Least Cost Cell Method | In case of Tie | Transportation Problem in Operations research | Kauserwise
Summary
TLDRThis video tutorial focuses on solving a balanced transportation problem using the least cost cell method. The presenter guides viewers through the process of finding an initial basic feasible solution by selecting the least cost cell and allocating resources based on supply and demand. The video includes a step-by-step demonstration using a cost matrix with three sources and four destinations, and it concludes with the calculation of the total transportation cost. Viewers are encouraged to explore more videos on the topic and on handling unbalanced transportation problems.
Takeaways
- 🚚 The video is a tutorial on solving transportation problems using the least cost cell method.
- 🔍 The presenter begins by ensuring the transportation problem is balanced, confirming that the total supply equals the total demand.
- 📊 A cost matrix with three sources and four destinations is provided, with specific supply and demand figures.
- 📝 The least cost cell method involves selecting the cell with the lowest cost to start the allocation process.
- ✂️ After allocating, cells that are fully utilized are 'deleted' from further consideration.
- 🔄 In case of a tie in the lowest cost, the presenter explains how to choose the cell that allows for the maximum allocation.
- 🔄 The term 'Thai' is mentioned to describe a situation where the same cost value appears in multiple cells.
- 📉 The process is iterative, with the presenter repeatedly selecting the least cost cell and allocating resources until all cells are utilized.
- 📋 The video concludes with a calculation of the total transportation cost based on the allocations made.
- 🎥 A follow-up video is teased, which will cover solving unbalanced transportation problems using the same method.
Q & A
What is the main topic of the video?
-The main topic of the video is solving the Transportation Problem using the least cost cell method.
What is the first step in solving a Transportation Problem as described in the video?
-The first step in solving a Transportation Problem is to check whether the problem is balanced or unbalanced by comparing the total supply with the total demand.
How is a balanced Transportation Problem defined in the video?
-A balanced Transportation Problem is defined as one where the total supply equals the total demand.
What is the total supply and demand in the given problem according to the video?
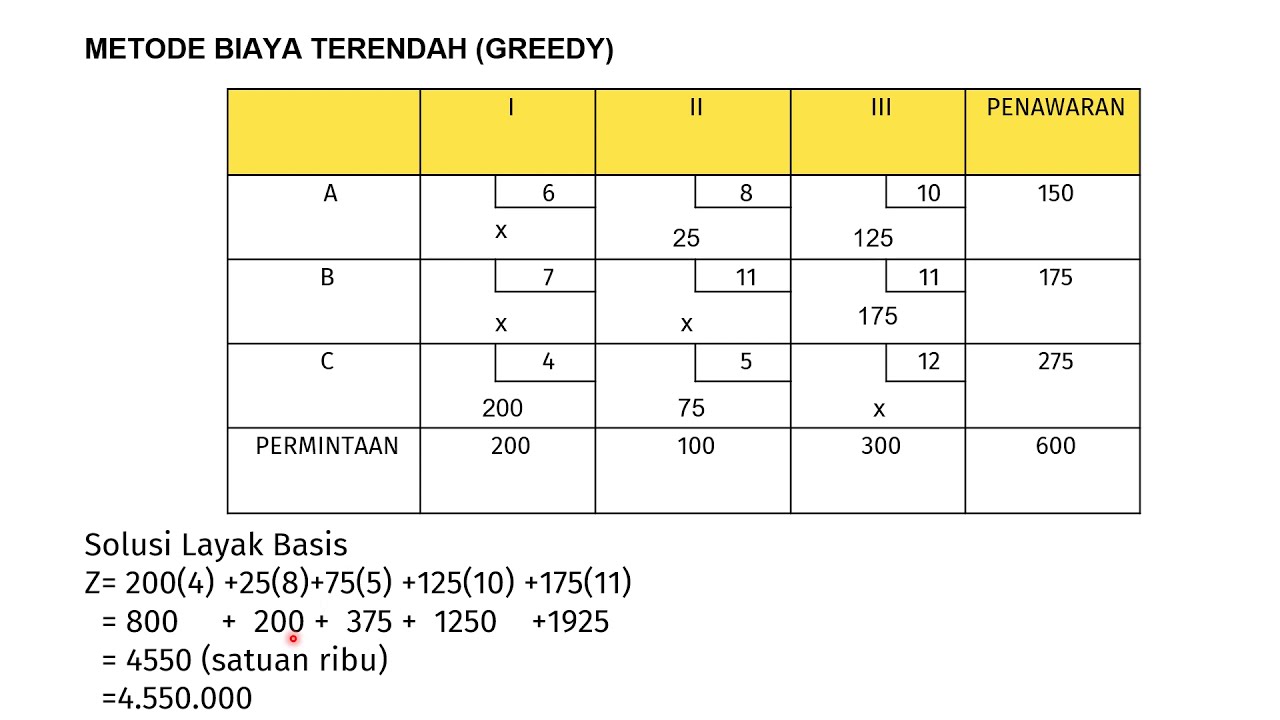
-The total supply is 600 units (150 + 200 + 250) and the total demand is also 600 units (125 + 175 + 200 + 100), making the problem balanced.
What is the least cost cell method as explained in the video?
-The least cost cell method is a technique used to solve Transportation Problems by selecting the cell with the lowest cost in the cost matrix and allocating the minimum of the corresponding supply and demand to that cell.
What is the procedure when a tie occurs in the least cost cell method, as described in the video?
-When a tie occurs, meaning the same lowest cost is found in multiple cells, the procedure is to select the cell that allows for the maximum allocation based on the remaining supply and demand.
How does the video demonstrate the allocation of the least cost cell?
-The video demonstrates the allocation by comparing the demand and supply for the selected cell, allocating the minimum of the two, and then updating the matrix by cancelling the row or column if the supply or demand is met.
What is the total transportation cost calculated at the end of the video?
-The total transportation cost calculated at the end of the video is 900 rupees.
What is the next topic the video series will cover according to the video?
-The next topic the video series will cover is how to solve unbalanced Transportation Problems using the least cost cell method.
How can viewers find more videos on this topic as mentioned in the video?
-Viewers can find more videos on this topic by looking in the description box of the video for links to additional related content.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео
METODE BIAYA TERENDAH - GREEDY - LEAST COST - Transportasi - Program Linear - GASS MATEMATIKA

Operations Research 06A: Transportation Problem

PROGLIN - Transportasi bagian 2 (VAM/Vogel Aproximation Method)

Transportasi Menggunakan Excel
7 Branch and Bound Introduction
3.1 Knapsack Problem - Greedy Method
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
