SCHEMA THEORY, LEARNING, AND COMPREHENSION
Summary
TLDRThis video script explores schema theory, focusing on how our mental structures, or schemas, help us organize and comprehend new information. Schemas are built from personal experiences and shape how we learn and understand the world. The script delves into assimilation (adding new info to existing schemas) and accommodation (restructuring schemas for unfamiliar information). It also emphasizes how schema theory impacts teaching, highlighting the importance of activating prior knowledge, using graphic organizers, and integrating new and existing knowledge for deeper learning. The script concludes with a practical 321 activity for engaging students and enhancing comprehension.
Takeaways
- 😀 Schemas are mental structures that organize knowledge, helping us learn and remember new information.
- 😀 The more developed your schemas are, the easier it is to learn and comprehend new concepts.
- 😀 Schemas are shaped by personal experiences, which is why learning and comprehension are unique to each individual.
- 😀 Assimilation occurs when new information fits into an existing schema, while accommodation happens when new information doesn't fit, requiring schema restructuring.
- 😀 Comprehension involves constructing a schema that provides a coherent explanation of what we experience or learn.
- 😀 Reading comprehension is an interactive process where prior knowledge and the text work together through hypothesis testing and prediction.
- 😀 Using graphic organizers can help structure information, enhancing comprehension and memory by providing a clear external representation of the internal schema.
- 😀 Teachers should avoid having students read texts cold (without prior context) and should always integrate new knowledge with what students already know.
- 😀 When teaching, it’s more effective to cover fewer topics in-depth rather than superficially covering too much material.
- 😀 The '321' activity encourages students to connect prior knowledge with new information by listing what they know, what they want to learn, and what they learned after the lesson.
Q & A
What is a schema, and how does it relate to learning and comprehension?
-A schema is an organized knowledge structure in the brain, akin to a file folder. It helps us organize and process information, making it easier to comprehend, learn, and remember new information. The more developed our schemas are, the easier it is to understand and absorb new content.
How do schemas impact reading comprehension?
-Schemas play a crucial role in reading comprehension by providing a mental framework that helps readers make sense of new material. As readers encounter text, their existing schemas help them predict and understand what they're reading, facilitating meaning construction from the text.
What is the difference between assimilation and accommodation in schema theory?
-Assimilation occurs when new information fits into an existing schema without requiring major changes, while accommodation happens when new information doesn’t fit into the existing schema and forces a restructuring or adaptation of the schema.
Why are personal experiences important when building schemas?
-Personal experiences shape how we organize knowledge in our brains. These experiences help build individual schemas, which influence how we process new information and make sense of the world around us.
How does the process of constructing meaning in comprehension work?
-Comprehension involves constructing a coherent schema that explains what we experience. This construction is not a direct replication of reality but rather a blend of past knowledge and new information, helping us make sense of what we encounter.
What is the role of graphic organizers in schema theory?
-Graphic organizers serve as external representations of the internal structure of schemas. They help students visualize the organization of information before, during, and after a lesson, aiding in better encoding and internalizing of new material.
How do schemas help with memorization and summarization?
-Schemas provide a structured framework that organizes new information, making it easier to remember and summarize. Rather than storing a disorganized collection of facts, schemas help group related concepts, enhancing retention.
What is the role of hypothesis testing in reading?
-In reading, the brain constantly tests hypotheses about the meaning of the text. Readers predict what will happen next or what a sentence means, and then confirm or adjust their understanding based on context clues and other text information.
Why is it important to integrate prior knowledge with new learning?
-Integrating prior knowledge with new material helps create connections between what students already know and what they are learning, making new information easier to understand, remember, and apply in different contexts.
What is the '321' activity, and how does it relate to schema theory?
-The '321' activity involves three things a student knows about a topic, two questions they have, and one thing they learned after the lesson. This activity helps activate prior knowledge (schemas) and creates a structured way for students to reflect on new learning.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示
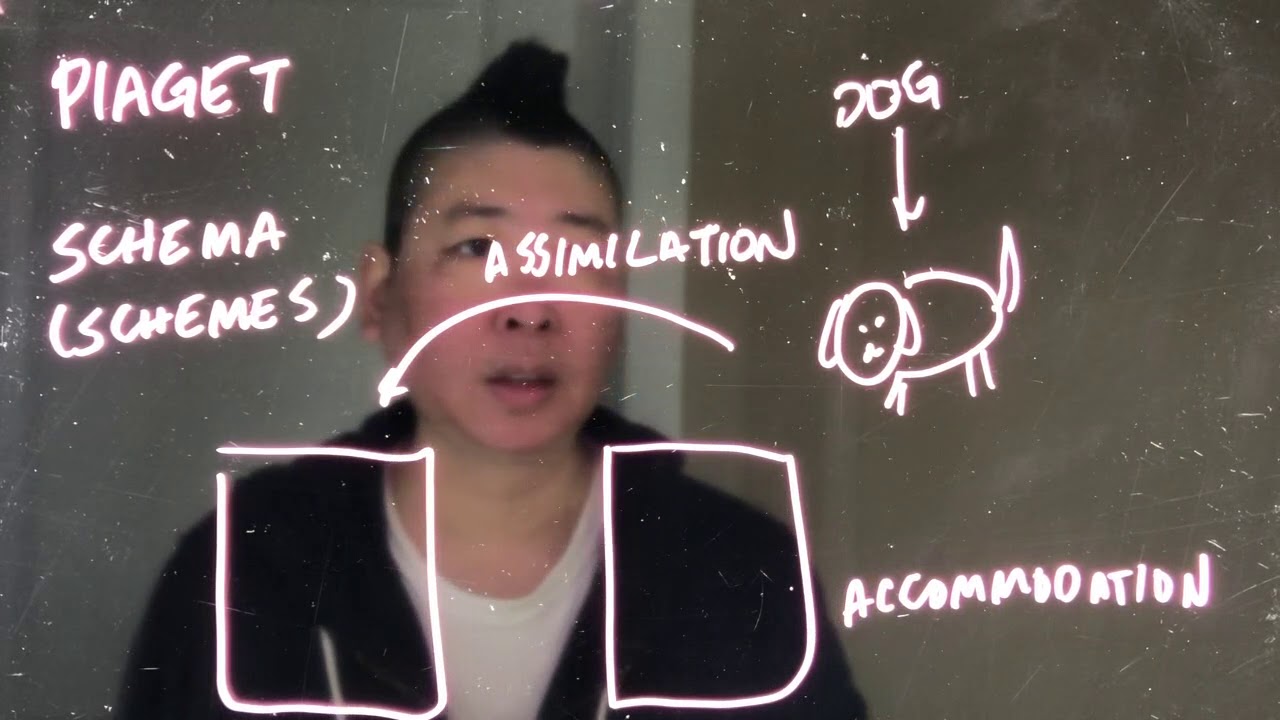
Piaget: Schema, Assimilation, and Accommodation

Development: Schemas, Assimilation, & Accommodation
What is Schema Theory in Psychology?

Social Psychology: Chapter 3 (Social Cognition) Part 2

Eduqas A-Level Psychology Component 1 - Assumptions REVISION GUIDE

Piaget’s Schema: Accommodation and Assimilation of New Information
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
