Grade 10 SCIENCE | Quarter 4 Modules 3-4 | Biomolecules
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, Mam Deya introduces the topic of biomolecules, focusing on carbohydrates, proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids, and their importance in human health. She explains the role of these biomolecules in the body, such as energy production, growth, and repair. Through examples from everyday food, like donuts and fruits, she explains how different biomolecules contribute to well-being. The video also includes simple scientific tests to identify these biomolecules in food, such as the iodine test for starch and the Benedict’s test for sugars. The lesson offers a thorough yet engaging exploration of the molecules of life.
Takeaways
- 😀 Biomolecules are large molecules crucial for life and are obtained from food.
- 😀 The four main types of biomolecules are carbohydrates, proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids.
- 😀 Carbohydrates are the body's primary energy source, and they come in the forms of sugars (monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides).
- 😀 The simplest form of carbohydrates is monosaccharides (e.g., glucose, fructose, galactose), which can combine to form disaccharides and polysaccharides.
- 😀 Carbohydrates can be tested using iodine (for starch) and Benedict’s test (for simple sugars).
- 😀 Proteins are body-building molecules, essential for growth, tissue repair, and enzyme functions, and are made up of amino acids.
- 😀 Proteins can be identified using the Biuret test, which turns purple in the presence of protein.
- 😀 Nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) are essential for genetic information storage and transfer, and are composed of nucleotides.
- 😀 Nucleic acids are made up of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and phosphorus, and play a key role in heredity.
- 😀 Lipids are energy-storing molecules that provide long-term energy and protection for internal organs. They include fats, oils, and cholesterol.
- 😀 The presence of lipids can be tested using the ethanol emulsion test, which results in a cloudy solution when lipids are present.
Q & A
What are biomolecules, and why are they important for life?
-Biomolecules are large molecules produced by living organisms, essential for life. They include macromolecules like proteins, polysaccharides, lipids, and nucleic acids, which are necessary for various bodily functions, energy, and growth.
How are biomolecules classified, and what are the four main types?
-Biomolecules are classified into four main types: carbohydrates, proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids. These molecules play different roles, such as providing energy, aiding growth, and storing genetic information.
What is the significance of carbohydrates in the body?
-Carbohydrates are the primary energy source for the body. They provide quick energy and are broken down into simple sugars like glucose, which is vital for cellular functions.
What are monosaccharides, and can you give examples?
-Monosaccharides are the simplest form of carbohydrates, consisting of single sugar molecules. Examples include glucose (blood sugar), fructose (fruit sugar), and galactose (milk sugar).
What is the difference between monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides?
-Monosaccharides are simple sugars (e.g., glucose), disaccharides consist of two monosaccharides (e.g., sucrose), and polysaccharides are complex carbohydrates made of many sugar units (e.g., starch, glycogen, cellulose).
How do proteins contribute to the body’s functions?
-Proteins are essential for growth and repair. They serve as building blocks for tissues like muscles and skin, and help in transporting molecules, controlling chemical reactions, and producing enzymes.
What is the monomer of proteins, and how are they structured?
-The monomer of proteins is an amino acid, which contains carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and sometimes sulfur. Amino acids form peptide bonds to create protein structures.
What are nucleic acids, and why are they important?
-Nucleic acids, like DNA and RNA, store and transmit genetic information. They are essential for heredity and the proper functioning of cells. Their monomers are nucleotides, consisting of a sugar, phosphate group, and nitrogenous base.
What role do lipids play in the body, and what are they made of?
-Lipids are energy storage molecules and help protect organs. They are made of fatty acids and glycerol, and they are important for long-term energy storage and forming protective barriers around cells and organs.
How can we test for the presence of carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids?
-We can test for carbohydrates using the iodine test (for starch) and the Benedict's test (for simple sugars). The Biuret test is used for proteins, and the ethanol emulsion test helps detect lipids.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

La Química de los Alimentos: Cómo los Compuestos Influyen en tu Nutrición y Salud
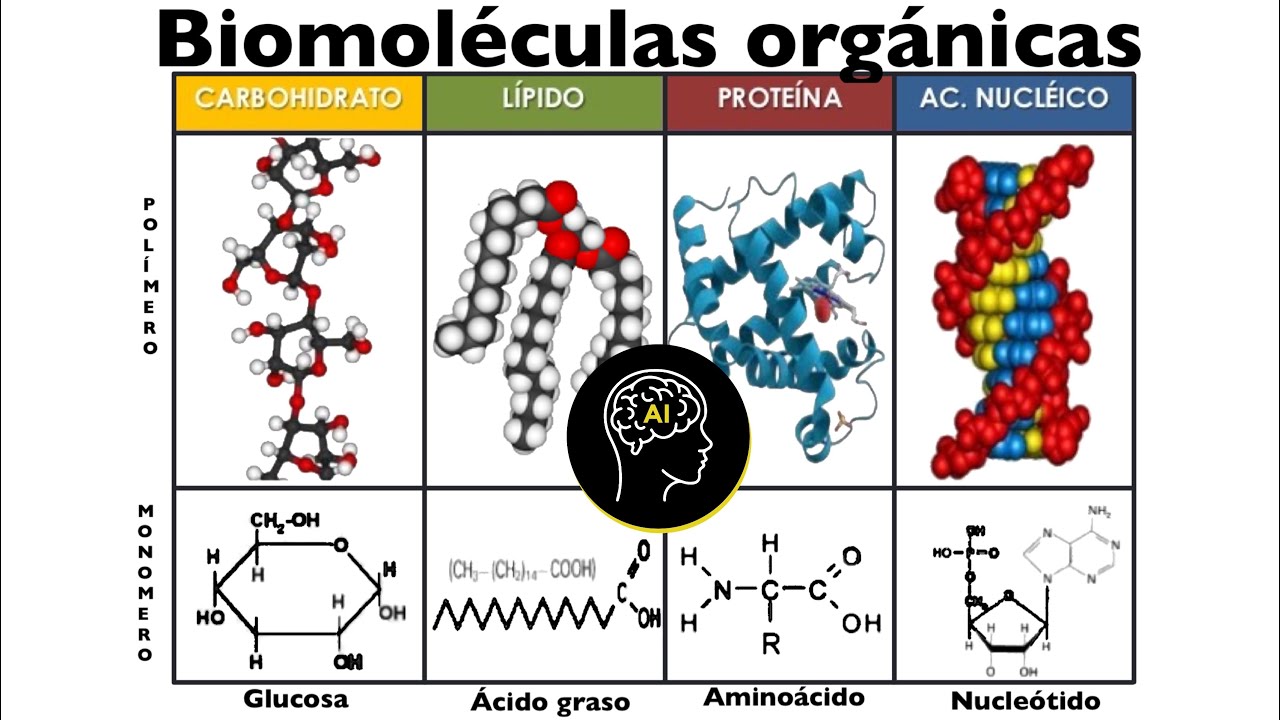
Biomoléculas presentes en células (orgánicas): carbohidratos, lípidos, proteínas y ácidos nucleicos
Cellteorin (Biologi 2)
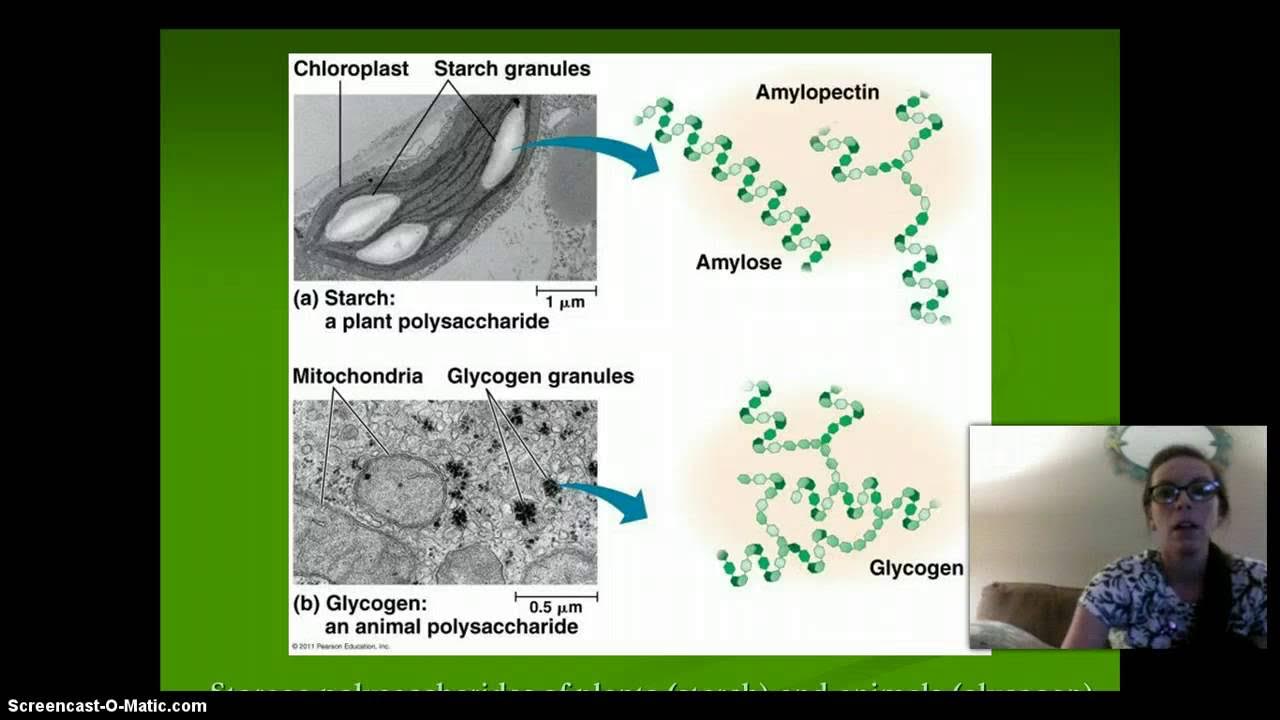
AP Biology Macromolecules Carbs, Lipids and DNA

Biomolecules (Updated 2023)

Biomoléculas (atualizado em 2023)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)