Periodic Table Explained: Introduction
Summary
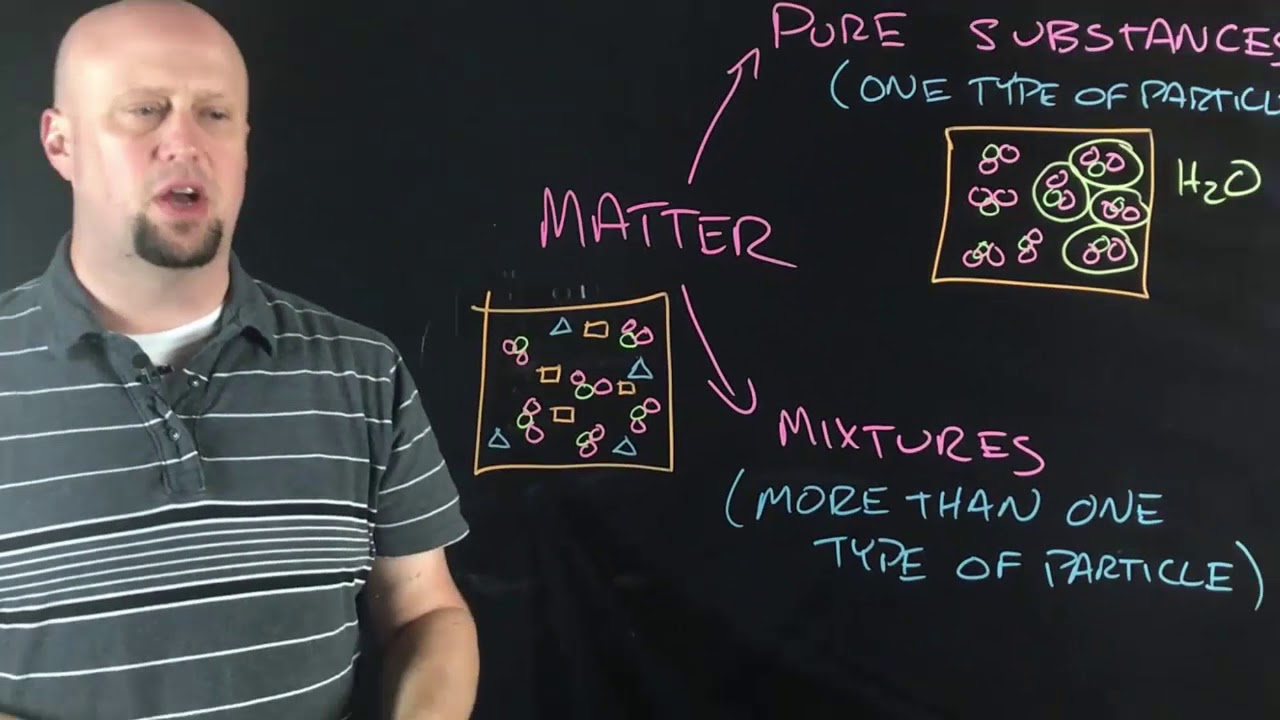
TLDRThe video script explores the concept of elements, defined as substances composed of a single type of atom, with 92 naturally occurring ones and additional man-made ones. It introduces the periodic table, a systematic arrangement of elements by atomic number and properties, highlighting groups that share similar characteristics. The script also explains how elements can be identified by their atomic number and symbol, and discusses the distinction between metals and nonmetals, with metals typically to the left of a diagonal band on the table and nonmetals to the right. Hydrogen is noted as a unique case, not fitting neatly into any group. The periodic table is likened to an alphabet, essential for understanding the composition of all matter in the universe.
Takeaways
- 🌌 All matter is composed of tiny particles called atoms.
- 🔍 There are 92 naturally occurring types of atoms, known as elements.
- 📚 A pure substance made of only one type of atom is called an element.
- 📈 The periodic table lists all the elements in order of increasing atomic number.
- 📝 Elements are represented by one or two-letter symbols, like 'H' for hydrogen.
- 🔢 Hydrogen has the atomic number 1 and is the lightest element.
- 📏 The periodic table has seven horizontal rows, with additional rows for the lanthanides and actinides.
- 👨🔬 Scientists have created artificial elements, extending the list beyond 92.
- 👪 Elements in the same vertical group have similar properties.
- 🛡 Metals are typically found on the left side of the periodic table and have properties like conductivity and malleability.
- ⚗️ Nonmetals are on the right side and often do not conduct electricity or heat.
- 💎 Elements within the diagonal band have properties intermediate between metals and nonmetals, known as semiconductors or metalloids.
- 🌐 Hydrogen is unique and does not fit neatly into any group; it is considered a group by itself.
Q & A
What are the fundamental building blocks of all things in the world?
-The fundamental building blocks of all things in the world are incredibly tiny particles called atoms.
How many different kinds of atoms are there?
-There are 92 different kinds of atoms, which are the basis for the elements found in nature.
What is an element and how is it related to atoms?
-An element is a pure substance made of only one kind of atom. For example, a nugget of pure gold contains only gold atoms.
What is the purpose of the periodic table?
-The periodic table is a list that shows all the elements, arranged according to the atomic number and chemical properties, making it easier to understand and remember the different elements.
What is the atomic number and how is it related to the periodic table?
-The atomic number is a number that indicates an element's position in the periodic table, representing the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom of that element.
How many horizontal rows does the periodic table have?
-The periodic table has seven horizontal rows, known as periods.
What are the special rows at the bottom of the periodic table called, and what do they represent?
-The special rows at the bottom of the periodic table are called the lanthanides and actinides, which are elements that fit into the sixth and seventh periods, respectively.
What is the significance of the vertical columns in the periodic table?
-The vertical columns in the periodic table, also known as groups, contain elements that have similar chemical properties, making them akin to families.
How can you determine if an element is a metal or a nonmetal using the periodic table?
-Elements to the left of the diagonal gray band in the periodic table are metals, while those to the right are nonmetals. Elements within the band are often semiconductors or metalloids, having properties of both.
What is unique about the element hydrogen in terms of its placement on the periodic table?
-Hydrogen is unique because it is placed to the left of the diagonal band but is not considered a metal. It does not belong to any group and is considered to be a group by itself.
Why are there more elements listed on the periodic table than the original 92?
-In addition to the original 92 elements, scientists have created artificial elements in laboratories, extending the list of known elements beyond uranium to a total of 118.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenant5.0 / 5 (0 votes)