Introdução à óptica | Fenômenos ópticos
Summary
TLDRIn this lesson, Professor Gabi explores the fascinating world of light through the lens of optics. She explains how light is fundamental to what we see, discussing primary and secondary light sources, as well as key optical phenomena like reflection, refraction, and absorption. The video covers how light behaves as it interacts with different materials, from opaque to transparent, and introduces the principles of light propagation. The discussion also includes practical examples, such as the behavior of light through various mediums, and real-life applications of optical principles like the aurora borealis and mirages.
Takeaways
- 😀 Light is essential for us to see the world around us, and it depends on three factors: observers, the surroundings, and light itself.
- 😀 Optics is the branch of physics dedicated to studying light, with two main subfields: physical optics and geometric optics.
- 😀 Geometric optics focuses on the behavior of light and its propagation, leading to phenomena like reflection, refraction, and absorption.
- 😀 Primary light sources, such as the sun and a candle, emit their own light, while secondary sources, like the moon, reflect light from primary sources.
- 😀 Reflection can be either diffuse (light scattered in all directions) or regular (creating clear images, like in mirrors).
- 😀 In regular reflection, the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection, while in diffuse reflection, light is scattered in all directions.
- 😀 The principles of light propagation include straight-line propagation, independence of light rays, and symmetry in its trajectory.
- 😀 Light encounters different types of mediums: opaque (which reflect light), translucent (allowing light to pass but scattering it), and transparent (allowing light to pass through easily).
- 😀 Refraction occurs when light passes from one medium to another and changes speed due to differences in the refractive index of the mediums.
- 😀 Absorption of light by materials, such as dark clothes under the sun, results in the conversion of light into heat energy, explaining the sensation of warmth.
- 😀 Reflection, refraction, and absorption are all phenomena that can occur simultaneously when light interacts with various mediums.
Q & A
What is the main focus of the field of optics?
-The field of optics focuses on studying light, including its propagation, behavior, and interactions with different materials, such as reflection, refraction, and absorption.
What are the two main divisions of optics?
-Optics is divided into two main areas: physical optics, which studies the nature of light, and geometric optics, which focuses on the behavior and propagation of light.
What is the difference between primary and secondary light sources?
-Primary light sources emit their own light due to physical or chemical processes, such as the Sun or a candle. Secondary light sources, like the Moon, do not emit their own light but reflect light from primary sources.
How can light sources be classified in terms of size?
-Light sources can be classified as extensive, where their size doesn't matter in relation to the surrounding objects (like the Sun), or point sources, where their size is significant in comparison to nearby objects (like a candle).
What is the difference between diffuse and regular reflection?
-Diffuse reflection occurs on rough surfaces, scattering light in many directions without forming a clear image. Regular reflection happens on smooth surfaces, reflecting light in a way that forms a sharp, clear image.
What is the law of reflection?
-The law of reflection states that the angle of incidence (the angle between the incident ray and the normal) is equal to the angle of reflection (the angle between the reflected ray and the normal).
What are the key principles that light follows as it propagates?
-The key principles of light propagation are: (1) light travels in straight lines (rectilinear propagation), (2) light rays are independent of each other (they do not interfere when crossing), and (3) the path of light does not depend on its direction of travel.
What happens when light encounters opaque, translucent, and transparent materials?
-When light encounters opaque materials, it is reflected. With translucent materials, like frosted glass, light passes through but is scattered, while transparent materials, like clear glass, allow light to pass through easily without scattering.
What is refraction, and how does it relate to light?
-Refraction occurs when light passes from one medium to another, experiencing a change in speed and direction due to differences in the refractive index of the materials. The change in speed leads to bending of the light ray.
Why do dark-colored clothes absorb more heat in the sun?
-Dark-colored clothes absorb more light and, consequently, more heat because they absorb a larger portion of electromagnetic radiation, converting it into thermal energy, making them feel hotter compared to lighter-colored clothes.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示

REFLEXÃO TOTAL DA LUZ - ÓPTICA - Aula 9 - Prof. Boaro

REFRAÇÃO DA LUZ E DISPERSÃO LUMINOSA - ÓPTICA - Aula 8 - Prof Boaro

Óptica - Princípio da Propagação Retilínea da Luz | Sala do Saber

CAHAYA DAN ALAT OPTIK (PART 3) : CERMIN CEMBUNG DAN LENSA CEKUNG IPA KELAS 8 SMP

Química - Aminoácidos, Peptídeos e Proteínas
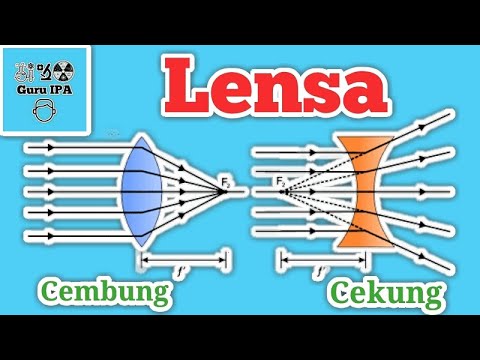
Lensa Cekung dan Lensa Cembung
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
