DIY Vapor Compression Refrigeration System
Summary
TLDRThis video script details the construction of a DIY vapor compression refrigeration system, aiming for liquid nitrogen production. The host explains the science behind the phase change of substances under varying pressure and temperature, and how it can be harnessed to create cooling effects. The script walks through the process of building a refrigerator using propane as a refrigerant, including the selection of components, assembly, and testing. It also discusses the challenges faced, such as achieving optimal cooling power and the importance of insulation and component sizing for efficiency.
Takeaways
- 🔬 The video explains the vapor compression refrigeration cycle and its application in creating a DIY cryo cooler for liquid nitrogen production.
- 📚 After unsuccessful attempts with hydrogen as a refrigerant, the presenter explores alternative methods like cascading vapor compression cycles or using a mixture in a Joule-Thomson cycle.
- 🌡️ The phase change of a liquid depends on both temperature and pressure, as illustrated by the boiling point of water varying with changes in ambient pressure.
- 🧊 The concept of using a refrigerant that boils at temperatures below ambient, thus cooling the surroundings, is similar to how a freeze dryer works, but is adapted for more efficient refrigeration.
- 🌟 Common refrigerants like Freon, R22, ammonia (R717), and propane (R290) are discussed, with propane being highlighted as a cheaper and more available option, despite being flammable.
- 🔧 The build process involves assembling a compressor, condenser coil, evaporator coil, and using a capillary tube to create a pressure drop in the system.
- ⚙️ A detailed explanation of the components and their functions is provided, including the importance of the compressor oil, the construction of the condenser and evaporator coils, and the use of a capillary tube.
- 🔩 The presenter discusses the challenges of sizing the capillary tube correctly to balance pressure drop and flow rate for optimal cooling performance.
- 🔋 The system must be charged with the correct amount of refrigerant, which is done by adding refrigerant while the compressor is running until the desired pressure is reached.
- 🛠️ The importance of insulation is highlighted to minimize heat leakage into the evaporator coil and to achieve lower temperatures.
- 📉 The testing of the system's cooling power reveals a coefficient of performance lower than expected, attributed to factors like excessive fan power, imperfect heat transfer, and environmental heat losses.
Q & A
What is the main purpose of the vapor compression refrigeration cycle explained in the script?
-The main purpose is to create a DIY cryo cooler for liquid nitrogen production, using a vapor compression cycle that can be built from standard refrigeration or air conditioning components with some modifications.
Why does water boil at a lower temperature at high elevations?
-Water boils at a lower temperature at high elevations due to the lower ambient pressure, which affects the boiling point of water.
What happens to water in space where the pressure is almost zero?
-In space, where the pressure is almost zero, the boiling point of water is so low that it would cool down, freeze to ice, and continue to boil and cool off through sublimation, making liquid water non-existent.
How can the relationship between pressure and temperature be used to produce cooling?
-The relationship can be used to produce cooling by having a liquid boil at a temperature below ambient by pulling a vacuum on it, effectively creating an outer space situation on Earth.
What are some common refrigerants mentioned in the script?
-Some common refrigerants mentioned include Freon, R22 (being phased out for environmental reasons), ammonia (R717), and flammable substances like propane (R290) and butane (R600a).
Why is using a flammable substance as a refrigerant considered safe in small systems?
-Using a flammable substance as a refrigerant is considered safe in small systems because these systems are sealed off from the environment, minimizing the risk of ignition or explosion.
What is the role of a capillary tube in a refrigeration system?
-A capillary tube creates a fixed pressure drop for a given flow rate in a refrigeration system, which is simple and reliable, though it is only optimal for one particular load.
What is the significance of the phase curve for refrigerants like R22, ammonia, and propane?
-The phase curve shows the relationship between pressure and temperature for a refrigerant, which is crucial for understanding how the refrigerant will behave in a refrigeration cycle.
How does the size of a capillary tube affect the performance of a refrigeration system?
-The size of a capillary tube affects the pressure drop and flow rate in the system. A tube that is too long can result in a high pressure drop and low cooling power, while a tube that is too short can lead to a low pressure drop and high flow rate but insufficient cooling.
What is the reason for using a rotary compressor instead of a reciprocating one in the script?
-A rotary compressor is used because it can run at a much higher inlet pressure, has a geometry that allows more power for its size, and is suitable for the project's requirements.
What is the coefficient of performance (COP) and why is it important in refrigeration systems?
-The coefficient of performance (COP) is a measure of the efficiency of a heat pump or air conditioning system, indicating the ratio of heat pumped out for every watt of power put into the system. It is important because it helps determine the energy efficiency of the system.
Why is insulation important in the evaporator coil of a refrigeration system?
-Insulation is important in the evaporator coil to minimize heat leakage from the surroundings, which can reduce the system's cooling efficiency and prevent it from reaching the desired low temperatures.
What is the purpose of a vacuum pump in charging a refrigeration system?
-A vacuum pump is used to remove air from the system during the initial charging process. This is important because air can occupy space that refrigerant could fill and can carry moisture that could damage the compressor. Additionally, for flammable refrigerants, removing air prevents the formation of explosive mixtures.
How does the size of the capillary tube affect the cooling power and efficiency of a refrigeration system?
-The size of the capillary tube affects the pressure drop and flow rate, which in turn affects the cooling power and efficiency. A capillary tube that is too long can result in a high pressure drop and low flow rate, leading to low cooling power and efficiency. Conversely, a capillary tube that is too short can result in a low pressure drop and high flow rate, but the temperature drop may be insufficient for effective cooling.
What is the significance of the condenser pressure and temperature readings in the script?
-The condenser pressure and temperature readings are crucial for monitoring the performance of the refrigeration system. High pressure and temperature readings can indicate that the condenser is not effectively dissipating heat, which can affect the cooling capacity of the system.
What is the role of a coaxial heat exchanger in the evaporator coil?
-A coaxial heat exchanger, which consists of two concentric tubes, is used in the evaporator coil to enhance heat transfer. The inner tube carries the refrigerant, while the outer tube or the space between the tubes can be used for other purposes, such as pre-cooling the refrigerant of a second, colder stage in a cascade system.
Why is ethylene chosen as the refrigerant for the second stage in the cascade system mentioned in the script?
-Ethylene is chosen for the second stage of the cascade system because it can evaporate to much colder temperatures, closer to -100°C, which is suitable for the project's goal of achieving very low temperatures for liquid nitrogen production.
What is the reason for the discrepancy between the expected and actual cooling power measured in the script?
-The discrepancy is due to several factors, including the power consumed by the fans, imperfect heat transfer from the test water to the refrigerant, losses in the test tubing and reservoir from the environment, and a load mismatch due to the capillary tube being sized for peak efficiency at the lowest possible temperature rather than the actual operating temperature.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示
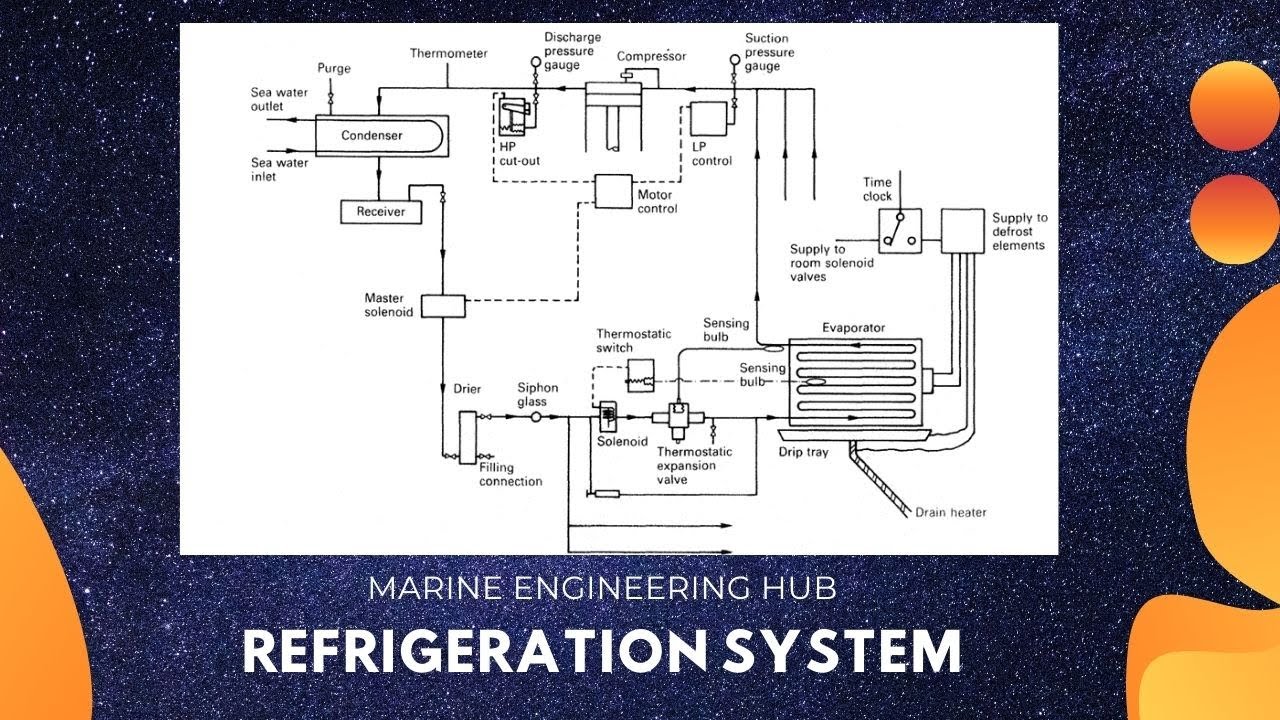
REFRIGERATION SYSTEM| (PART-1)|
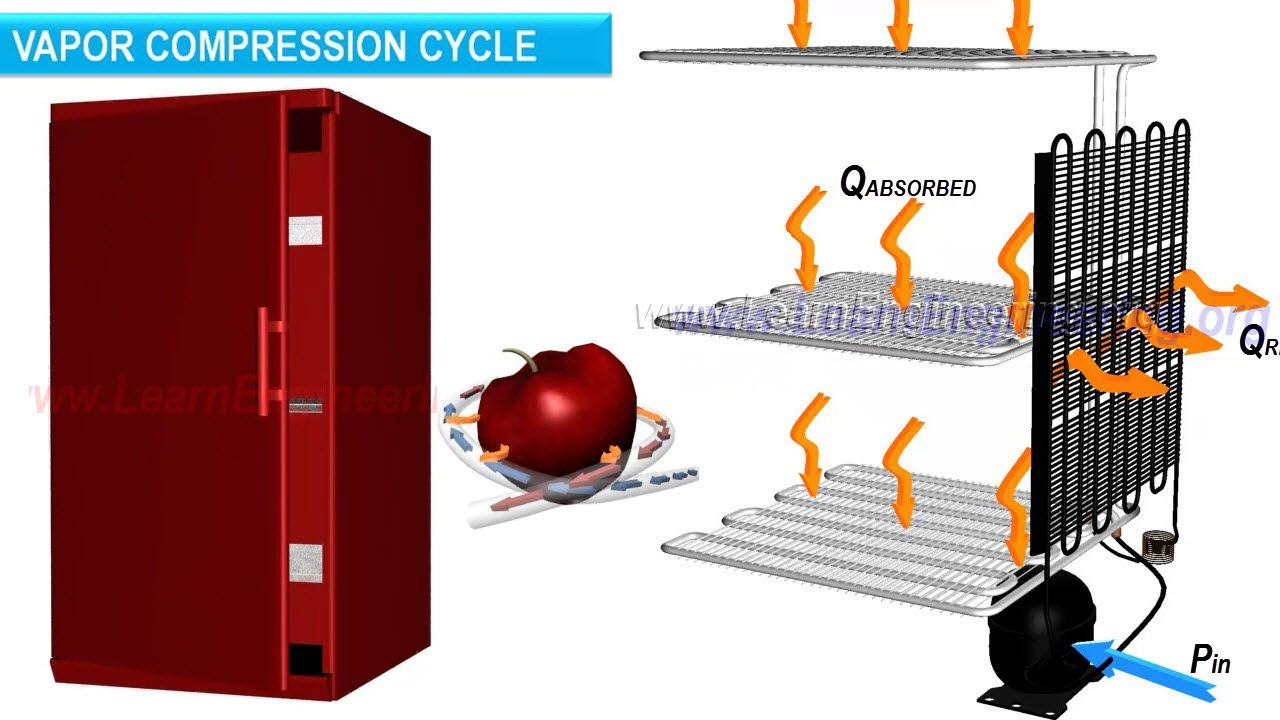
Refrigerator working - The Basics
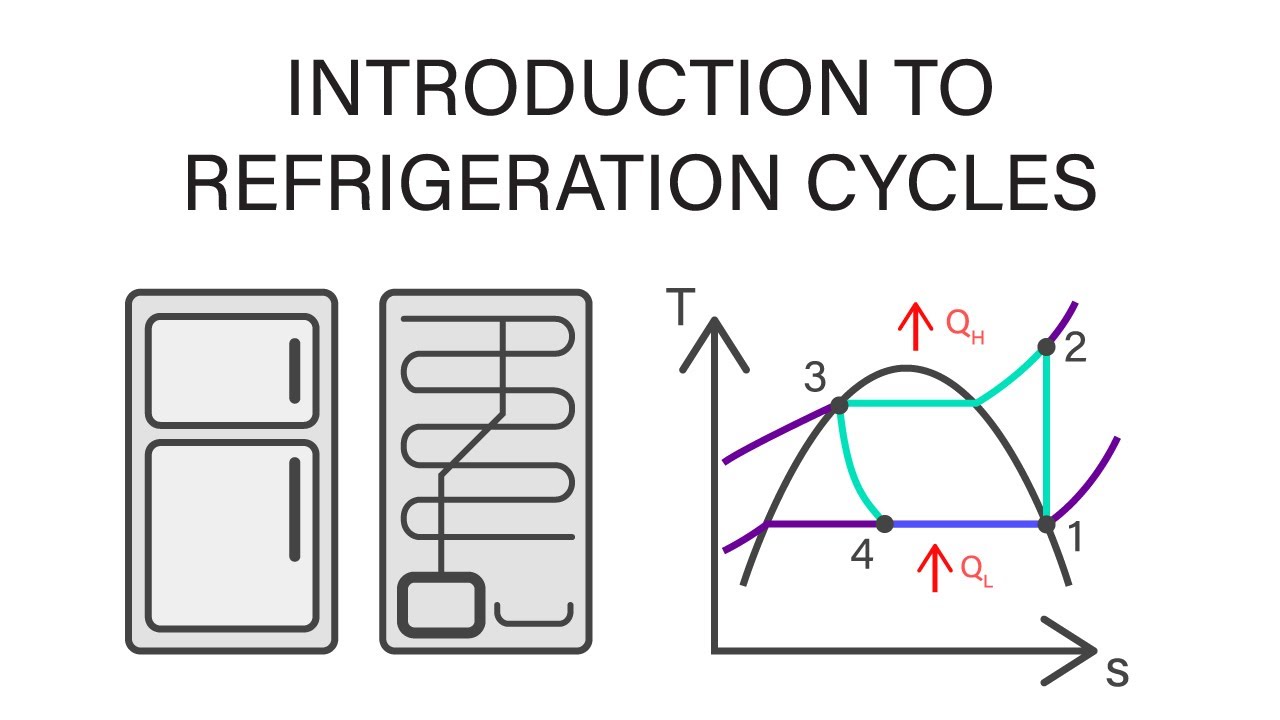
Mechanical Engineering Thermodynamics - Lec 23, pt 1 of 4: Introduction to Refrigeration Cycles
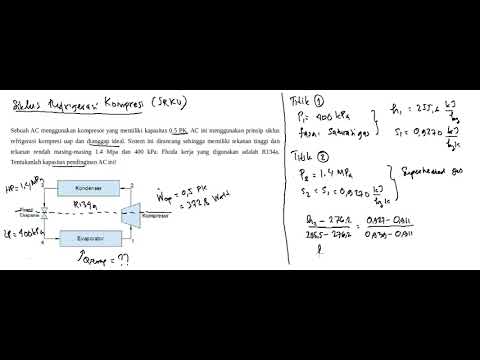
Analisis Siklus Refrigerasi Kompresi Uap Ideal
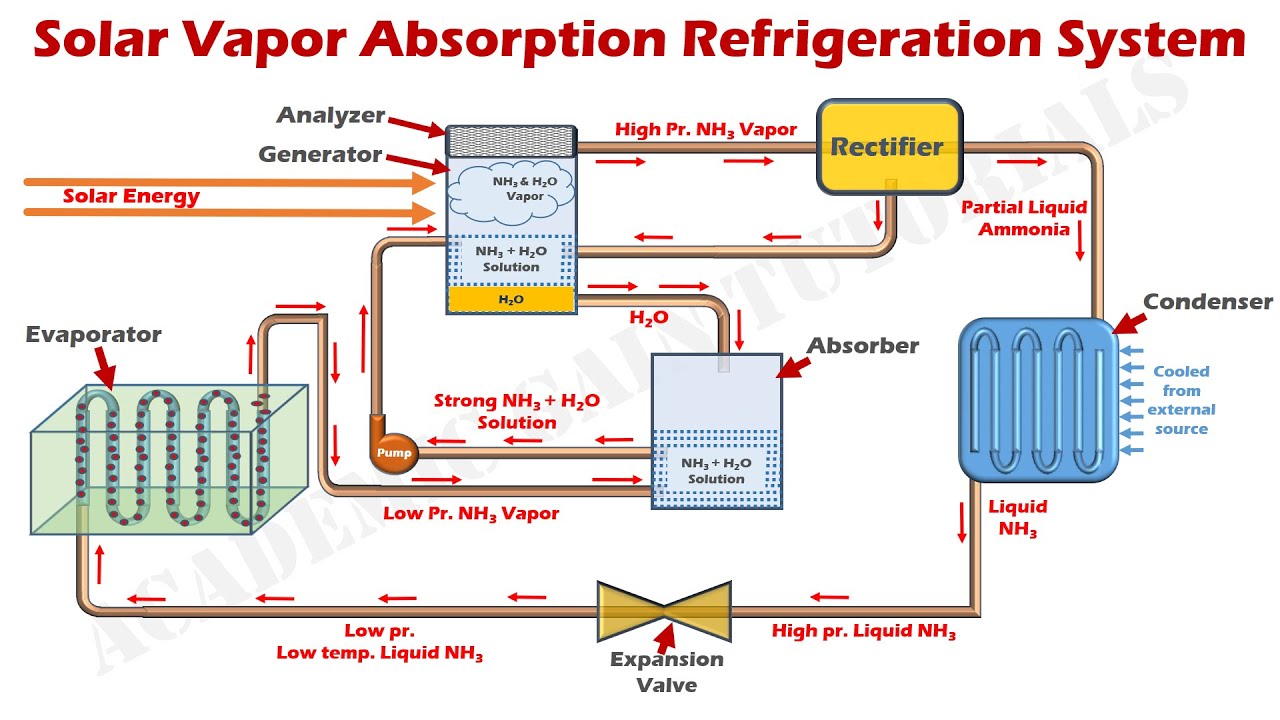
Solar Vapor Absorption Refrigeration System (Ammonia-Water Solar Cooling System) Explained.

Bill Nye: Phases of Matter
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
