Mathematicians Reveal Soft Cells: A New Class of Shapes
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the fascinating concept of 'soft cells' in geometry, moving beyond rigid shapes like triangles and squares to more fluid, adaptable forms found in nature. Soft cells have curved edges and smooth deformations, resembling bubbles or flowing water. They are prevalent in biological structures like muscle tissues, sea shells, and flower petals. These organic shapes challenge traditional geometric principles and inspire creativity in both art and science, emphasizing the beauty, flexibility, and complexity of nature's design.
Takeaways
- 🌐 Geometry extends beyond common shapes like squares, circles, and triangles into a softer, more organic realm known as soft cells.
- 💧 Soft cells are flexible shapes with curved edges and smooth deformations, contrasting with rigid traditional shapes.
- 🌿 Soft cells are prevalent in nature, from muscle tissues in the body to sea shells and flower petals, showing adaptability in their structures.
- 🔬 These shapes in nature challenge the traditional view of geometric form, introducing a more fluid and dynamic understanding of geometry.
- 🏞 Nature frequently favors soft cells, as seen in the intricate spirals of sea shells, the flexible structure of petals, and the wings of butterflies.
- 🔄 Soft cells represent natural forms that adapt and morph, embodying the fluidity and resilience of organic structures.
- 📚 Soft cells offer a different perspective on how geometry governs the natural world, suggesting that nature balances flexibility and structure.
- 🎨 Artists have drawn inspiration from soft cells, incorporating their fluidity into art, sculpture, and architectural design.
- 🧬 In biology, understanding soft cells can provide insights into how living organisms grow and function on both a microscopic and macroscopic level.
- 🌈 Soft geometry reveals the elegance and beauty of nature, demonstrating that geometry isn't limited to sharp angles and straight lines but can be as dynamic as life itself.
Q & A
What are soft cells in geometry?
-Soft cells are shapes that have curved edges and smooth deformations, unlike traditional geometric shapes such as squares, triangles, and circles. They are more flexible, able to morph, bend, twist, expand, and contract, adapting to their surroundings.
How do soft cells differ from traditional geometric shapes?
-Traditional geometric shapes like squares, triangles, and hexagons have well-defined, rigid edges and fixed forms. Soft cells, on the other hand, are fluid and dynamic, with curved edges and the ability to deform in response to external conditions.
Where can soft cells be found in nature?
-Soft cells are prevalent in nature, found in places like muscle tissues within our bodies, sea shells, flower petals, and butterfly wings. These structures demonstrate flexibility and smooth deformations, making them examples of soft geometry.
Why are soft cells important in biology?
-In biology, soft cells play a crucial role by allowing flexibility and adaptability in living organisms. For example, muscle tissue can contract and expand due to its soft geometry, and the curved structure of cellular components helps organisms function efficiently.
What is the significance of soft cells in art?
-Soft cells inspire creativity in art by offering fluid and graceful forms that contrast with rigid geometric shapes. Sculptures, paintings, and architectural designs often use soft cells to create aesthetically pleasing, organic forms that reflect the natural world.
How do soft cells challenge traditional geometric principles?
-Soft cells challenge traditional geometry by showing that nature often favors curved and adaptable forms over rigid, straight-edged shapes. This contrasts with classical geometric expectations, where precise lines and angles are emphasized.
What are some examples of soft cells outside the human body?
-Examples of soft cells outside the human body include the spiral curves of sea shells, the soft petals of flowers, and the smooth wings of butterflies. These natural forms illustrate the prevalence of curved, flexible geometry in the organic world.
How do soft cells reflect the adaptability of nature?
-Soft cells reflect nature’s adaptability by allowing organisms to grow, move, and function in a dynamic environment. Their flexibility helps organisms withstand external forces, such as environmental changes or physical stress, making them a key factor in survival.
In what ways do soft cells bridge the gap between science and art?
-Soft cells bridge science and art by demonstrating how fluid, organic forms found in nature can inspire artistic creations. Their adaptable, graceful structures influence both scientific understanding of biology and artistic expressions in sculpture and design.
Why is it important to appreciate the role of soft cells in our world?
-Appreciating soft cells helps us understand the hidden complexity of the natural world. They reveal that geometry is not just about rigid lines and shapes but also about fluid, dynamic forms that govern the structure of life and inspire artistic creativity.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示
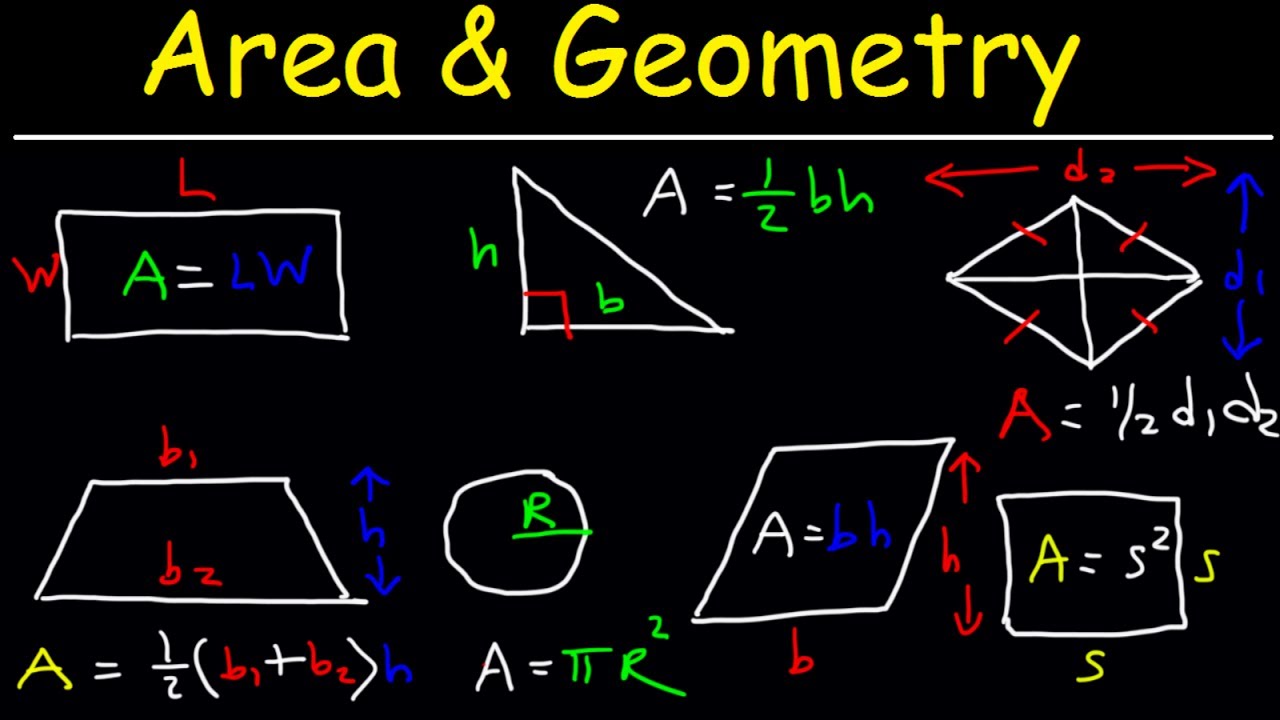
Area of a Rectangle, Triangle, Circle & Sector, Trapezoid, Square, Parallelogram, Rhombus, Geometry

مينيو المصممين: عناصر التصميم الجرافيكي—الشكل | Graphic Design Elements: Shape

Intro to Symmetry: All About Symmetry for Kids - FreeSchool

Video 2: Shape

Kekongruenan Hal 177-180 Bab 3 TRANSFORMASI Kelas 9 SMP Kurikulum Merdeka

A New Pattern in Nature
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
