Prokaryotic Vs. Eukaryotic Cells
Summary
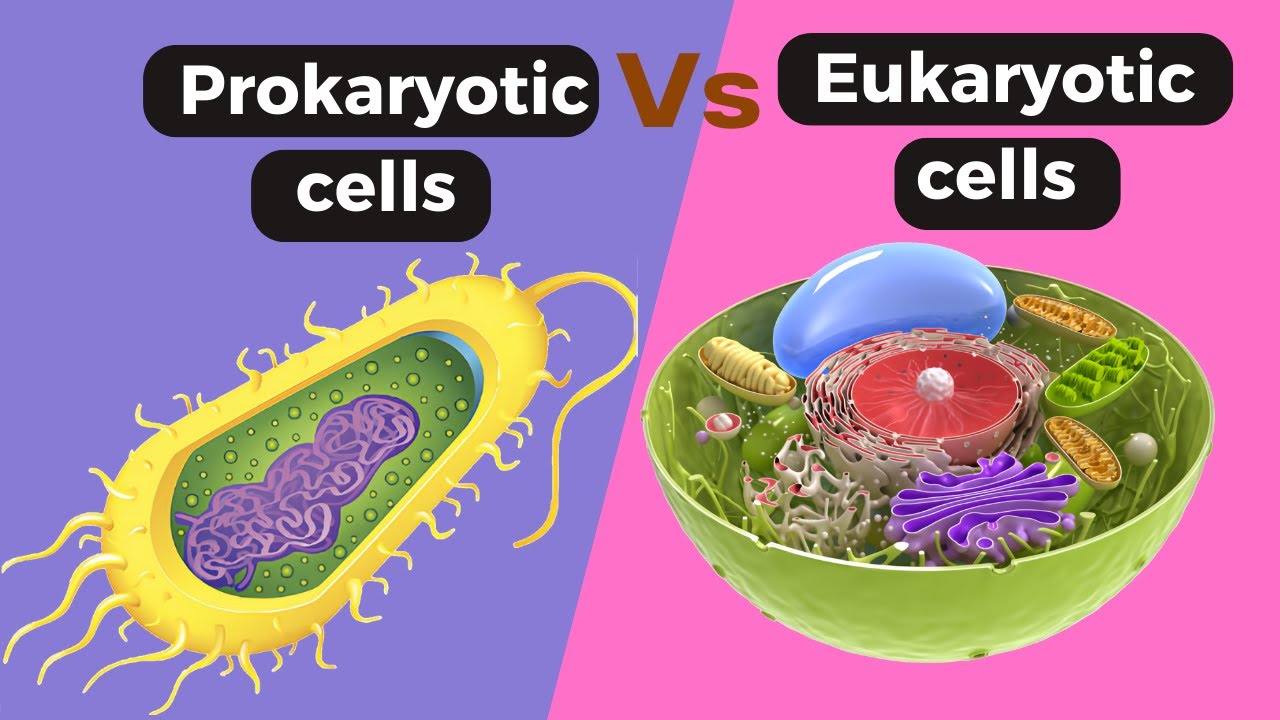
TLDRThis script explores the fundamental differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, the two primary cellular types on Earth. Prokaryotic cells, being simpler and smaller, lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, featuring a nucleoid region for DNA and often a cell wall. Eukaryotic cells, more complex and larger, possess a true nucleus and various organelles. Both cell types share DNA as their genetic material, ribosomes, cytoplasm, and a plasma membrane, but diverge in structure and complexity, with eukaryotes evolving from prokaryotes and potentially being either single-celled or multicellular.
Takeaways
- 🌏 There are two major types of cells on Earth: prokaryotic and eukaryotic.
- 📚 Prokaryotic cells are the simplest and most ancient, existing for billions of years before eukaryotic cells.
- 🔍 Prokaryotic cells are smaller and have a simpler structure compared to eukaryotic cells.
- 🚀 The simplicity of prokaryotic cells allows for rapid and efficient reproduction.
- 🌀 Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, having an open unit structure.
- 🧬 The DNA of prokaryotes is located in the nucleoid region, which is not enclosed by a membrane.
- 🏰 Prokaryotes possess a cell wall made of complex polysaccharides, with composition varying between archaea and bacteria.
- 🚶 Prokaryotes often have flagella for movement, a feature not mentioned for eukaryotes in the script.
- 💼 Eukaryotic cells contain a true nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles, indicating more complexity.
- 🔄 Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells share DNA as their genetic material, ribosomes, cytoplasm, and a plasma membrane.
- 🔄 Prokaryotic cells are single-celled, while eukaryotes can be either single-celled or multicellular.
- 🔗 The DNA organization differs, with prokaryotes having a single circular chromosome and eukaryotes having linear chromosomes.
Q & A
What are the two major types of cells found on Earth?
-The two major types of cells on Earth are prokaryotic and eukaryotic.
Why are prokaryotic cells considered the simplest and most ancient type of cells?
-Prokaryotic cells are the simplest and most ancient because they were the only form of life on Earth for billions of years before eukaryotic cells evolved.
How do prokaryotic cells reproduce?
-Prokaryotic cells reproduce quickly and effectively due to their simple structure, which lacks complex internal compartments.
What is the main structural difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
-The main structural difference is that prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, while eukaryotic cells have a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles.
What is the significance of the term 'prokaryote' in relation to its structure?
-The term 'prokaryote' means 'before nucleus,' indicating that these cells do not have a nucleus enclosed by a membrane.
Where is the DNA located in a prokaryotic cell?
-In a prokaryotic cell, the DNA is located in a region of the cytoplasm called the nucleoid region, which is not enclosed by a membrane.
What is the composition of the cell wall in prokaryotic cells?
-The cell wall of prokaryotic cells consists of complex polysaccharides, and its composition depends on whether the cell is an archaean or a bacterium.
How do prokaryotic cells move?
-Prokaryotic cells often possess one or more flagella, which are used for movement.
What does the term 'eukaryote' imply about the cell structure?
-The term 'eukaryote' means 'true nucleus,' indicating that these cells have a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles.
What common features do prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells share?
-Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells share the presence of DNA as their genetic material, ribosomes, cytoplasm, and a plasma membrane.
How is the DNA organization different between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
-Prokaryotic cells have DNA organized as a single, circular chromosome, while eukaryotic cells have DNA organized as linear chromosomes.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes
Prokaryotic cell Vs Eukaryotic cells|| Difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell

SEL 1 (Komponen Kimia Sel)

Comparing prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells | High school biology | Khan Academy

Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes

Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell | Differences and Similarities | Video 16

Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic Cells - High School Biology
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
