exam | Continuity and Differentiability in 20 Min | Exam Winner Plus Two

GDA-110 Metnum | Aturan Cramer

Algorithm Design | Network Flow | Ford-Fulkerson Algorithm | MAXIMAL FLOW PROBLEM | MAX FLOW PROBLEM

Analisis Node (Simpul)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
