BIO - Unit 6 - DNA Replication BU6
Summary
TLDRThis video script explains the essential concept of DNA replication, emphasizing its importance in preserving genetic information. It introduces the semi-conservative model of replication, where one strand serves as a template for creating a new strand. The script explores the impact of mutations and highlights the consequences of even a single nucleotide change, using sickle cell anemia as an example. Additionally, it touches on the roles of enzymes like DNA polymerase and telomerase, and how environmental factors, including exercise, can influence telomere length and aging. The script concludes by discussing the challenges of immortality related to telomere degradation.
Takeaways
- 😀 DNA replication must be precise to ensure that the nucleotide sequence is maintained correctly, similar to following instructions in a recipe.
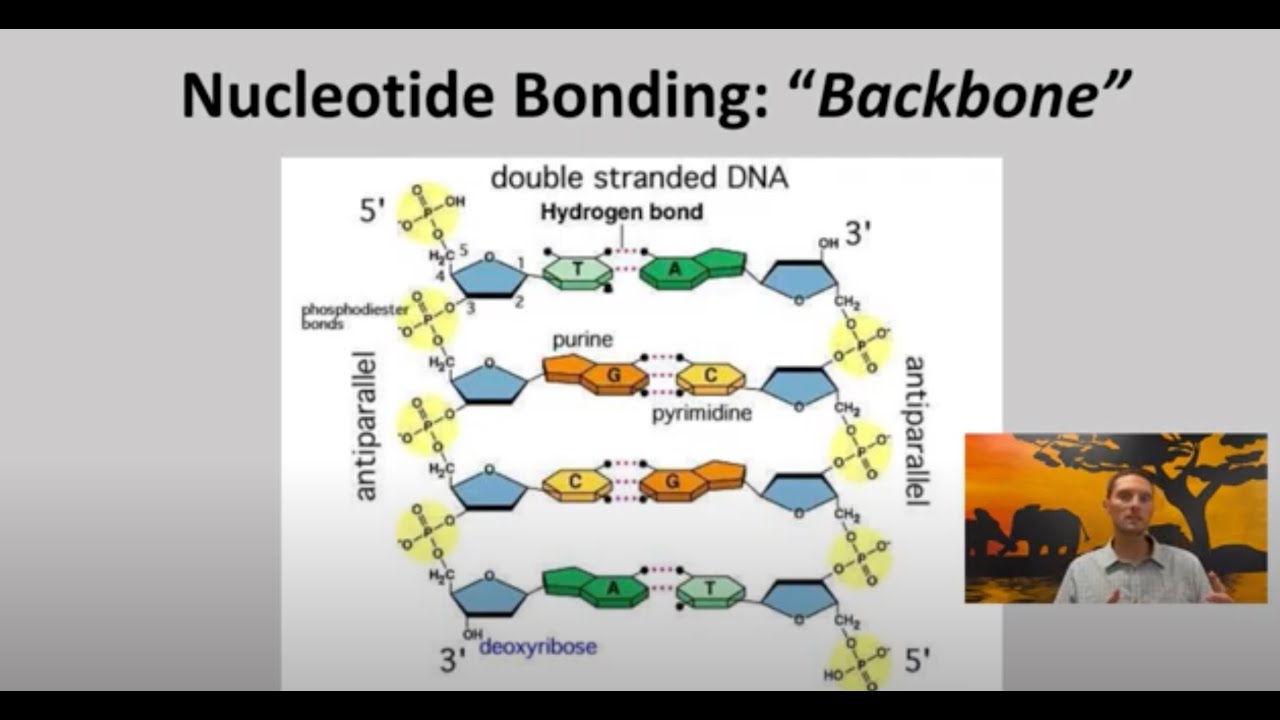
- 😀 DNA consists of base pairs (A-T, G-C) that follow strict pairing rules, and errors in replication can lead to mutations.
- 😀 Mutations, like the one in sickle cell anemia, can occur from a single nucleotide change, impacting functions like oxygen delivery in red blood cells.
- 😀 DNA replication uses one strand as a template to create a new complementary strand, a process known as semi-conservative replication.
- 😀 The semi-conservative model of DNA replication conserves one original strand, and the other strand is newly synthesized, which is the established mechanism.
- 😀 Other early models of replication, like conservative and dispersive, were eventually disproven because they couldn't explain how new strands were formed.
- 😀 DNA polymerase is the enzyme responsible for adding nucleotides to the growing DNA strand, following base pairing rules, and has an error rate of about 1 in 10,000.
- 😀 DNA polymerase can fix some replication errors, but it misses some, which can accumulate and lead to diseases like cancer as we age.
- 😀 In eukaryotes, replication happens at multiple origins, whereas prokaryotes only need one origin due to their circular chromosomes.
- 😀 Telomeres are protective buffers at the ends of chromosomes that prevent loss of important genetic material during replication, but they shorten with age, contributing to aging and disease.
- 😀 The enzyme telomerase, active during fetal development, helps maintain telomere length, but its activity stops after birth, and scientists are exploring ways to reactivate it for longevity.
Q & A
What is the importance of DNA replication?
-DNA replication is crucial for maintaining the genetic material of cells. It ensures that each new cell receives an exact copy of the genetic instructions, which is essential for growth, development, and the functioning of organisms.
What is the semi-conservative model of DNA replication?
-The semi-conservative model of DNA replication suggests that each new DNA molecule consists of one original strand and one newly synthesized strand. This model ensures the accurate copying of genetic material.
What is the role of base pairing in DNA replication?
-Base pairing is fundamental to DNA replication. The bases adenine (A) pairs with thymine (T), and guanine (G) pairs with cytosine (C). This ensures that the new strand is an exact complement of the template strand, preserving genetic integrity.
What happens if a single nucleotide is changed during DNA replication?
-If a single nucleotide is changed during DNA replication, it can lead to mutations that affect the function of the encoded protein. For example, a mutation in the gene responsible for hemoglobin can result in sickle cell anemia.
How does DNA polymerase ensure the accuracy of DNA replication?
-DNA polymerase ensures the accuracy of DNA replication by adding nucleotides according to base pairing rules. It has a proofreading function that checks and corrects errors, although it doesn't catch all mistakes.
What are the differences between the conservative, dispersive, and semi-conservative models of DNA replication?
-The conservative model suggests both original strands remain together after replication, while the dispersive model proposes that original DNA is randomly interspersed with newly synthesized parts. The semi-conservative model, which is the correct one, involves each new DNA molecule having one original strand and one new strand.
What is the function of telomeres in DNA replication?
-Telomeres are protective sequences at the ends of chromosomes that prevent the loss of important genetic material during DNA replication. As cells divide, telomeres shorten, but they help safeguard the coding DNA from degradation.
Why is it difficult for older individuals to repair DNA errors?
-As people age, the efficiency of DNA repair mechanisms, such as the proofreading function of DNA polymerase, declines. This leads to the accumulation of mutations, which can contribute to aging and diseases like cancer.
How does DNA replication differ between prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
-In prokaryotes, DNA replication occurs from a single origin of replication because their DNA is circular. Eukaryotes, on the other hand, have linear chromosomes, requiring multiple origins of replication to replicate their DNA efficiently.
Can telomerase be activated in adult cells to reverse aging?
-Currently, telomerase cannot be activated in adult cells to reverse aging. While it is active during fetal development to maintain telomere length, there is no known method to reactivate it in adults, which limits the potential for halting cellular aging.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード5.0 / 5 (0 votes)