Biomoléculas (atualizado em 2023)
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the four major biomolecules essential for life: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. It explains their role in living organisms, from providing energy to structural support and genetic information. Carbohydrates are vital for quick energy, lipids serve as long-term energy storage and insulation, proteins are crucial for cellular structures and functions like enzymes, and nucleic acids, including DNA and RNA, store genetic information. The script emphasizes the importance of understanding these molecules' structures and their components, such as monomers like glucose, amino acids, and nucleotides. It concludes with a reflection on the elegance of biomolecule structures.
Takeaways
- 😀 Biomolecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids) are essential for life and play key roles in cellular structure and function.
- 😀 A monomer is a building block of larger substances, and each class of biomolecules has its own monomer.
- 😀 Carbohydrates, like bread, pasta, fruits, and vegetables, are an important energy source, with their monomer being monosaccharides like glucose.
- 😀 Glucose is critical for energy production in cells, and combining two glucose molecules creates the disaccharide maltose.
- 😀 When many monosaccharides bond, they form large carbohydrates (polysaccharides) like starch and glycogen, which store energy.
- 😀 Lipids, including fats and oils, are hydrophobic and include triglycerides, phospholipids, and steroids, which are important for energy storage and insulation.
- 😀 Lipids make up the structure of cell membranes and provide long-term energy storage, helping to conserve heat in organisms like seals.
- 😀 Proteins, made from amino acids, are essential for structural support (e.g., muscle tissue, hair, collagen) and for various cell functions, including enzymes and receptors.
- 😀 Many enzymes, antibodies, and hormones like insulin are proteins, which regulate vital processes in the body.
- 😀 Nucleic acids, including DNA and RNA, store and transmit genetic information, and their monomer is the nucleotide.
- 😀 The mnemonic 'CHONP' (Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, Phosphorus) helps remember the common elements in biomolecules.
Q & A
What are biomolecules, and why are they important?
-Biomolecules, also known as macromolecules, include carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. They are essential for the structure and function of cells, which are the building blocks of organisms.
What is a monomer?
-A monomer is a basic building block or unit that makes up larger molecules, called polymers. For example, the monomer of carbohydrates is monosaccharides.
What is the monomer of carbohydrates?
-The monomer of carbohydrates is a monosaccharide. An example of a monosaccharide is glucose.
How are carbohydrates important for organisms?
-Carbohydrates are important as they provide quick energy for cells. They can also be stored as polysaccharides like starch in plants or glycogen in animals for later use.
What is the significance of glucose in cellular respiration?
-Glucose is a key energy source for cells. It is used in cellular respiration to produce ATP, which serves as the cell's primary energy currency.
What are lipids, and what are their functions in the body?
-Lipids include fats and oils and are important for long-term energy storage, insulation, and forming cell membranes. Lipids like phospholipids form the bilayer of cell membranes, and some act as hormones.
What is the role of phospholipids in cells?
-Phospholipids are essential in forming the structure of the cell membrane. They create a lipid bilayer that provides the membrane with both structural integrity and selective permeability.
What is the monomer of proteins?
-The monomer of proteins is an amino acid. Proteins are composed of many amino acids linked together in a specific sequence.
Why are proteins important for organisms?
-Proteins play a critical role in many functions, such as forming structures like muscle tissue, enzymes, and receptors in cell membranes. They are also involved in immune responses and signaling pathways.
What is the monomer of nucleic acids?
-The monomer of nucleic acids, like DNA and RNA, is the nucleotide. Nucleotides are made up of a sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base.
What is the function of DNA and RNA in cells?
-DNA stores genetic information, while RNA is involved in protein synthesis. Both nucleic acids are essential for the functioning of cells and the transmission of genetic information.
What mnemonic can help remember the common elements in biomolecules?
-The mnemonic 'CHONP' (Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, Phosphorus) helps recall the common elements found in biomolecules.
Can DNA be found in food?
-Yes, DNA can be found in food that comes from living organisms, such as fruits, vegetables, animals, and fungi. For example, eating a strawberry involves consuming the DNA from the strawberry cells.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

La Química de los Alimentos: Cómo los Compuestos Influyen en tu Nutrición y Salud

Beginners Guide to MACROMOLECULES

These are the 4 main types of carbon-based molecules necessary for life

Biomolecules (Updated 2023)

Biomolecules (Older Video 2016)
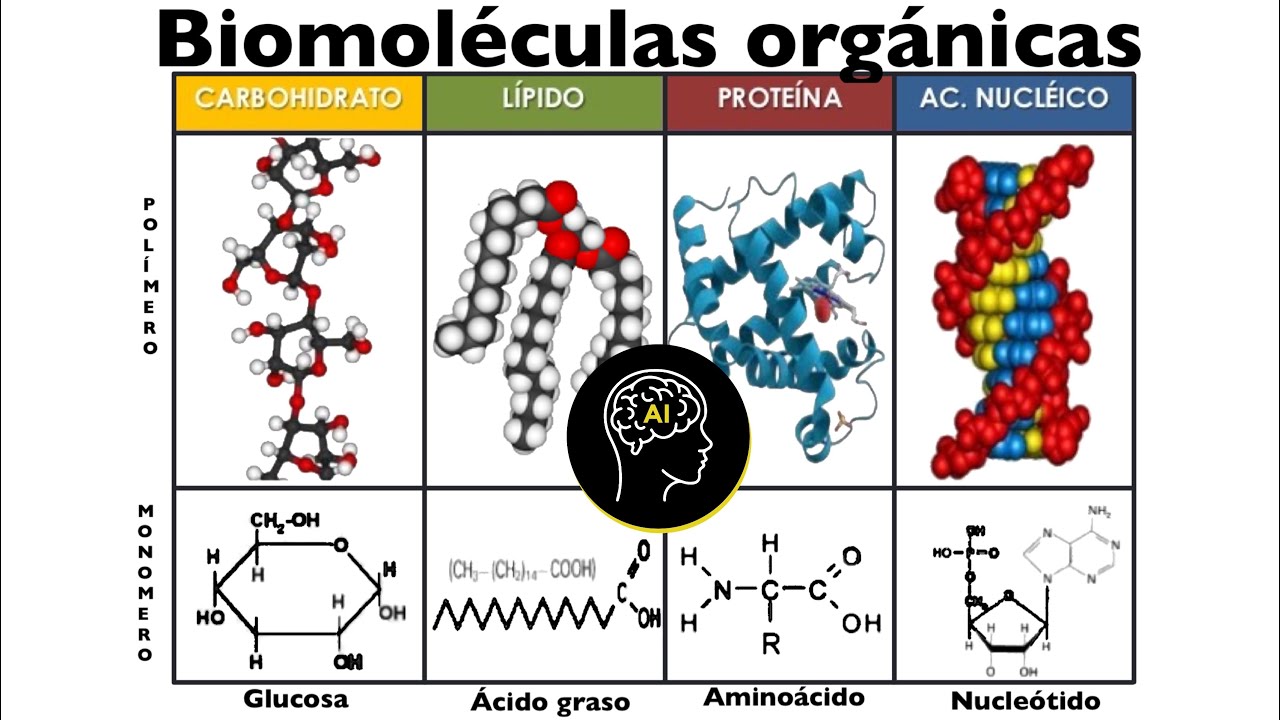
Biomoléculas presentes en células (orgánicas): carbohidratos, lípidos, proteínas y ácidos nucleicos
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)