PCSI - video 2 - SLCI cours asservissements : outil Laplace
Summary
TLDRThis video provides a detailed explanation of the Laplace transform and its key properties. It covers the mathematical definition, including the uniqueness, linearity, and rules for differentiation and integration in the Laplace domain. The video also introduces important theorems, such as the initial value and final value theorems, and the impact of time shifts (delays) on the transform. Functions like the Dirac delta function, step functions, ramp functions, and exponential functions are discussed along with their Laplace transforms. The video emphasizes the stability analysis of systems using Laplace transforms and how the position of poles in the complex plane determines system behavior.
Takeaways
- 😀 The Laplace Transform is a mathematical tool that converts time-domain functions into the s-domain using an integral from 0 to infinity.
- 😀 The Laplace Transform has several important properties, including uniqueness, linearity, and the ability to transform derivatives and integrals of time-domain functions.
- 😀 The Laplace Transform of the derivative of a function involves multiplying by 'p', and the initial condition plays a key role in this transformation.
- 😀 The Laplace Transform of the integral of a function involves dividing by 'p'. The condition of having a zero initial value is often assumed in practical scenarios.
- 😀 Key theorems associated with the Laplace Transform include the Initial Value Theorem and the Final Value Theorem, which help determine the initial and final behavior of functions.
- 😀 The Laplace Transform of a delayed or shifted function in time results in multiplying by an exponential term that involves the delay factor.
- 😀 The Dirac Delta function, a distribution used to model impulses or shocks, has a Laplace Transform that is simply '1'.
- 😀 Common time-domain functions such as step functions, ramps, and exponential functions have specific Laplace Transforms, which are useful for solving differential equations.
- 😀 The position of poles in the s-domain (complex plane) determines the stability of the system: a positive real part leads to instability, while a negative real part indicates stability.
- 😀 A transfer function in the Laplace domain relates the output of a system to its input, with poles and zeros in the s-domain determining the system's behavior.
- 😀 Stability analysis using the Laplace Transform involves understanding the locations of poles, where a single pole with a positive real part leads to system instability.
Q & A
What is the definition of the Laplace transform?
-The Laplace transform of a time-domain function f(t) is defined as the integral from 0 to +∞ of f(t) multiplied by e^(-pt) dt. It is represented as F(p) and the variable p is a complex number.
What is the significance of the Laplace transform being unique?
-The uniqueness of the Laplace transform ensures that each time-domain function has a distinct representation in the Laplace domain. This property is essential for solving differential equations and analyzing systems.
How is the Laplace transform of a linear combination of functions computed?
-The Laplace transform of a linear combination of functions, such as αf(t) + βg(t), is the linear combination of their individual Laplace transforms. In other words, L{αf(t) + βg(t)} = αF(p) + βG(p).
How does the Laplace transform handle the derivative of a time-domain function?
-The Laplace transform of the derivative of a time-domain function f(t) is given by pF(p) - f(0), where f(0) represents the initial condition of the function at time t=0.
What is the Laplace transform of an integral of a function?
-The Laplace transform of the integral of a function f(t) from 0 to t is given by F(p)/p, assuming the initial condition is zero.
What are the initial and final value theorems in the context of the Laplace transform?
-The initial value theorem states that the initial value of a time-domain function f(t) can be found as the limit of pF(p) as p approaches infinity. The final value theorem states that the final value of f(t) as t approaches infinity can be found as the limit of pF(p) as p approaches 0.
What is the impact of the time shift (retardation) on the Laplace transform?
-When a function f(t) is delayed by a time τ, the Laplace transform of the delayed function is F(p)e^(-τp). This property allows us to analyze time-shifted signals in the Laplace domain.
How does a step function (Heaviside function) behave in the Laplace domain?
-A step function, defined as u(t) with a value of 0 for t<0 and 1 for t≥0, has the Laplace transform F(p) = 1/p. It represents a sudden change or a constant value after t=0.
What is the Laplace transform of a Dirac delta function?
-The Laplace transform of a Dirac delta function, δ(t), is 1. The Dirac delta function is a distribution that is zero for all t ≠ 0, and infinite at t=0.
How does the position of poles in the Laplace transform influence system stability?
-The position of poles in the Laplace transform, particularly their real parts, determines system stability. If any pole has a positive real part, the system will be unstable. A system is stable if all poles have negative real parts.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示
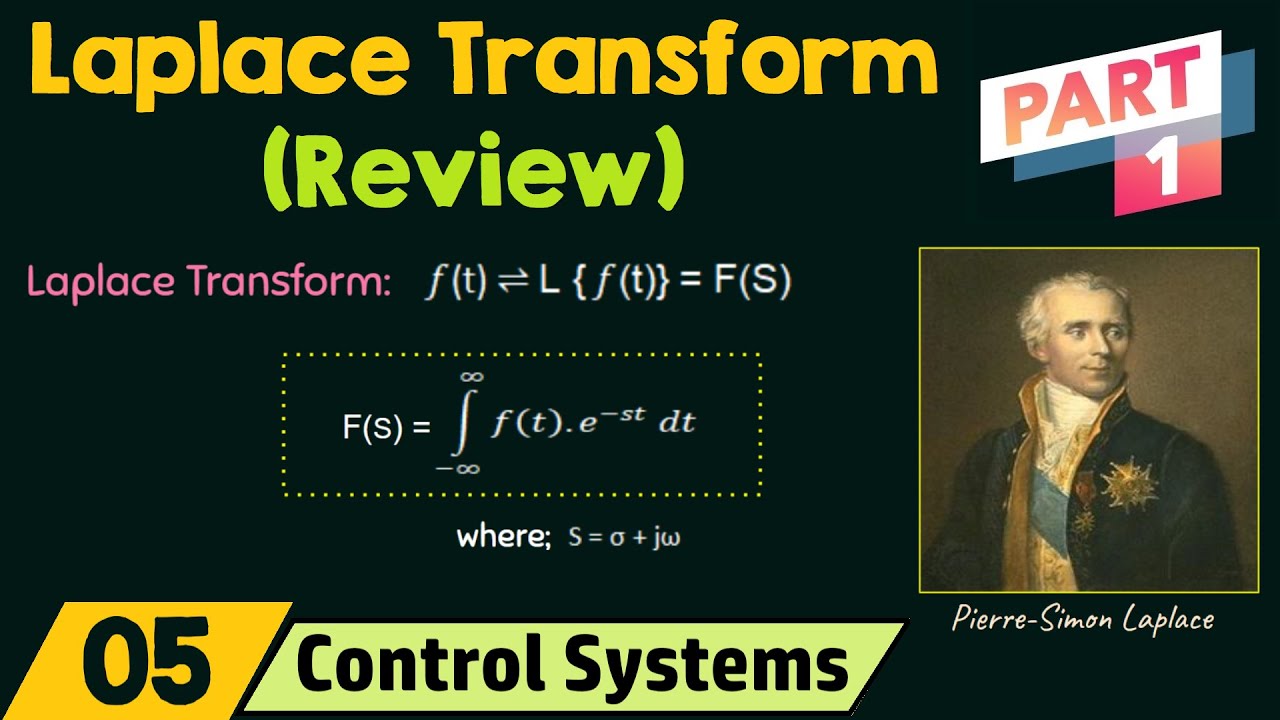
Review of Laplace Transform (Part 1)

Relation between Laplace transform, Fourier transform, z-transform, DTFT, DFT and FFT
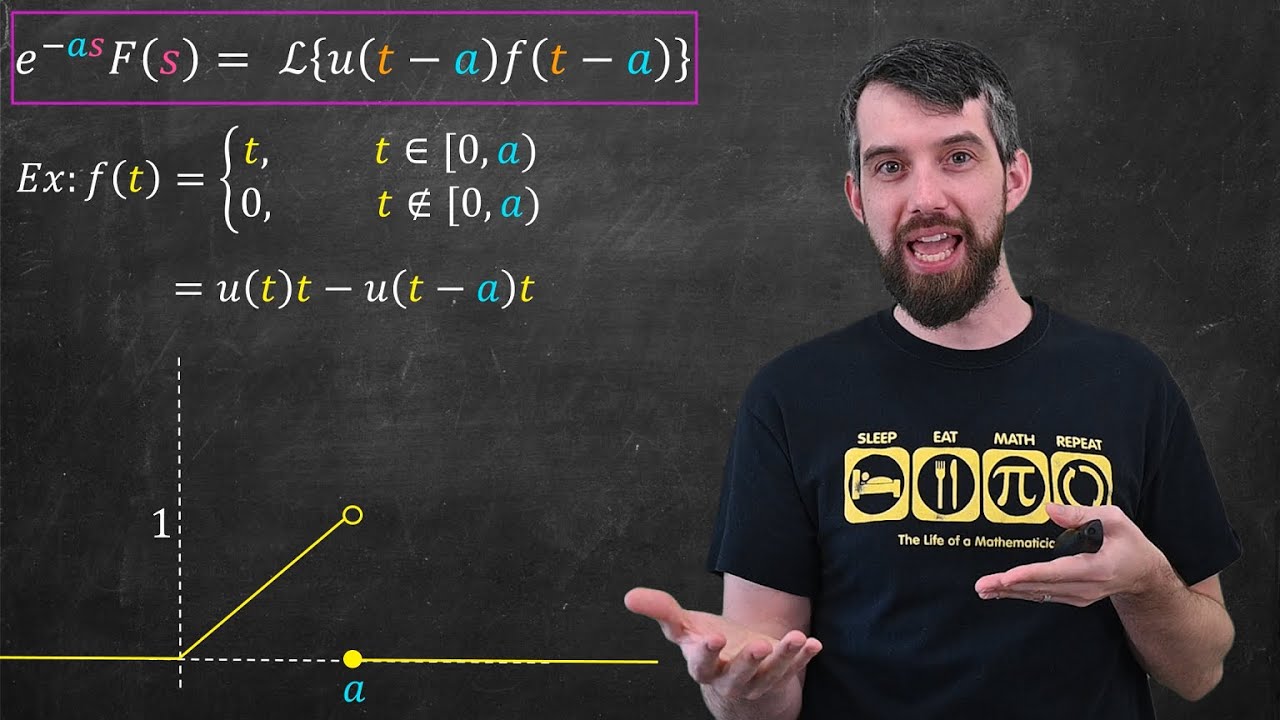
Laplace Transform and Piecewise or Discontinuous Functions

Sistem Kendali 2.2. Transformasi Laplace
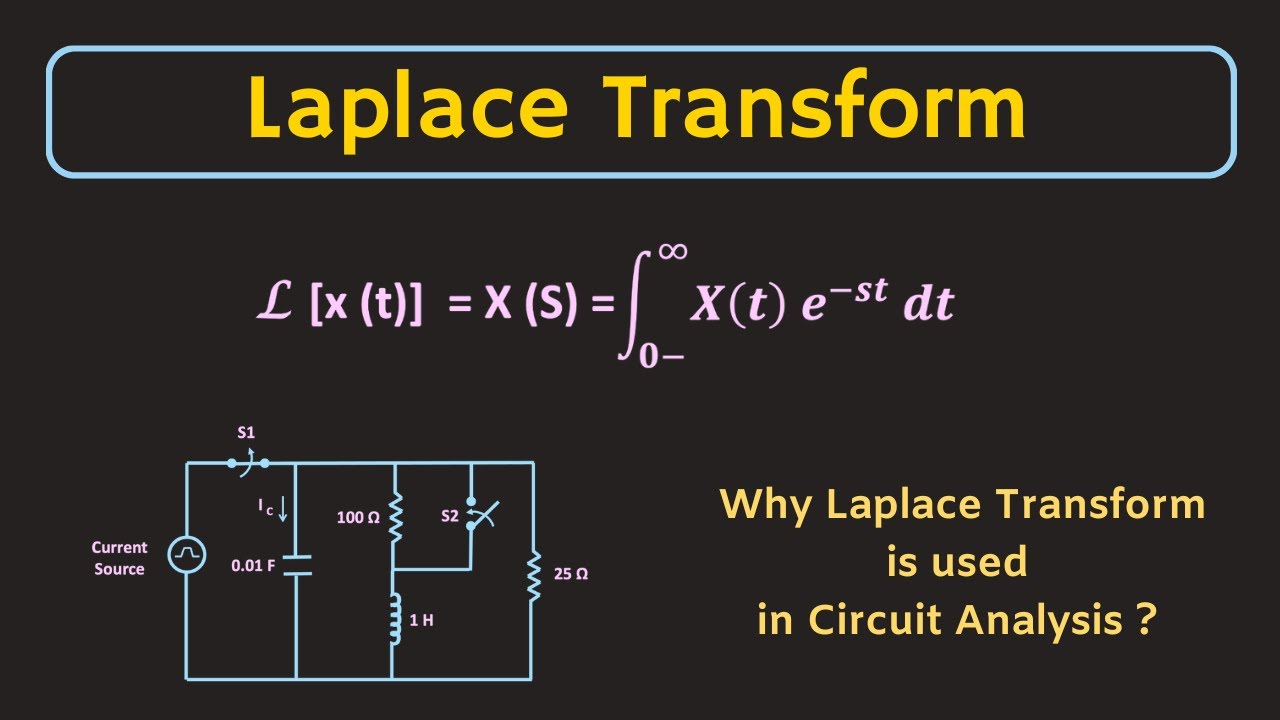
What is Laplace Transform? Why Laplace Transform is used in Circuit Analysis?

PROPERTIES OF LAPLACE TRANSFORM
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
