The Gulf Stream Explained
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the critical role of ocean currents, particularly the Gulf Stream, in regulating the Earth's climate. It explains how these currents, driven by temperature and salt differences, form a global circulation system that transfers heat from the equator to the poles. The Gulf Stream, a key component, significantly influences Europe's climate by bringing warm water and air. The video also discusses concerns about how climate change might disrupt this system, potentially leading to drastic shifts in global weather patterns.
Takeaways
- 🌊 Ocean currents significantly influence our weather and climate by transporting heat from the equator to the poles.
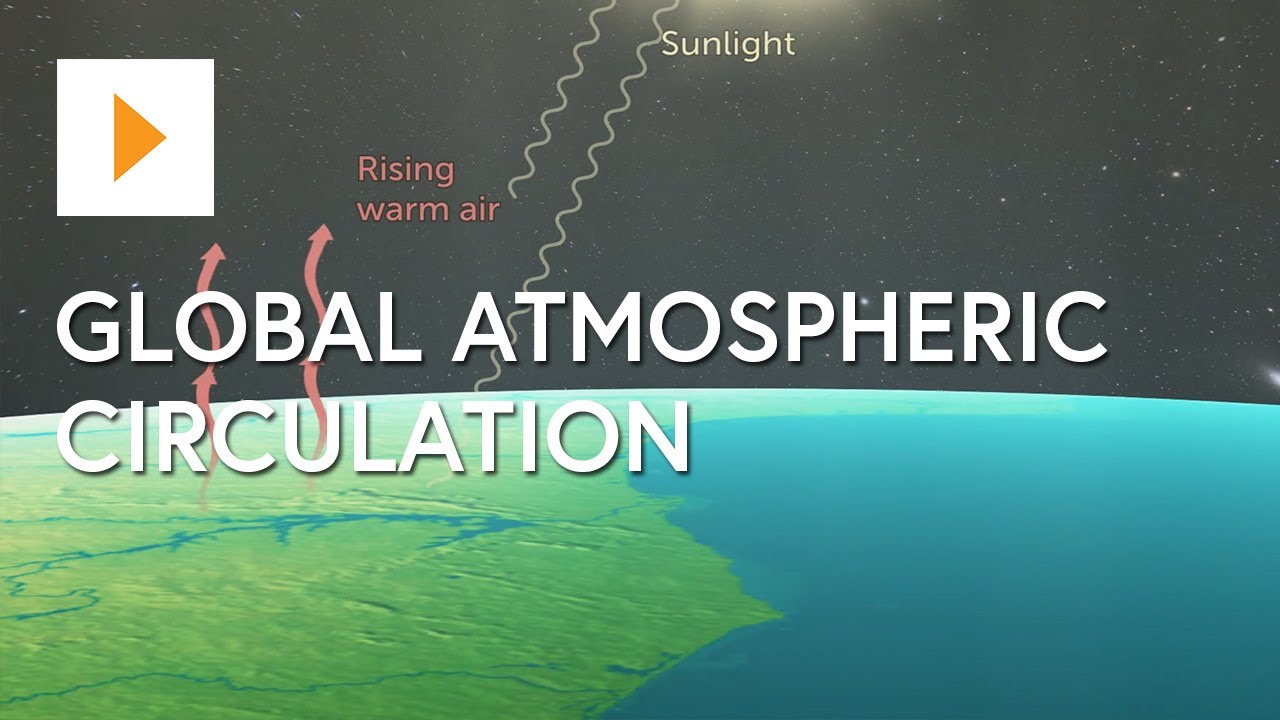
- 🔄 The ocean conveyor belt, also known as thermohaline circulation, involves a worldwide system of currents that exchange water among the global oceans.
- 🌡️ 'Thermo' and 'haline' in thermohaline circulation refer to the temperature and salt content of water, which determine its density and movement.
- 🌞 Warm water at the equator has a lower density and rises, while cold water is denser and sinks, influenced by solar heat and evaporation.
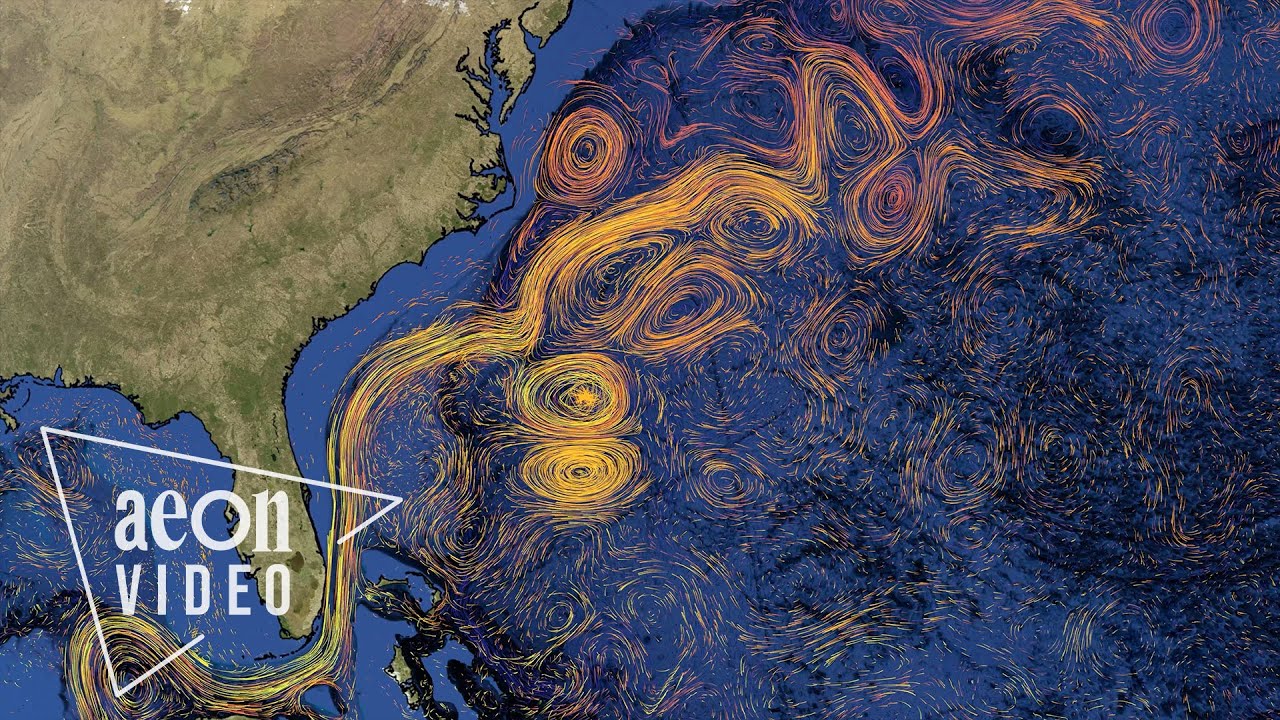
- 🌊 The Gulf Stream is a crucial component of the ocean conveyor belt, starting at the equator and significantly impacting the European climate.
- 🚀 The Gulf Stream is one of the largest and fastest ocean currents, carrying an immense volume of warm water towards Europe at a rate of up to 100,000,000 m³ per second.
- 🌀 The Gulf Stream is driven by the southeast trade winds and the Earth's rotation, which direct it towards Europe and cause it to split into different branches.
- 🌌 As the Gulf Stream moves north, it releases heat into the atmosphere, becoming colder and denser, eventually sinking between Greenland, Norway, and Iceland.
- 🌊 The sinking of the Gulf Stream creates the largest 'waterfall' on Earth, known as the 'Chimneys,' drawing in new water and maintaining the current's movement towards Europe.
- 🐠 The Gulf Stream serves as a vital transport route for countless marine species, facilitating their migration from the Caribbean to northern regions.
- 🌡️ The Gulf Stream acts as a 'heat pump,' bringing warmth to Europe that would otherwise require an enormous number of nuclear power plants to replicate.
- ❄️ Without the Gulf Stream, Europe would experience significantly colder temperatures and longer, harsher winters.
- 🌍 There are concerns that climate change could disrupt the Gulf Stream by altering the salt content and density of waters off Greenland, potentially stopping the current.
- 🔮 While scientists have differing views on the precise impact of climate change on the ocean conveyor belt, it is clear that climate shifts will lead to changes in the ocean current system that are not yet fully understood.
Q & A
What is the ocean conveyor belt and why is it important for our climate?
-The ocean conveyor belt, also known as thermohaline circulation, is a global system of ocean currents that transport heat from the equator to the poles, influencing weather and climate. It's crucial as it facilitates the exchange of water between four of the five global oceans, forming a worldwide circulation system.
How do ocean currents and wind systems operate as a large engine for the global climate?
-Ocean currents and wind systems move heat around the planet, redistributing warmth from the sunniest regions to colder areas. This movement is akin to a large engine, driving the global climate by maintaining temperature balances.
What factors determine the density of water in the ocean conveyor belt?
-The density of water in the ocean conveyor belt is determined by its temperature and salt content. Warm water is less dense and tends to rise, while cold water is denser and sinks. Additionally, higher salt content increases water density.
Why does the Gulf Stream begin at the equator and what role does it play in the European climate?
-The Gulf Stream begins at the equator due to strong solar heat causing evaporation, which increases the water's salt content. It is vital for the European climate as it transports warm water towards Europe, significantly warming the continent and contributing to a milder climate.
How does the Gulf Stream transport such a large volume of water?
-The Gulf Stream transports up to 100,000,000 cubic meters of water per second, driven by the southeast trade winds that push warm surface water to the northwest and the Earth's rotation that directs it towards Europe.
What is the significance of the North Atlantic Current in the Gulf Stream system?
-The North Atlantic Current is where the Gulf Stream releases a significant amount of heat into the atmosphere as it moves north. The water cools, increases in salt content and density due to evaporation, and sinks, driving the circulation.
What is the largest waterfall on Earth mentioned in the script, and how does it relate to the Gulf Stream?
-The largest waterfall on Earth mentioned is the 'Chimneys,' which are 15-km-wide pillars with water falling up to 4,000 meters. This phenomenon is part of the maelstrom created by the sinking of cold, dense water, pulling in new water and contributing to the Gulf Stream's movement towards Europe.
How does the Gulf Stream serve as a means of transport for countless species?
-The Gulf Stream provides a natural pathway for numerous marine species to migrate from the Caribbean to northern areas, utilizing the current for their journeys.
What is the Gulf Stream's role in bringing warm air to Europe, and how significant is this?
-The Gulf Stream acts as a heat pump, bringing an enormous quantity of warm air to Europe. The heat it provides is so significant that it would require 1,000,000 nuclear power plants to produce the same amount of heat.
What are the potential impacts of climate change on the Gulf Stream and the ocean conveyor belt?
-Climate change could potentially disrupt the Gulf Stream and the ocean conveyor belt by melting polar caps, which might decrease the salt content and density of water off Greenland, affecting the sinking of the North Atlantic Current. However, some climate experts believe that climate change could also compensate for this effect, as the Earth's climate naturally fluctuates.
How might the Gulf Stream's cessation due to climate change affect Europe's climate and landscape?
-If the Gulf Stream were to stop due to climate change, Europe would experience significantly colder temperatures, by at least five to ten degrees. Instead of lush fields, there would be long winters and sparse, ice-covered landscapes.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード5.0 / 5 (0 votes)