GCSE Biology - Cell Types and Cell Structure #2
Summary
TLDRThis educational video explores the fundamental nature of cells, the basic building blocks of life, focusing on the comparison between eukaryotic cells found in animals and plants, and prokaryotic cells in bacteria. It explains the common subcellular structures like cell membranes, nuclei, cytoplasm, mitochondria, and ribosomes, while highlighting the unique features of plant cells, such as cell walls, vacuoles, and chloroplasts. The video also clarifies the differences in genetic material organization and the presence of flagella in bacteria, aiming to help viewers understand and label the parts of a cell and their functions.
Takeaways
- 🌱 Cells are the basic building blocks of life, capable of independent replication and functioning as the smallest unit of life.
- 🔬 Both animal and plant cells are eukaryotic, meaning they have a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles.
- 🌼 Plant cells have additional structures like a cell wall made of cellulose, which provides support and prevents bursting from excess water intake.
- 🍃 Plant cells also contain a large central vacuole filled with cell sap, used for storage and maintaining turgor pressure.
- 🌞 Chloroplasts in plant cells are responsible for photosynthesis, using sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose, with chlorophyll aiding in light absorption.
- 🐠 Animal cells differ from plant cells in that they lack a cell wall, large central vacuole, and chloroplasts.
- 🚀 Mitochondria are present in both animal and plant cells, acting as the 'powerhouses' by breaking down glucose to produce energy through aerobic respiration.
- 🧬 Ribosomes are found in all types of cells, serving as the sites of protein synthesis where amino acids are assembled into proteins.
- 🌌 Bacterial cells are prokaryotic, consisting of a single cell without a nucleus, and their genetic material is a single circular DNA strand floating in the cytoplasm.
- 🛢 Some bacteria possess plasmids, which are small rings of DNA carrying additional genes that may provide advantages such as antibiotic resistance.
- 🚶 Flagella are thread-like structures in some bacteria that enable movement by rotating and propelling the bacteria through their environment.
Q & A
What are cells considered as in the context of life?
-Cells are considered as the basic building blocks of life, being the smallest unit of life that can replicate independently.
What is the primary function of the cell membrane?
-The cell membrane controls which substances can pass in and out of the cell, allowing some chemicals through but not others.
What is the role of the nucleus in a cell?
-The nucleus contains the genetic material or DNA of the cell, effectively controlling the activities of the cell.
What is the gel-like substance within cells called, and what is its role?
-The gel-like substance within cells is called cytoplasm. It is where all the other subcellular structures sit in and where chemical reactions take place.
What is the main function of mitochondria in cells?
-Mitochondria provide the cells with the energy they need to function by breaking down sugars like glucose in a process called aerobic respiration.
What is the site of protein synthesis in cells?
-Ribosomes are the site of protein synthesis in cells, where proteins are made.
How does the presence of a cell wall in plant cells differ from animal cells?
-Plant cells have a rigid cell wall made of cellulose that provides support and structure to the cell, which is important to prevent bursting from too much water intake.
What is the purpose of the permanent vacuole in plant cells?
-The permanent vacuole in plant cells is a large sac that contains cell sap, a mixture of sugars, salts, and water that the cell can use when needed.
What is the primary function of chloroplasts in plant cells?
-Chloroplasts are where photosynthesis happens, using energy from the sun to make sugars like glucose, and they contain chlorophyll which absorbs the light energy needed for this process.
How do bacterial cells differ from eukaryotic cells in terms of genetic material storage?
-Bacterial cells, being prokaryotic, do not have a nucleus. Instead, they have a single circular strand of DNA that floats freely in the cytoplasm, which is sometimes referred to as the circular chromosome or nucleoid.
What are plasmids in bacteria and what role do they play?
-Plasmids are small rings of DNA in bacteria that carry extra genes, such as antibiotic resistance, which the bacteria may not need on a daily basis but can be beneficial in certain situations.
How do flagella help bacteria move?
-Flagella are thread-like structures that protrude from bacteria and can rotate to propel the bacteria along, allowing them to move around.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

Biology: Cell Structure I Nucleus Medical Media

Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic Cells - High School Biology

Perbedaan Sel Prokariotik & Sel Eukariotik | Pembelajaran Daring - Dunia Biologi
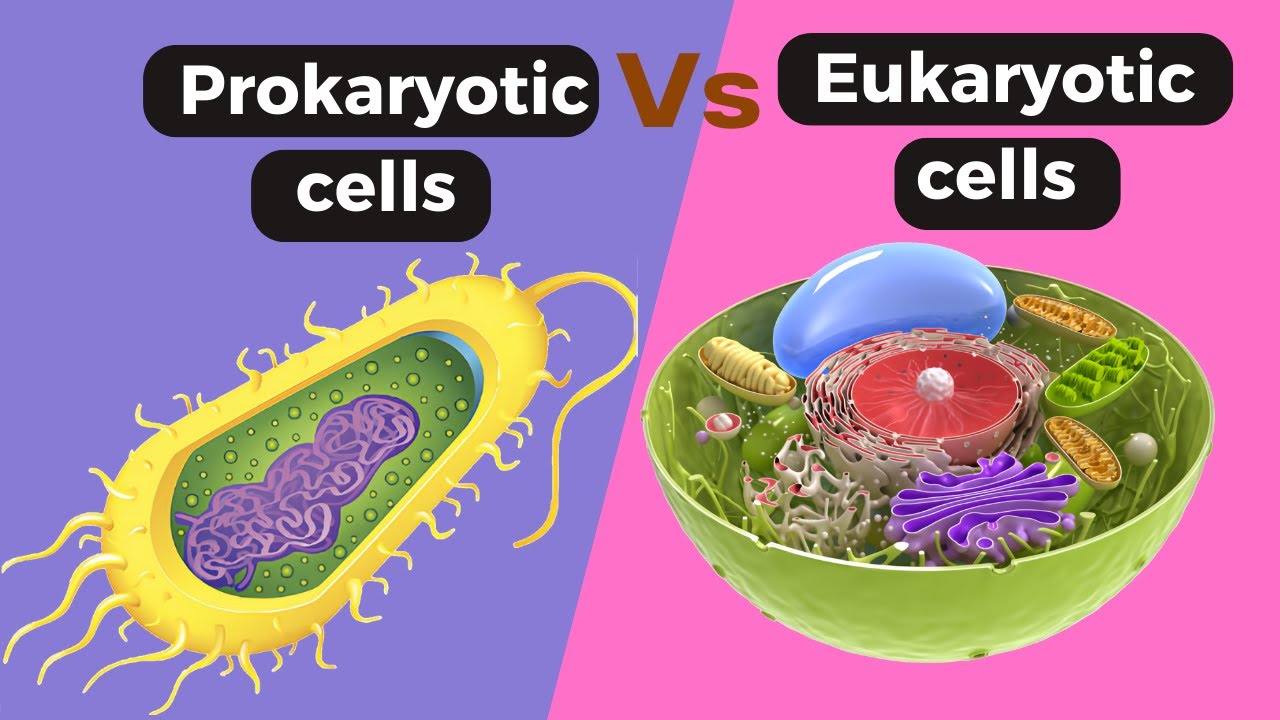
Prokaryotic cell Vs Eukaryotic cells|| Difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell

Overview of Cell Structure

CÉLULAS EUCARIONTES E PROCARIONTES - DIFERENÇAS | ANIMAÇÃO
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
