X-Ray Interactions with Matter
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the five primary interactions between x-ray photons and matter, focusing on their relevance to diagnostic radiology. Key interactions include coherent scattering, the Compton effect, and the photoelectric effect, which affect image quality through differential absorption. The video highlights how factors like kVp, atomic number, and tissue density influence absorption, contrast, and overall image clarity. Additionally, it clarifies the difference between absorption and attenuation. By the end, viewers will understand how these interactions shape radiographic images and how to optimize them for accurate diagnostics.
Takeaways
- 😀 X-rays are a type of electromagnetic energy that travel in a sinusoidal fashion, with shorter wavelengths corresponding to higher frequency and energy.
- 😀 There are five main types of interactions between x-rays and matter: coherent scattering, Compton effect, photoelectric effect, pair production, and photo disintegration.
- 😀 Coherent scattering occurs when an x-ray photon interacts with an atom, causing it to become excited and release an equal wavelength photon in a different direction, contributing minimally to image noise.
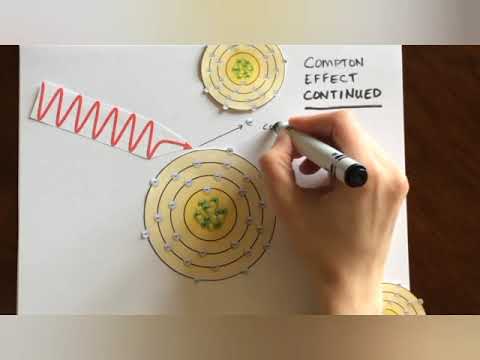
- 😀 The Compton effect involves an x-ray photon interacting with an outer shell electron, causing ionization and the scattering of the photon in a different direction. It negatively impacts image contrast due to scattered photons providing no useful information.
- 😀 The photoelectric effect occurs when an x-ray photon is absorbed by an inner shell electron, causing ionization and the emission of a photoelectron. This is essential for diagnostic radiology.
- 😀 Higher effective atomic numbers, like those of bone, lead to greater x-ray absorption, creating brighter areas on radiographs. The atomic number has no effect on the Compton effect.
- 😀 Increasing the energy of x-rays reduces the probability of the photoelectric effect, which may lead to a darkened radiograph if the photon bypasses electron interactions.
- 😀 Pair production occurs when x-ray photons with energy above 1.02 MeV interact with the nuclear field, producing a positron and negatron, but is not relevant in diagnostic radiology.
- 😀 Photo disintegration happens with high-energy photons (>10 MeV) that are absorbed by the nucleus, causing emission of nuclear fragments, but this interaction does not occur in diagnostic radiology.
- 😀 Differential absorption is the variation in absorption of x-rays by different tissues and is critical for image contrast. Bone, with a higher atomic number, absorbs more x-rays than soft tissue.
- 😀 Factors affecting differential absorption include kVp, atomic number, and mass density. A balance must be found between increasing absorption for contrast and minimizing patient dose.
Q & A
What are the five types of interactions that x-rays have with matter?
-The five types of interactions are: coherent scattering, Compton effect, photoelectric effect, pair production, and photo disintegration.
Which two interactions are most important for diagnostic radiology?
-The Compton effect and the photoelectric effect are the most important interactions in diagnostic radiology.
What happens during coherent scattering?
-In coherent scattering, a low-energy x-ray photon interacts with an atom, causing the atom to become excited. The atom then re-emits an x-ray photon of the same energy, but in a different direction.
How does the Compton effect affect image quality?
-The Compton effect scatters x-ray photons in different directions, leading to reduced image contrast and increased image noise, which negatively impacts image quality.
What is the significance of the photoelectric effect in diagnostic radiology?
-The photoelectric effect is crucial in diagnostic radiology as it leads to the complete absorption of an x-ray photon, creating high-contrast areas on the radiograph, especially in dense tissues like bone.
What role does atomic number play in x-ray interactions?
-In the photoelectric effect, the higher the atomic number of a material, the greater the x-ray absorption, which results in brighter areas on the radiograph. Atomic number does not affect the Compton effect.
What is differential absorption, and how does it affect image contrast?
-Differential absorption refers to the varying degrees of x-ray absorption by different tissues, leading to differences in image brightness. It is key to image contrast and is influenced by factors like kVp, atomic number, and tissue density.
How does tissue density influence differential absorption?
-Tissues with higher density, like bone, absorb more x-rays, leading to greater differential absorption. This results in brighter areas on the radiograph, while less dense tissues, like lungs, absorb fewer x-rays and appear darker.
What is the difference between absorption and attenuation?
-Absorption is the complete disappearance of an x-ray photon after interaction with matter. Attenuation refers to the total reduction in the number of x-ray photons remaining in the beam after passing through a material, caused by both absorption and scattering.
Why is it important to adjust kVp in diagnostic radiology?
-Adjusting kVp is important because it affects differential absorption. Lower kVp increases absorption and contrast but also increases patient dose, while higher kVp decreases absorption, leading to lower contrast but reduced patient exposure.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード5.0 / 5 (0 votes)