Rotational and irrotational flow [Aerodynamics #7]
Summary
TLDRThis lecture delves into the concepts of rotational and irrotational flows in aerodynamics. It introduces vorticity, the measure of rotation within a fluid, and explains how circulation, the total vorticity around a loop, plays a key role in calculating lift. The lecture also covers the creation of the velocity potential for irrotational flows, allowing for simplified analysis of flow behavior. Using real-world analogies like the Ferris wheel and Gravitron, the content clarifies these concepts while emphasizing their importance in aerodynamic applications, particularly in the study of airfoil flow and boundary layer effects.
Takeaways
- 😀 Rotational flow occurs when a fluid element spins as it moves, while irrotational flow means the fluid element doesn't change its orientation.
- 😀 A good analogy for rotational flow is the Gravitron ride, where you rotate and change orientation, while the Ferris wheel is an example of irrotational flow, as you don't change orientation.
- 😀 Vorticity represents the rotation of a fluid element and is defined as the curl of the velocity field, indicating whether the flow is rotational or irrotational.
- 😀 If vorticity is non-zero, the flow is rotational; if vorticity is zero, the flow is irrotational.
- 😀 Circulation is the total vorticity enclosed around a loop and plays a crucial role in calculating aerodynamic lift.
- 😀 The circulation around an enclosed area is related to the vorticity inside that area, as per Stokes' theorem, which connects the circulation to the curl of the velocity.
- 😀 The velocity potential is a scalar function used for irrotational flows, where the velocity field is the gradient of the potential.
- 😀 The velocity potential is similar to the stream function but applies to 3D, irrotational flows, while the stream function is limited to 2D or axi-symmetric flows.
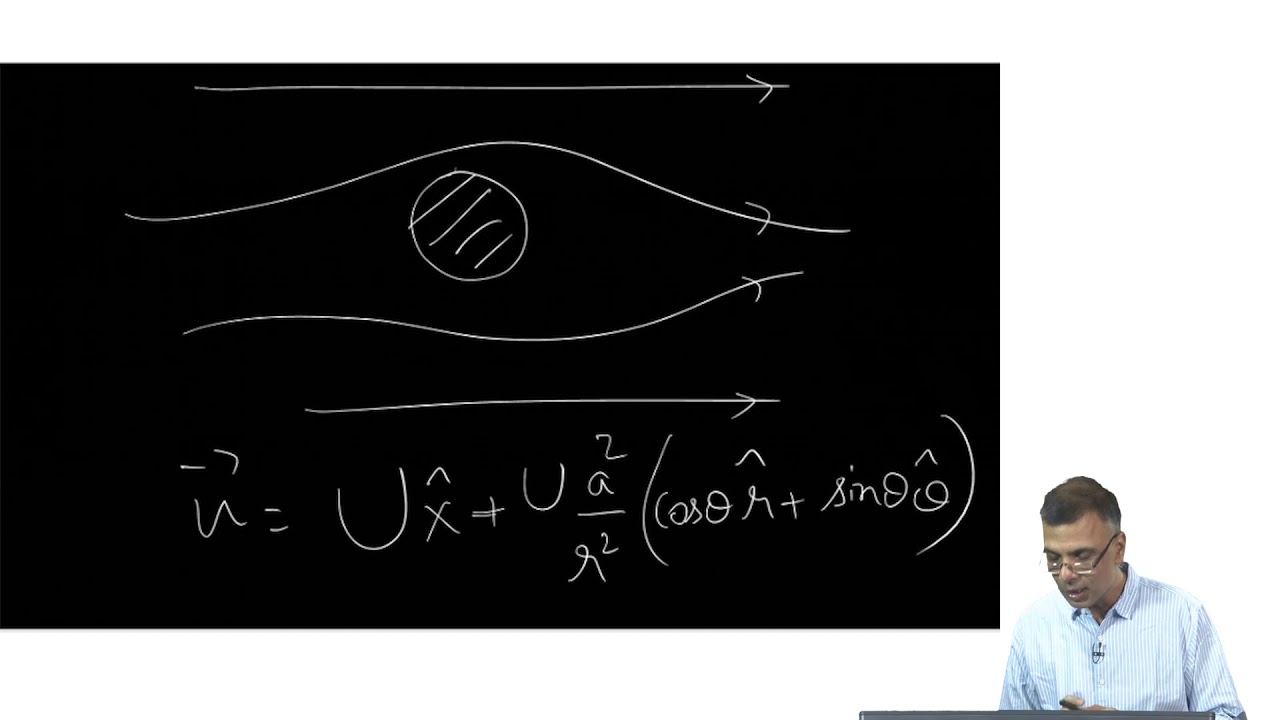
- 😀 Many aerodynamic flows, especially those far from surfaces, are considered irrotational, but close to surfaces, such as in the boundary layer, the flow becomes rotational due to viscosity and velocity gradients.
- 😀 When analyzing aerodynamic flows, the velocity potential can be used for irrotational analysis, but near boundaries, a more complex, rotational analysis may be necessary, incorporating viscosity.
Q & A
What is the difference between rotational and irrotational flow?
-Rotational flow occurs when the fluid elements change their orientation as they move along a streamline (e.g., like in the Gravitron ride), while irrotational flow occurs when the fluid elements maintain the same orientation (e.g., like in the Ferris wheel).
Why is the concept of rotational flow important in aerodynamics?
-Rotational flow is important because it can lead to more complex analyses in fluid dynamics, especially in the calculation of forces like lift. It involves the concept of vorticity and circulation, which are critical for understanding the behavior of air around objects such as airfoils.
What does vorticity represent in fluid dynamics?
-Vorticity represents the rotational component of the fluid flow, specifically the angular velocity of fluid elements. It is mathematically defined as twice the angular velocity and is calculated using the curl of the velocity field.
How does circulation relate to vorticity?
-Circulation is the total vorticity enclosed around a loop. It is calculated by integrating the dot product of velocity and position vectors along the loop. According to Stokes' Theorem, the circulation can also be expressed as the surface integral of the curl of the velocity field.
What is the practical significance of circulation in aerodynamics?
-Circulation is used in aerodynamics to estimate lift forces, especially when analyzing airflow over wings. The circulation around a closed loop enclosing the flow over the wing can provide information about the lift generated.
How does the concept of vorticity help differentiate between rotational and irrotational flow?
-Vorticity helps differentiate the two types of flow by measuring the rotation of the fluid. If vorticity is non-zero everywhere, the flow is rotational. If vorticity is zero everywhere, the flow is considered irrotational.
Can we assume that most aerodynamic flows are irrotational? Why or why not?
-Yes, in many cases, aerodynamic flows are considered irrotational, especially far from surfaces like airfoils. However, near surfaces, such as within the boundary layer, flow may become rotational due to strong velocity gradients.
What is the velocity potential and how is it used in irrotational flow?
-The velocity potential is a scalar function used to describe irrotational flows. It exists when the curl of the velocity field is zero, and it allows the velocity field to be expressed as the gradient of this scalar function, simplifying flow analysis.
What is the relationship between the stream function and the velocity potential?
-Both the stream function and velocity potential are scalar functions used to describe flow. The stream function applies to two-dimensional or axi-symmetric flows, while the velocity potential is used for three-dimensional, irrotational flows. Both functions help calculate the velocity field by taking spatial gradients.
Why do we need to consider viscosity and rotationality in boundary layer analysis?
-In boundary layer analysis, viscosity and rotationality must be considered because near the surface of an object, strong velocity gradients occur, leading to rotational flow. These factors must be included in the analysis to get accurate predictions of fluid behavior and forces.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード5.0 / 5 (0 votes)