2-Minute Neuroscience: Trigeminal Nerve (Cranial Nerve V)
Summary
TLDRThe trigeminal nerve is the primary sensory nerve of the head, responsible for touch, pain, temperature, and proprioception. It controls chewing muscles and plays a role in protecting the ear from loud noises. The nerve has three divisions: ophthalmic, maxillary, and mandibular, with sensory and motor functions. Its nuclei help process sensory information, and damage can cause abnormal sensations, pain, and muscle weakness. Trigeminal neuralgia, a condition causing intense facial pain, can occur due to nerve damage. This video explores the trigeminal nerve's functions, structure, and the impact of its dysfunction.
Takeaways
- 😀 The trigeminal nerve is the main sensory nerve of the head.
- 😀 It carries information about touch, pain, temperature, and proprioception (awareness of body position).
- 😀 The trigeminal nerve controls muscles involved in chewing and some small muscles in the ear and throat.
- 😀 The tensor tympani muscle helps dampen loud sounds in the middle ear.
- 😀 The tensor veli palatini muscle helps prevent food from entering the nasopharynx and opens the Eustachian tube.
- 😀 The trigeminal nerve has three divisions: ophthalmic, maxillary, and mandibular, each supplying different regions of the head and face.
- 😀 The ophthalmic and maxillary divisions are sensory, while the mandibular division is both sensory and motor.
- 😀 The trigeminal nerve has three sensory nuclei and one motor nucleus located in the brainstem and spinal cord.
- 😀 The main sensory nucleus processes touch and proprioception, while the spinal trigeminal nucleus handles pain and temperature sensations.
- 😀 The mesencephalic nucleus receives proprioceptive information from the jaw and teeth to prevent damage while chewing.
- 😀 Damage to the trigeminal nerve can lead to abnormal sensation, muscle weakness, and conditions like trigeminal neuralgia, which causes intense facial pain.
Q & A
What is the primary function of the trigeminal nerve?
-The trigeminal nerve is the main sensory nerve of the head. It carries information about touch, pain, temperature, and proprioception (the awareness of the position of muscles and joints). It also controls muscles involved in chewing.
What are the two muscles controlled by the trigeminal nerve mentioned in the script, and what are their functions?
-The trigeminal nerve controls the tensor tympani and tensor veli palatini muscles. The tensor tympani helps dampen the sound of loud noises in the middle ear, while the tensor veli palatini prevents food from entering the nasopharynx during swallowing and opens the eustachian tube to equalize pressure in the middle ear.
What are the three divisions of the trigeminal nerve, and what regions do they supply?
-The trigeminal nerve has three divisions: the ophthalmic, maxillary, and mandibular divisions. These supply different regions of the head and face.
Which divisions of the trigeminal nerve carry sensory information?
-The ophthalmic and maxillary divisions carry sensory information.
Which division of the trigeminal nerve has both sensory and motor components?
-The mandibular division has both sensory and motor components.
What are the four main nuclei associated with the trigeminal nerve, and what are their functions?
-The trigeminal nerve has three sensory nuclei and one motor nucleus: the main sensory nucleus (receives touch and proprioception information), the spinal trigeminal nucleus (receives pain and temperature sensations), the mesencephalic nucleus (receives proprioceptive information from the jaw and teeth), and the motor nucleus (controls the muscles of chewing).
What does the mesencephalic nucleus do?
-The mesencephalic nucleus receives proprioceptive information from the jaw and teeth to help prevent damage while biting and chewing.
How does damage to the trigeminal nerve affect a person?
-Damage to the trigeminal nerve or its associated nuclei can cause abnormal sensations, such as decreased sensation, increased pain, and/or weakening of the chewing muscles.
What is trigeminal neuralgia, and how does it affect patients?
-Trigeminal neuralgia is a condition caused by damage to the trigeminal nerve, leading to short but intense bouts of facial pain.
What is the role of the eustachian tube, and how is it related to the trigeminal nerve?
-The eustachian tube connects the upper throat with the middle ear. The trigeminal nerve controls the tensor veli palatini, which helps open the eustachian tube to equalize pressure between the middle ear and the outside air.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示
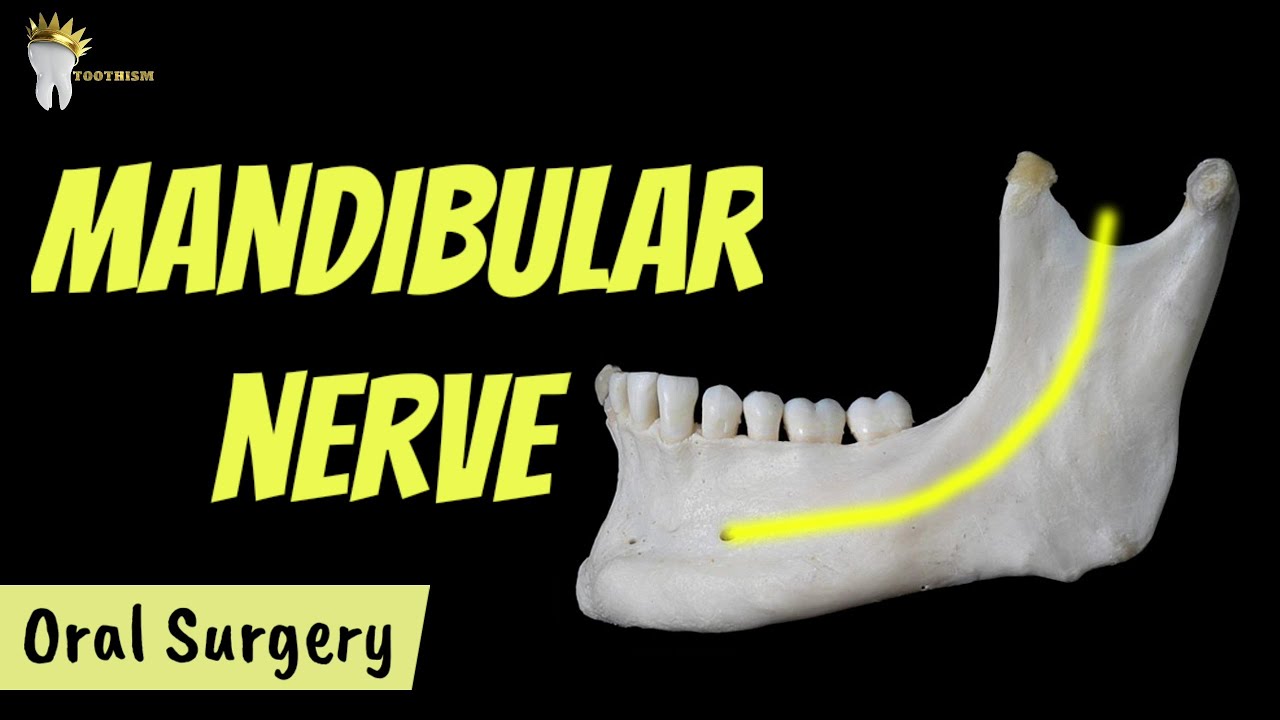
MANDIBULAR NERVE AND ITS BRANCHES
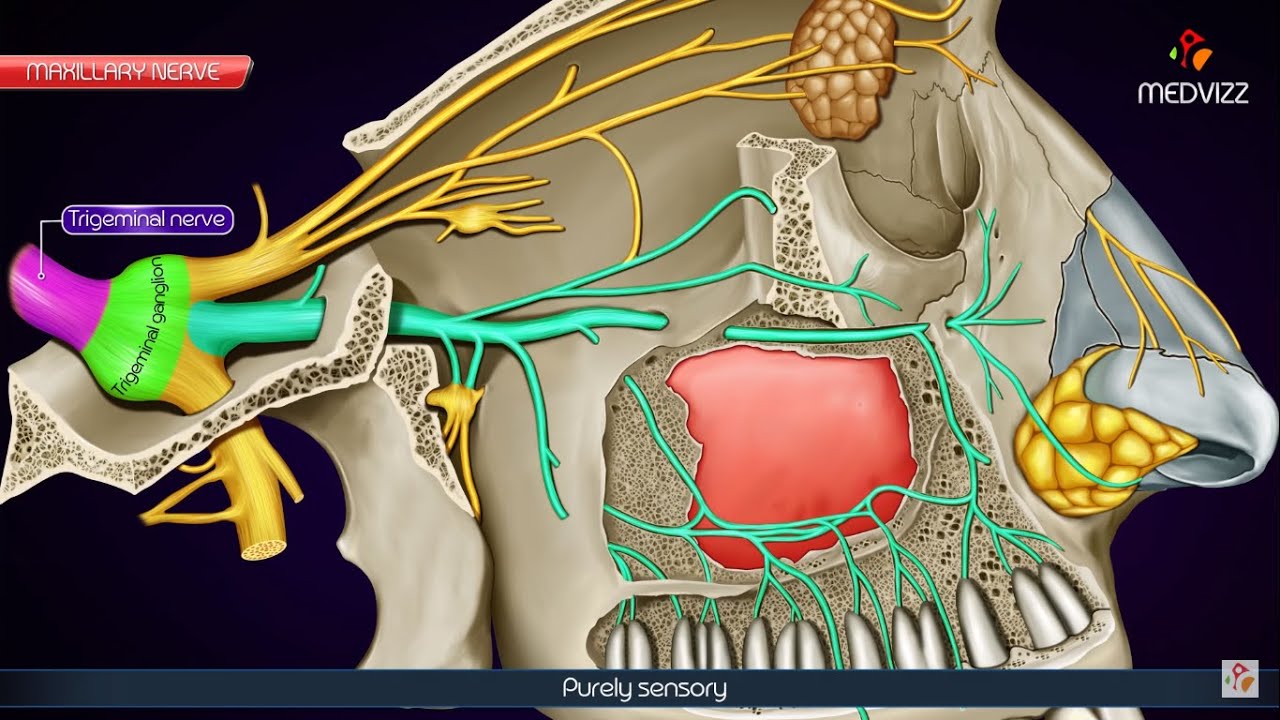
Maxillary division of Trigeminal nerve (V2 or Vb) / Maxillary nerve - Anatomy Animation
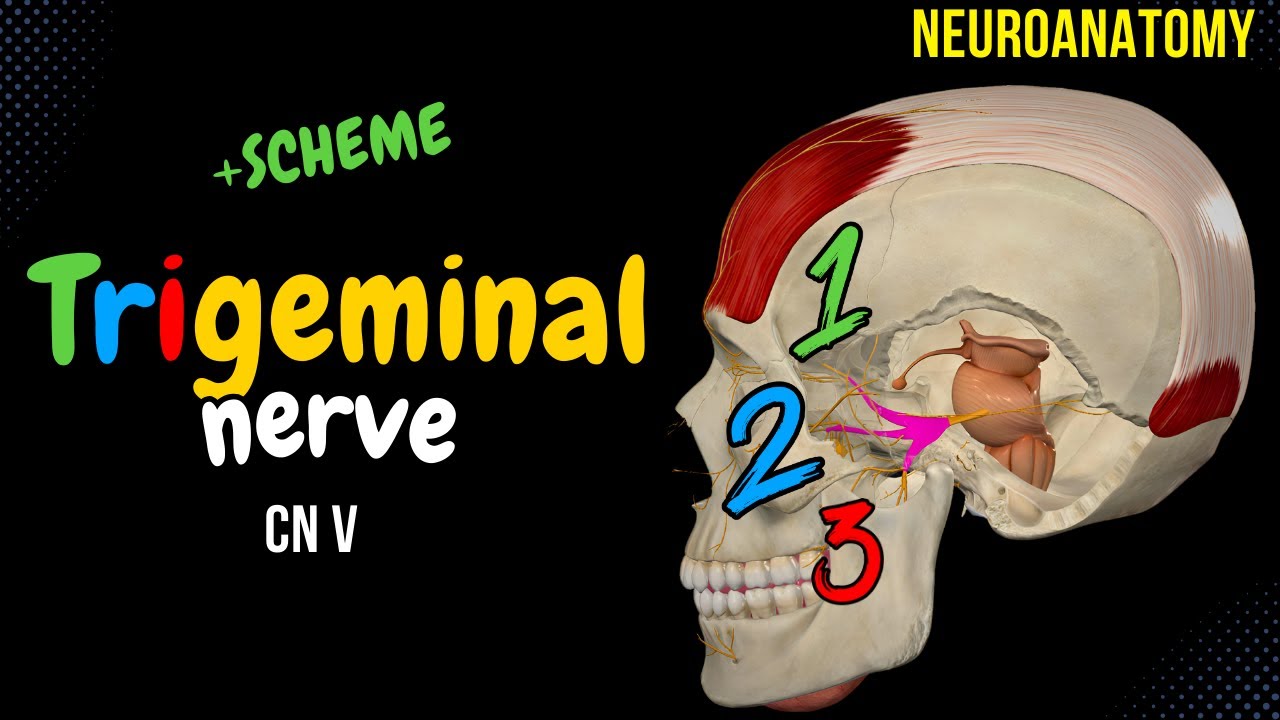
CN 5: Trigeminal Nerve (Scheme, Divisions, Pathway) | Neuroanatomy
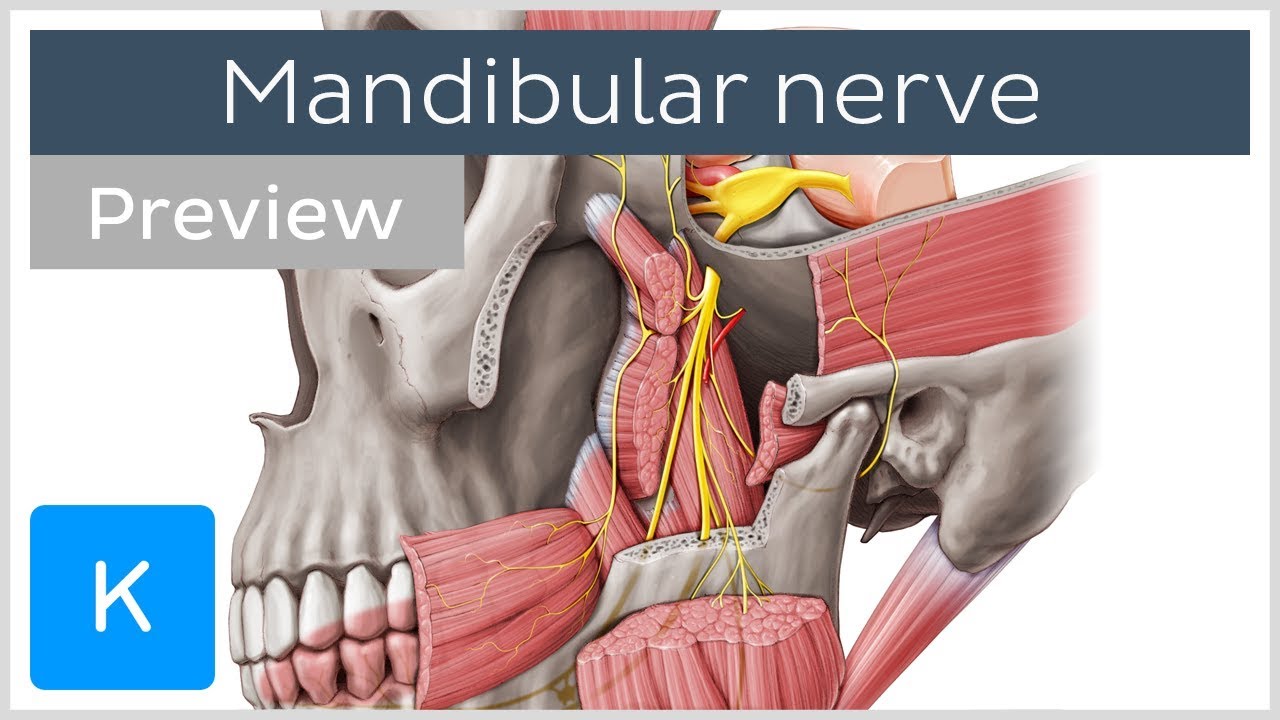
What is the Mandibular Nerve? (preview) - Human Anatomy | Kenhub

NERVE SUPPLY / INNERVATION OF MAXILLA AND MANDIBLE

Sensory Pathways MADE EASY!!
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
