Introduction to Carbohydrates
Summary
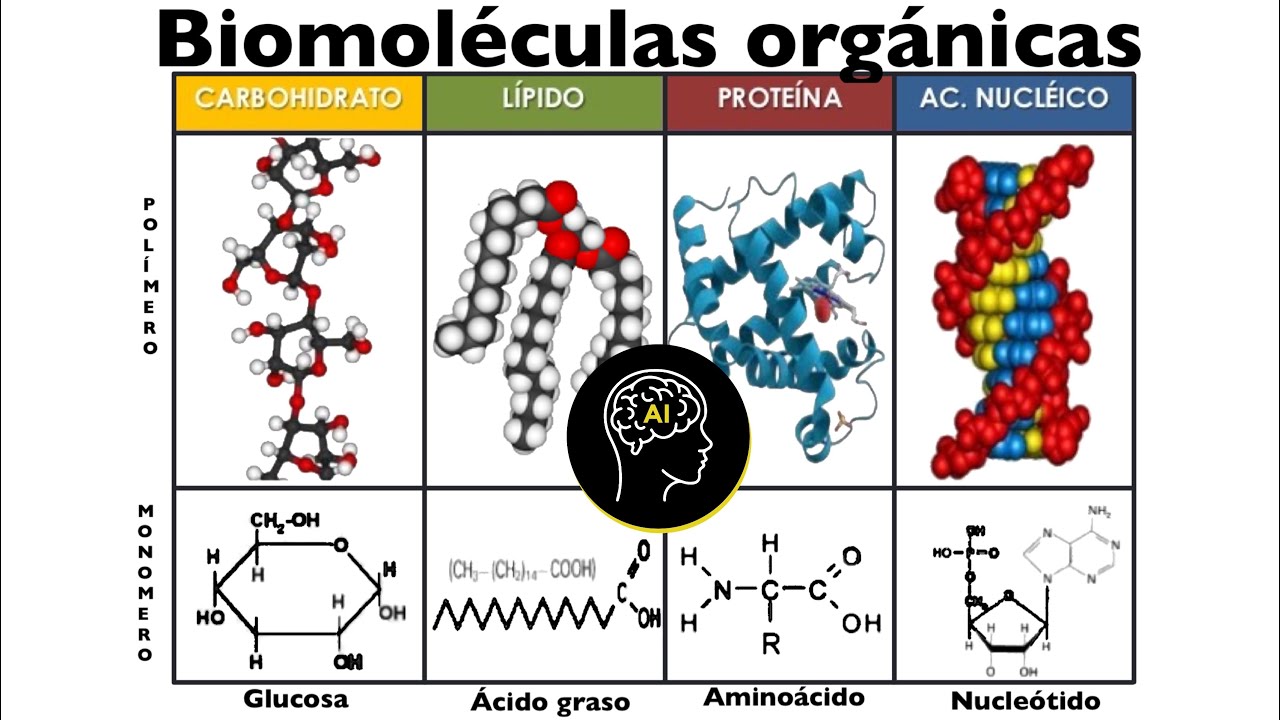
TLDRThis lecture delves into the third class of biomolecules: carbohydrates or sugars. It outlines their diverse roles in nature, emphasizing glucose as the primary sugar molecule used by organisms. Plants produce sugars by harnessing solar energy, which is then stored in chemical bonds. These sugars serve as energy sources, components of nucleic acids like RNA and DNA, modifiers of lipids and proteins, and structural components of cell walls in plants and bacteria. The lecture also touches on the significance of sugars in energy storage, genetic information transfer, and the enhancement of molecular capabilities.
Takeaways
- 🌿 Carbohydrates, or sugars, are the third class of biomolecules discussed after proteins and nucleic acids.
- 🌞 Sugar molecules, like glucose, primarily come from plants which capture and transform solar energy into chemical bonds.
- 🔋 The energy stored in sugar molecules is used by organisms, including humans, for various cellular processes and energy storage in the form of ATP.
- 🍞 When we consume carbohydrates like bread or pasta, our body breaks them down into monomer sugars, often converting them into glucose for energy production.
- 🧬 Sugars are also components of nucleic acids such as RNA and DNA, playing a role in storing and passing genetic information.
- 🔗 Sugars can modify proteins and lipids, enhancing their capabilities and functionality, as seen in glycoproteins like the tissue factor involved in blood clotting.
- 🌱 In plant and bacterial cells, sugars form part of the cell walls, providing protection, structure, and facilitating communication and transport.
- 🌐 The process of photosynthesis in plants involves the conversion of sunlight into chemical energy stored in sugar molecules.
- 🔬 The script briefly mentions the upcoming detailed discussion on how sugars modify lipids and proteins in future lectures.
- ♻️ Excess glucose can be stored as glycogen for later use, demonstrating the body's ability to manage energy resources.
Q & A
What are the four major classes of biomolecules?
-The four major classes of biomolecules are carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids.
What is the primary role of sugars in biological systems?
-The primary role of sugars in biological systems is energy storage and fuel source, as they can be broken down to produce ATP molecules.
How do plants produce sugar molecules?
-Plants produce sugar molecules through the process of photosynthesis, where they capture energy from sunlight and convert it into chemical bonds within the sugar molecules using carbon dioxide and water.
What is the source of energy that plants use to produce sugar molecules?
-The source of energy that plants use to produce sugar molecules is sunlight, which is captured and transformed into chemical energy stored in the sugar molecules.
How does the human body utilize glucose?
-The human body utilizes glucose as a primary source of energy. It is broken down through glycolysis and aerobic cellular respiration to produce ATP, which is used for various cellular processes.
What happens to excess glucose in the body?
-If the body has an excess of glucose, it can be stored as glycogen for later use, preventing the overproduction of ATP molecules.
What is the second role of sugars mentioned in the script?
-The second role of sugars is being a component of nucleic acids such as RNA and DNA, where they form the backbone of these molecules and are essential for storing and passing genetic information.
What is the difference between ribose and deoxyribose sugars?
-The difference between ribose and deoxyribose is that deoxyribose lacks a hydroxyl group on the second carbon, which is present in ribose. This difference is significant in the structure of DNA and RNA.
How do sugars modify the functionality of proteins and lipids?
-Sugars can be attached to proteins and lipids to form glycoproteins and glycolipids, respectively. This modification diversifies their capabilities and functionality, allowing for increased molecular interactions and roles in biological processes.
What is the role of sugars in the coagulation cascade?
-In the coagulation cascade, sugars are part of glycoproteins like tissue factor, which initiates the blood clotting process by interacting with other molecules such as Factor 7, specifically starting the extrinsic pathway of the cascade.
Why are cell walls important in plant and bacterial cells?
-Cell walls in plant and bacterial cells are important because they provide protection, structure, and play roles in communication and transport processes essential for the cell's survival and function.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)