Introduction to Linked List | C++ Placement Course | Lecture 22
Summary
TLDRThe transcript discusses a data structure known as 'Linked List Liquid for Data', which is stored in Ruby. It explains the concept with the help of a person who can hold memory elements in a single clock of memory. The discussion covers the limitations of this structure, such as size constraints and memory allocation preferences. It also touches upon the challenges of inserting elements between nodes and the impact on international relations within the list. The speaker provides a detailed walkthrough of how to traverse and manipulate these lists, emphasizing the importance of understanding the start and end points, and the use of pointers to navigate through the list.
Takeaways
- 📚 Introduction to an interesting data structure called 'Linked List'.
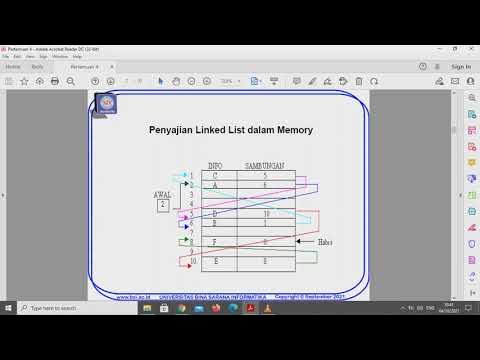
- 🔗 Linked Lists store elements in memory blocks that are connected to each other.
- ⚖️ Linked Lists differ from arrays because elements in arrays are stored in contiguous memory locations, while Linked Lists do not require this.
- 🧠 Linked Lists can be dynamically expanded, allowing insertion of more elements as needed, unlike arrays with fixed size.
- 🚧 Deletion and insertion operations in Linked Lists can be slower due to the need to update pointers.
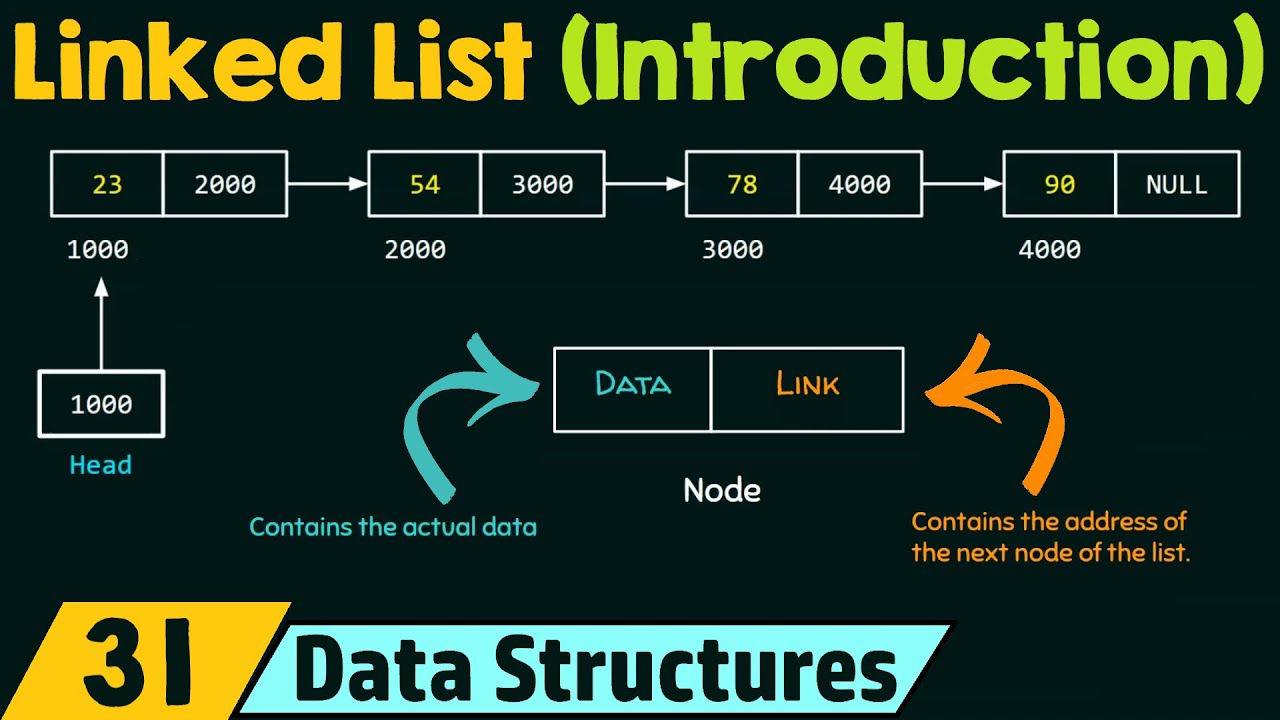
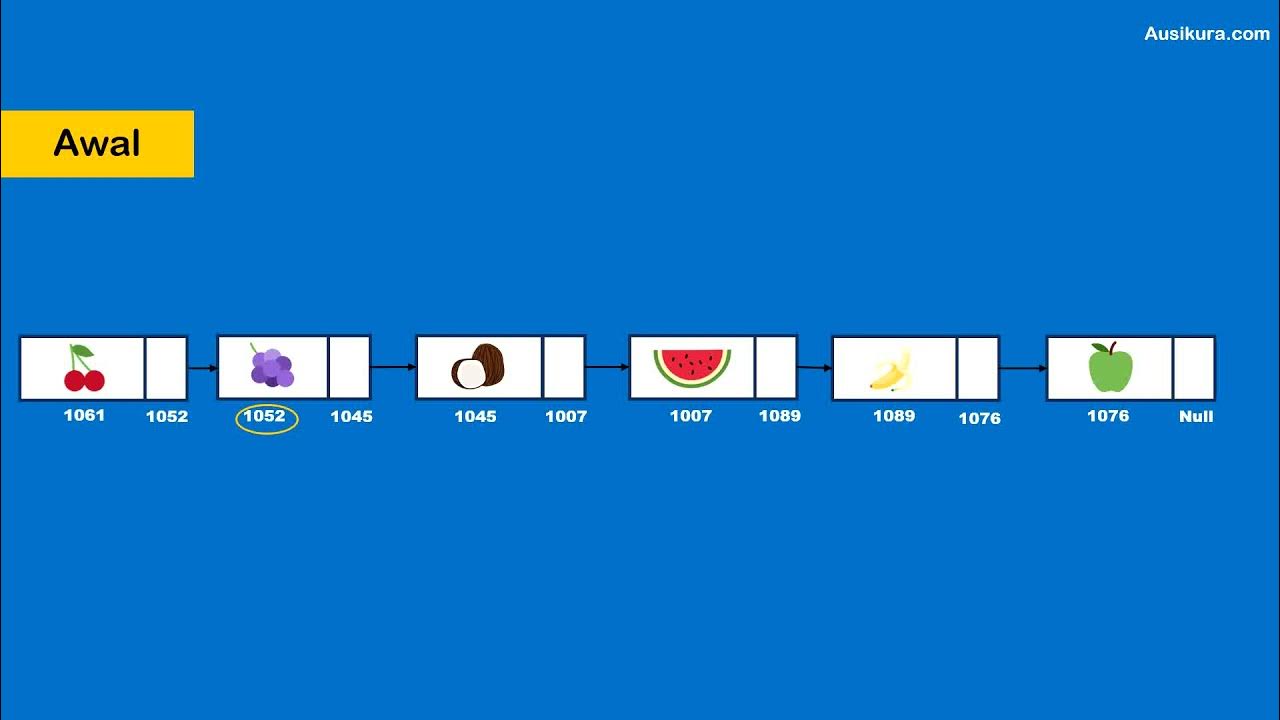
- 💡 The concept of a head pointer is introduced, which points to the first node in the Linked List.
- 🚀 Linked Lists are flexible and can handle memory fragmentation efficiently.
- 🔄 Linked Lists use 'next' pointers to traverse from one node to the next until reaching the end.
- 🛠️ Example of node structure: each node contains data and a pointer to the next node.
- 🎯 Practical usage in programming includes functions for inserting nodes at the end, printing the list, and searching for specific values.
Q & A
What is the main topic discussed in the script?
-The main topic discussed in the script is about data structures, specifically focusing on 'Linked List' and its properties and operations.
What is the term used for a linked list that stores data in memory?
-The term used for a linked list that stores data in memory is 'Linked List Data Structure'.
What is the difference between a singly linked list and a doubly linked list as mentioned in the script?
-A singly linked list allows traversal in one direction, while a doubly linked list allows traversal in both directions due to the presence of links to both the next and previous nodes.
What are the limitations of a linked list as discussed in the script?
-The limitations include the inability to directly access elements by index, the overhead of memory allocation for each element, and the complexity introduced by insertions and deletions, especially when considering the need to update links between elements.
How does the script describe the memory allocation for elements in a linked list?
-The script describes memory allocation for elements in a linked list as being allocated wherever there is free memory, and that each element may be spread out in memory with links to connect them.
What is the term used for the pointer that connects one node to another in a linked list?
-The term used for the pointer that connects one node to another in a linked list is 'next'.
What is the purpose of the 'head' pointer in a linked list as described in the script?
-The 'head' pointer in a linked list is used to keep track of the starting node of the list, allowing for easier traversal and manipulation of the list.
How does the script explain the process of inserting a new node into a linked list?
-The script explains that to insert a new node, you create a new node with the data and a 'next' pointer. Then, you traverse to the last node of the list, update its 'next' pointer to point to the new node, and finally, update the 'next' pointer of the new node to 'null'.
What is meant by 'tail' in the context of the linked list discussed in the script?
-In the context of the linked list, 'tail' refers to the last node in the list, which is significant for operations like appending new elements to the end of the list.
How does the script handle the scenario where the linked list is empty?
-The script handles an empty linked list by checking if the 'head' is equal to 'null', indicating no nodes are present. In such a case, it directly assigns the new node as the head of the list.
What is the significance of the 'next' field in a node of a linked list according to the script?
-The 'next' field in a node of a linked list is significant as it stores the memory address of the next node in the sequence, allowing the list to be traversed and manipulated.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード5.0 / 5 (0 votes)