Types of Matter - Elements, Compounds, Mixtures, and Pure Substances
Summary
TLDRThis educational video explores the classification of matter, distinguishing between pure substances and mixtures. Pure substances are further categorized into elements, which consist of a single type of atom, and compounds, which are made up of different elements combined. Mixtures are divided into homogeneous, where components are uniformly distributed, exemplified by saltwater, and heterogeneous, where components are not uniformly mixed, like oil and water. The video promises additional resources for deeper understanding.
Takeaways
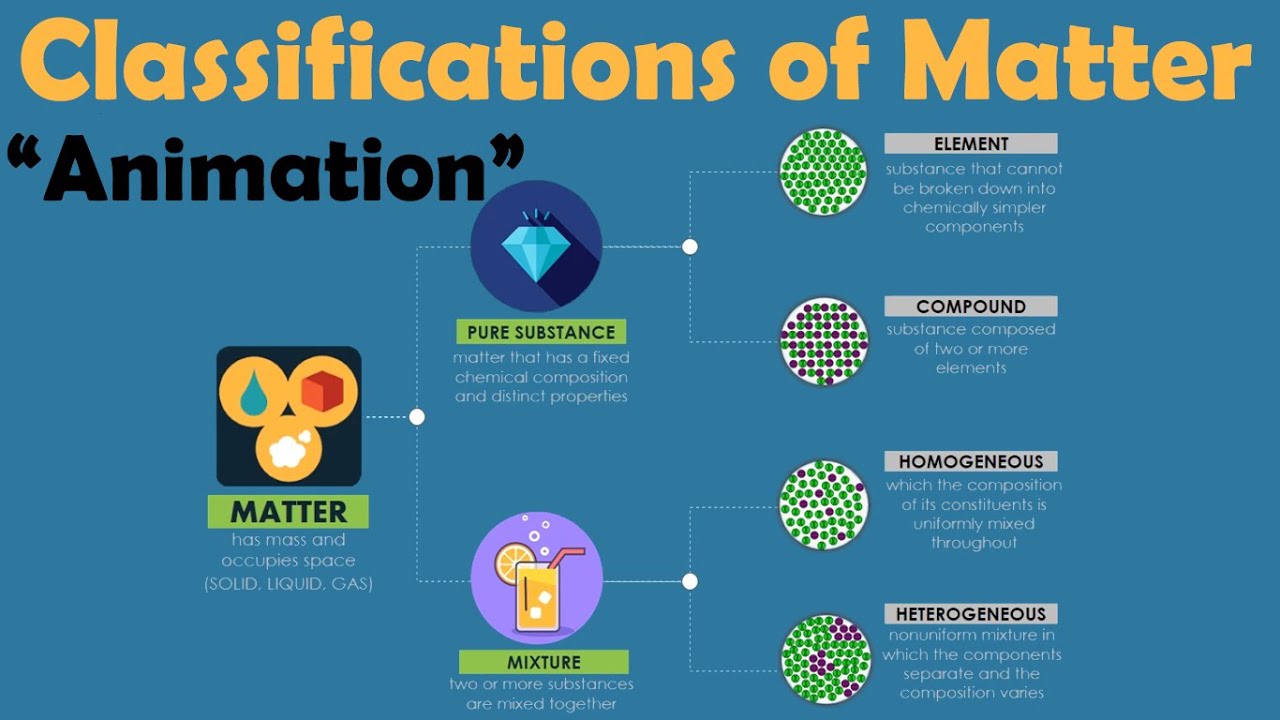
- 🧪 Matter is categorized into two main types: pure substances and mixtures.
- 🌐 Pure substances consist of a single type of matter, either elements or compounds.
- 🔍 Elements are pure substances made up of only one kind of atom, like oxygen or iron.
- 🔗 Compounds are also pure substances but consist of two or more different elements chemically bonded together, such as water (H2O).
- 🤖 Mixtures are combinations of two or more different pure substances that are not chemically bonded.
- 🌀 Homogeneous mixtures have a uniform composition throughout, like salt dissolved in water.
- 🌁 Heterogeneous mixtures have a non-uniform composition, with different parts having different properties, such as oil floating on water.
- 🌬️ Air is an example of a homogeneous mixture, containing a uniform blend of gases like oxygen and nitrogen.
- 🏖️ Sand and water form a heterogeneous mixture, as the sand does not dissolve and remains distinct from the water.
- ⚙️ Understanding the classification of matter is fundamental to grasping chemical concepts and reactions.
Q & A
What are the two main categories of matter?
-The two main categories of matter are pure substances and mixtures.
What is a pure substance?
-A pure substance is a material that consists of only one kind of substance, which can be either an element or a compound.
What is the difference between an element and a compound?
-An element is a pure substance made up of only one kind of atom, while a compound is a pure substance composed of two or more different elements chemically bonded together.
Give an example of a homogeneous mixture.
-A homogeneous mixture is one where the composition is uniform throughout, such as salt dissolved in water, which appears as one clear solution.
What is a heterogeneous mixture?
-A heterogeneous mixture is a mixture where the components are not uniformly distributed, like oil and water, which do not mix and form two distinct layers.
Why is air considered a homogeneous mixture?
-Air is considered a homogeneous mixture because it is a uniform mixture of gases like oxygen, nitrogen, argon, and carbon dioxide, which are evenly distributed throughout the mixture.
Can you provide an example of a pure substance that is an element?
-Examples of pure substances that are elements include oxygen gas (O2), helium (He), nitrogen gas (N2), iron (Fe), and zinc (Zn).
What is sodium chloride and why is it considered a compound?
-Sodium chloride (NaCl) is considered a compound because it is made up of two different elements, sodium (Na) and chlorine (Cl), chemically bonded together.
How is ethanol different from carbon dioxide in terms of composition?
-Ethanol (C2H5OH) is a compound composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, while carbon dioxide (CO2) is a compound consisting only of carbon and oxygen.
What are some other examples of heterogeneous mixtures mentioned in the script?
-Other examples of heterogeneous mixtures mentioned in the script include oil and water, and sand and water, where the components do not mix uniformly and can be visually separated.
Where can viewers find more information and example problems on pure substances and mixtures?
-Viewers can find more information and example problems on pure substances and mixtures by checking the links in the description section of the video.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)