Solar Vapor Absorption Refrigeration System (Ammonia-Water Solar Cooling System) Explained.
Summary
TLDRThis tutorial video delves into the workings of a solar-powered vapor absorption refrigeration system, utilizing an ammonia-water cycle. It highlights the key components, such as the absorber, pump, generator, analyzer, rectifier, condenser, expansion valve, and evaporator, and explains how solar energy drives the process of cooling by transferring heat and transforming ammonia and water into vapor and back, achieving continuous refrigeration.
Takeaways
- ❄️ Refrigeration is the process of lowering the temperature by removing unwanted heat from a selected object, substance, or space and transferring it to another object, substance, or space.
- 💧 The vapour absorption refrigeration system discussed uses the ammonia-water system and solar energy for the refrigeration process.
- ☀️ This system can be termed as an ammonia-water cooling system or a solar cooling system.
- 🔄 The major parts and components of the system include the absorber, pump, generator, analyzer, rectifier, condenser, expansion valve, and evaporator.
- 🛠️ The absorber contains a solution of ammonia and water. The pump transfers this solution from the absorber to the generator.
- 🔥 In the generator, heat from solar energy turns the ammonia-water solution into vapour. The analyzer separates the water vapour from the ammonia vapour.
- ⚗️ The rectifier further separates any remaining water vapour from the ammonia vapour, converting the water vapour into liquid form.
- ❄️ The pure ammonia, now in a partial liquid form, enters the condenser, where it is cooled and completely converted into liquid ammonia.
- 🔧 The liquid ammonia then passes through an expansion valve, reducing its pressure and temperature, resulting in very cold, low-pressure liquid ammonia.
- 📉 This cold liquid ammonia enters the evaporator, absorbs heat from its surroundings, and provides the cooling effect, turning into low-pressure ammonia vapour.
- 🔁 The low-pressure ammonia vapour returns to the absorber, where it mixes with water, and the cycle repeats, providing continuous refrigeration.
Q & A
What is the primary purpose of a refrigeration system?
-The primary purpose of a refrigeration system is to lower the temperature by removing unwanted heat from a selected object, substance, or unenclosed space and transferring this heat to another object, substance, or space.
What type of refrigeration system is discussed in the video?
-The video discusses a vapor absorption refrigeration system, specifically using the ammonia-water system and solar energy, which can also be termed as a solar cooling system.
What are the main components of a vapor absorption refrigeration system?
-The main components of a vapor absorption refrigeration system include an absorber, a pump, a generator, an analyzer, a rectifier, a condenser, an expansion valve, and an evaporator.
What is the role of the pump in the system?
-The pump's role is to transfer the ammonia and water solution from the absorber to the generator, which is powered by solar energy.
How does the generator contribute to the refrigeration process?
-The generator contributes by producing heat using solar energy, which causes the ammonia and water solution to turn into vapor.
What is the function of the analyzer in the vapor absorption refrigeration system?
-The analyzer sends the water vapor back to the generator and only lets the ammonia vapor pass through, ensuring the separation of ammonia and water vapor.
Why is a rectifier necessary in the system?
-A rectifier, also known as a separator, is necessary to separate the remaining limited amount of water vapor from the ammonia vapor through heat exchange, converting the water vapor into liquid form and separating it from the ammonia vapor.
What happens to the ammonia vapor after it leaves the rectifier?
-After leaving the rectifier, the ammonia vapor, which is in a partial liquid state due to heat exchange, enters the condenser where it is cooled and converted into liquid form.
What is the purpose of the expansion valve in the refrigeration cycle?
-The expansion valve is used to reduce the pressure of the high-pressure liquid ammonia, causing it to expand and cool down, resulting in a low-pressure, low-temperature liquid ammonia.
How does the evaporator contribute to the cooling effect?
-The evaporator contributes to the cooling effect by absorbing heat from its surrounding surface, causing the low-pressure, chilled liquid ammonia to evaporate and turn into low-pressure ammonia vapor, thus cooling the surrounding space.
How does the refrigeration cycle continue after the evaporator stage?
-After the evaporator stage, the low-pressure ammonia vapor returns to the absorber, where it forms a solution with water. The pump then sends this solution back to the generator, and the cycle repeats, maintaining continuous refrigeration.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes
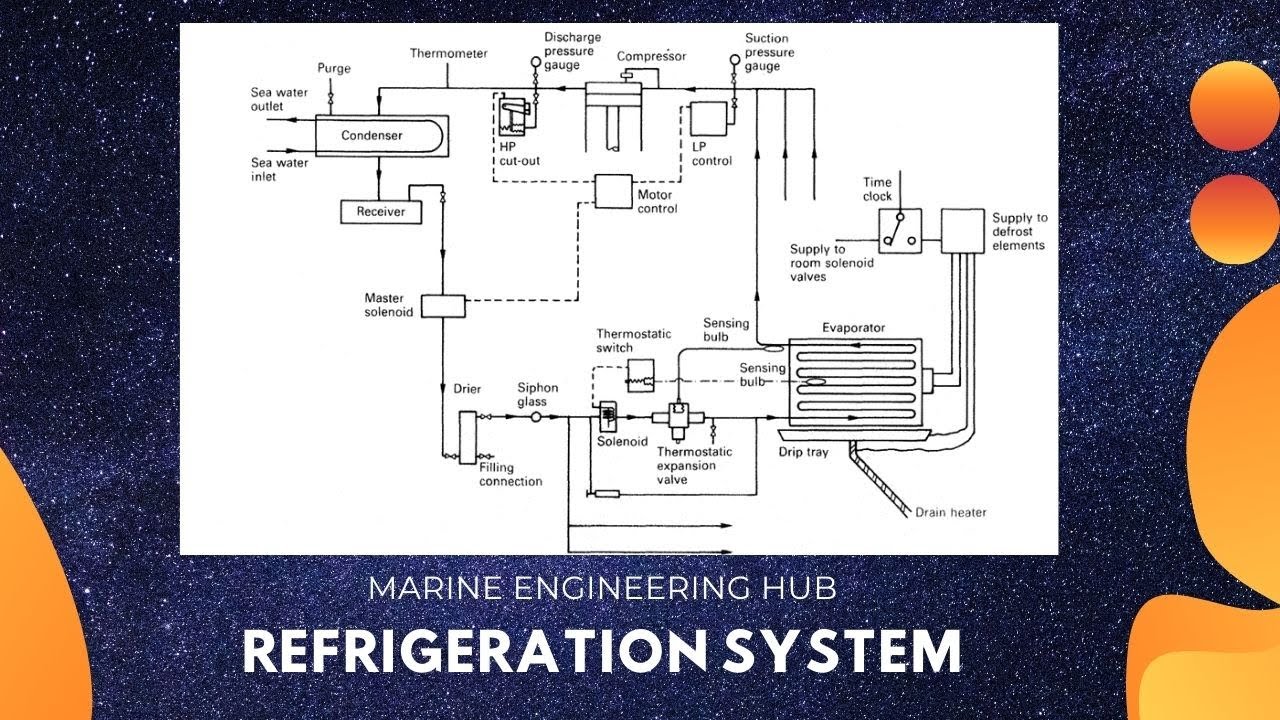
REFRIGERATION SYSTEM| (PART-1)|
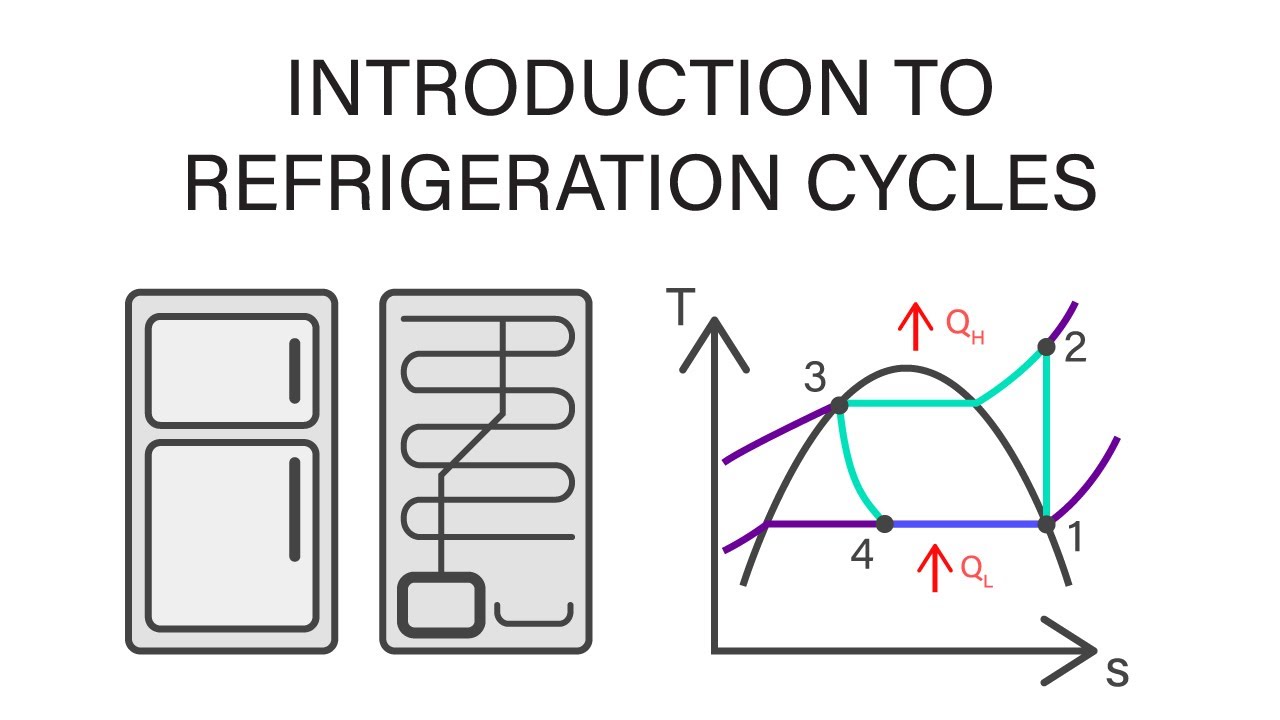
Mechanical Engineering Thermodynamics - Lec 23, pt 1 of 4: Introduction to Refrigeration Cycles

How does a Refrigerator work? 3D Animation

Siklus Air/Siklus Hidrologi Tugas UAS Animasi Pembelajaran
Analisis Siklus Refrigerasi Kompresi Uap Ideal
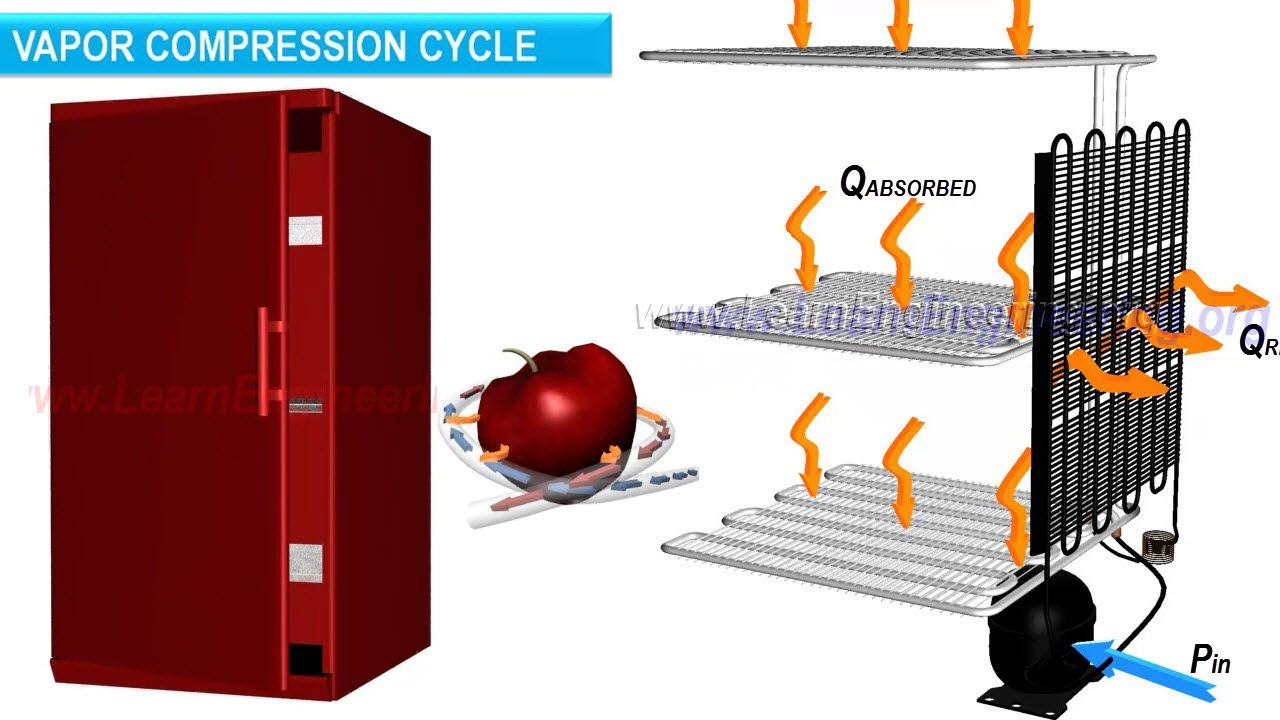
Refrigerator working - The Basics
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
