DNA vs RNA (Updated)
Summary
TLDRThis script delves into the often-overlooked importance of RNA alongside DNA, both essential nucleic acids in all living organisms. It explains the structural differences, such as DNA's double helix and RNA's single-stranded nature, and their respective roles in protein synthesis. The script also highlights the types of RNA—mRNA, rRNA, and tRNA—and their functions, concluding with a quiz to reinforce learning. It encourages viewers to explore the fascinating details of these biomolecules further.
Takeaways
- 🧬 DNA and RNA are both essential nucleic acids found in all living organisms, with DNA typically in the nucleus and RNA both in and out of the nucleus.
- 🌟 DNA is known for its double helix structure and is celebrated for its role in storing genetic information.
- 🔄 RNA plays a crucial role in protein synthesis, acting as a messenger to carry genetic information from DNA to ribosomes for protein production.
- 📜 The RNA World hypothesis suggests that RNA may have come before DNA in the early stages of life on Earth.
- 💠 Both DNA and RNA are composed of nucleotides, which consist of a phosphate, sugar, and a base.
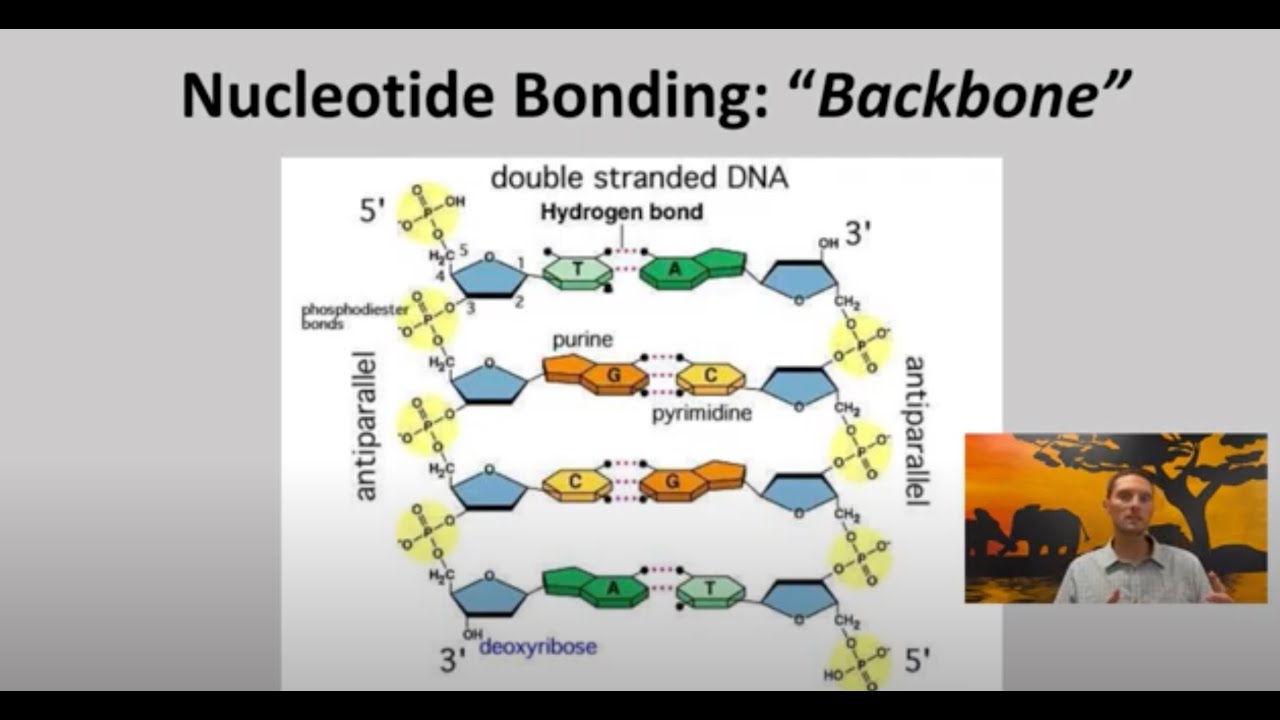
- 🔬 The sugar in DNA is deoxyribose, while in RNA it is ribose, which is reflected in their names: deoxyribonucleic acid and ribonucleic acid.
- 🔄 DNA has adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine as bases, while RNA has adenine, uracil, guanine, and cytosine, with uracil replacing thymine.
- 📝 mRNA (messenger RNA) carries the genetic message from DNA to the ribosomes, where proteins are synthesized.
- 🧲 rRNA (ribosomal RNA) is a major component of ribosomes, which are the sites of protein synthesis.
- 🔄 tRNA (transfer RNA) transfers amino acids to the ribosome to match the correct mRNA codon, facilitating the formation of polypeptide chains.
- 📚 The script encourages viewers to explore further details about DNA and RNA structures and their functions through provided links and resources.
Q & A
What is the primary function of DNA?
-DNA's primary function is to store genetic information and code for your traits.
Why is RNA considered as important as DNA?
-RNA is considered as important as DNA because it plays a crucial role in protein synthesis by carrying the genetic message from DNA to the ribosomes, where proteins are produced.
What is the 'RNA World hypothesis' mentioned in the script?
-The 'RNA World hypothesis' is a theory suggesting that RNA came before DNA in the early stages of life's evolution, with RNA molecules capable of both storing genetic information and catalyzing chemical reactions.
Where are DNA and RNA typically found within eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells?
-In eukaryotic cells, DNA is typically found in the nucleus, while RNA can be found both in and out of the nucleus. Prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus, contain both DNA and RNA in the cytoplasm.
What is the basic building block of nucleic acids like DNA and RNA?
-The basic building block of nucleic acids is a nucleotide, which consists of a phosphate, a sugar, and a base.
How does the sugar component differ between DNA and RNA?
-The sugar in DNA is deoxyribose, while in RNA it is ribose, which is why DNA is called deoxyribonucleic acid and RNA is called ribonucleic acid.
What are the four bases found in DNA?
-The four bases found in DNA are adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C).
What is the difference in the bases between DNA and RNA?
-In RNA, uracil (U) replaces thymine (T), while adenine (A), guanine (G), and cytosine (C) remain the same as in DNA.
What are the three main types of RNA involved in protein synthesis?
-The three main types of RNA involved in protein synthesis are messenger RNA (mRNA), ribosomal RNA (rRNA), and transfer RNA (tRNA).
What is the role of mRNA in protein synthesis?
-mRNA carries the genetic message from DNA, which is then used as a template for protein synthesis at the ribosome.
What is the purpose of tRNA in the process of protein synthesis?
-tRNA's purpose is to transfer the correct amino acids to the growing polypeptide chain during protein synthesis, matching them to the mRNA codons.
How many DNA bases are there in 8 DNA nucleotides?
-There are 8 DNA bases in 8 DNA nucleotides, as each nucleotide contains one base.
How many base pairs are there in 8 DNA nucleotides?
-There are 4 base pairs in 8 DNA nucleotides, as DNA is double-stranded and the bases pair up (A with T, and C with G).
If one DNA strand has the bases A, T, T, G, A, C, what would be the complementary bases on the opposite strand?
-The complementary bases on the opposite DNA strand would be T, A, A, C, T, G, following the base pairing rules (A with T and C with G).
In transcription, what would be the complementary RNA bases to the original DNA sequence A, T, T, G, A, C?
-The complementary RNA bases would be U, A, A, C, U, G, since RNA uses uracil (U) instead of thymine (T).
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenant5.0 / 5 (0 votes)