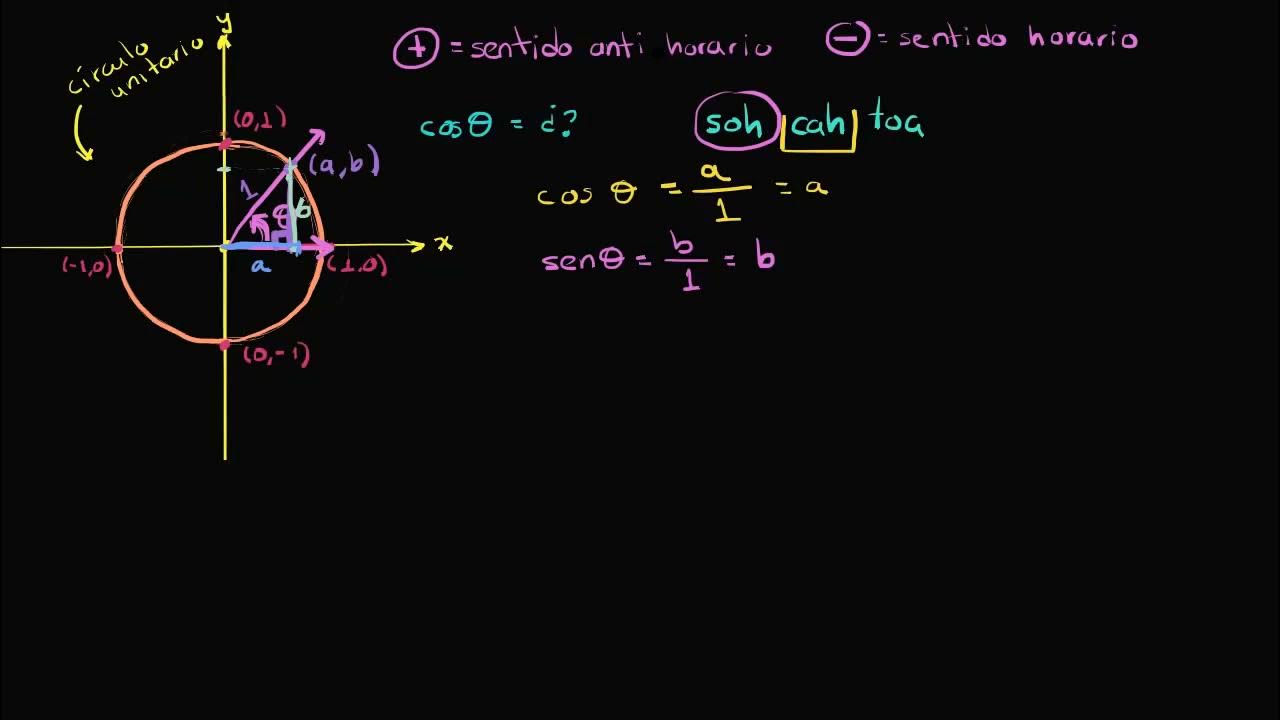The Unit Circle, Basic Introduction, Trigonometry
Summary
TLDRThis video provides a comprehensive explanation of the unit circle and how to evaluate sine and cosine functions using it. It covers the basic concepts of the unit circle, focusing on key angles like 30°, 45°, and 60°, and explains the relationship between the circle's coordinates and trigonometric functions. Through detailed examples, it shows how to use reference angles and symmetry to calculate sine and cosine values for all quadrants. The video also highlights the importance of understanding the unit circle in radians and provides step-by-step guidance on evaluating various trigonometric functions.
Takeaways
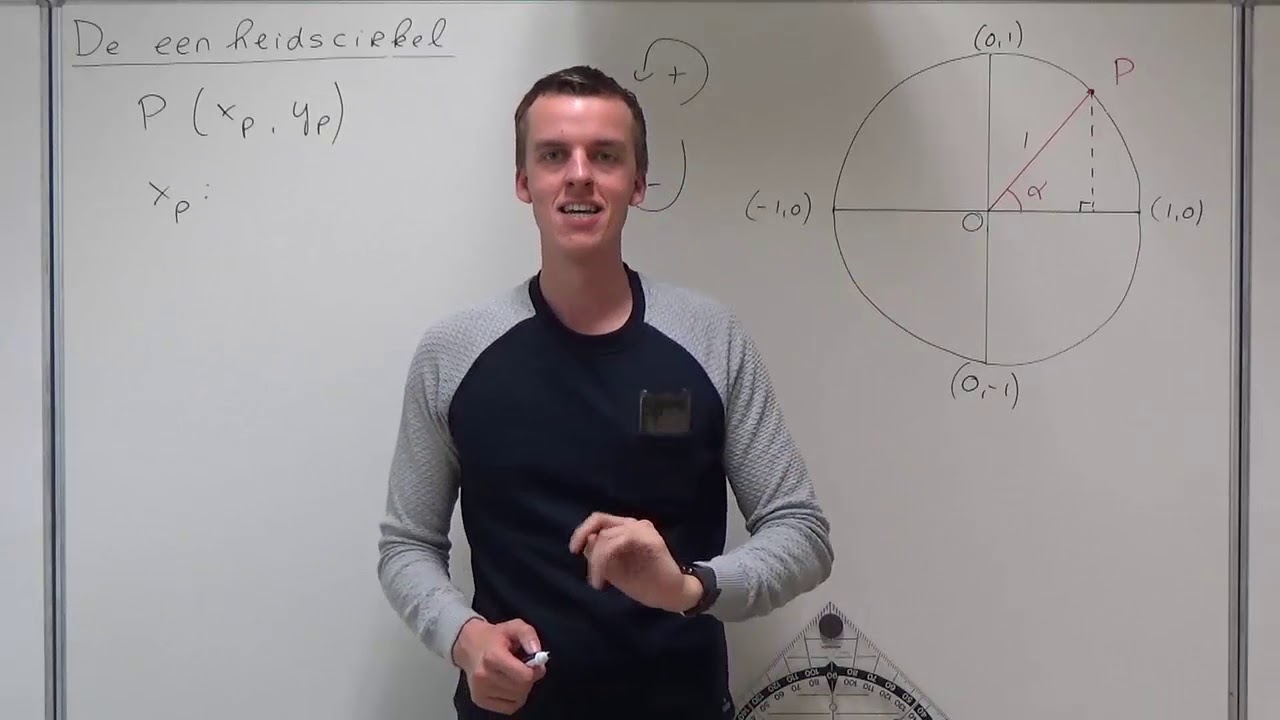
- 😀 The unit circle is a circle with a radius of one, where each point on the circle corresponds to a specific angle and its sine and cosine values.
- 😀 Sine and cosine are derived from the y and x coordinates, respectively, of points on the unit circle, where the radius (r) is always one.
- 😀 To evaluate sine and cosine for common angles like 30°, 45°, and 60°, you can refer to known coordinate pairs in the first quadrant of the unit circle.
- 😀 At a 45° angle, both sine and cosine have the same value of √2/2, reflecting symmetry in the unit circle.
- 😀 The key values for sine and cosine at special angles (like 30°, 45°, and 60°) repeat symmetrically in other quadrants.
- 😀 In quadrant one, both x and y are positive; in quadrant two, x is negative and y is positive; in quadrant three, both x and y are negative; and in quadrant four, x is positive and y is negative.
- 😀 The sine of an angle is the y-coordinate, and cosine is the x-coordinate of the corresponding point on the unit circle.
- 😀 The symmetry of the unit circle allows you to determine values in quadrants two, three, and four based on their reference angles in quadrant one.
- 😀 You don’t need to memorize the entire unit circle—knowing the values in quadrant one, along with the values along the axes, helps you determine all other values.
- 😀 To evaluate trigonometric functions for angles in radians (like π/3 or 5π/3), convert the angle to its corresponding degree measure and apply the same symmetry principles to find the sine and cosine values.
Q & A
What is the unit circle and why is it important?
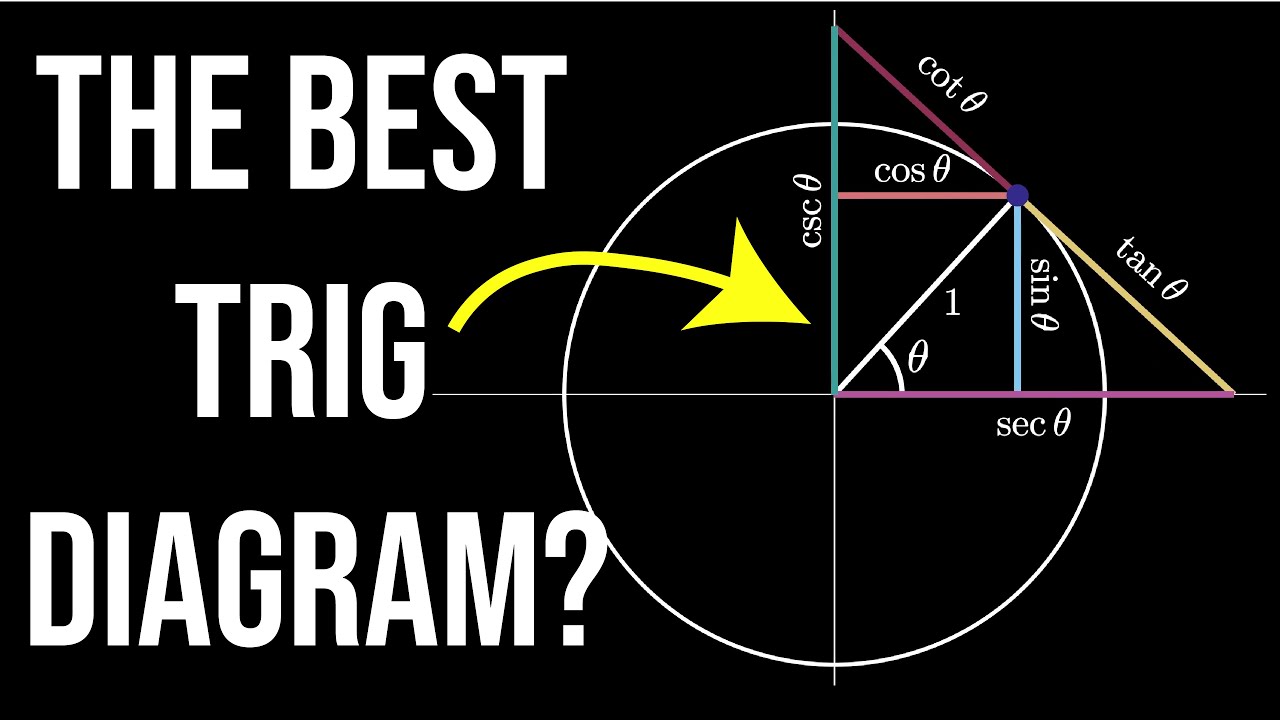
-The unit circle is a circle with a radius of one. It's important in trigonometry because it provides a way to easily evaluate sine and cosine functions for different angles, especially when the radius is 1, making calculations simpler.
How are sine and cosine values determined using the unit circle?
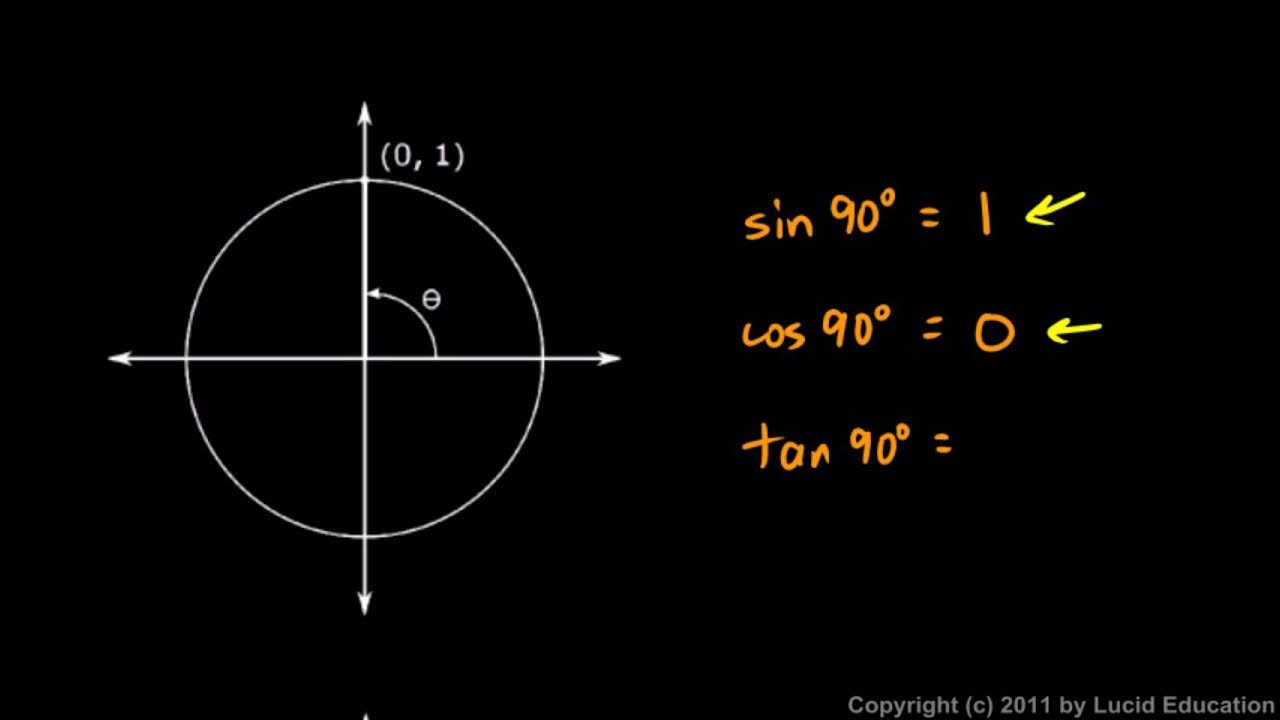
-In the unit circle, the sine of an angle is equal to the y-coordinate of the corresponding point on the circle, and the cosine is equal to the x-coordinate. The radius is always 1.
What are the sine and cosine values for a 45-degree angle on the unit circle?
-For a 45-degree angle, the sine and cosine values are both equal to √2 / 2. The coordinates for this angle on the unit circle are (√2/2, √2/2).
How do you find sine and cosine for angles greater than 90 degrees?
-You can use the symmetry of the unit circle. For example, for angles in quadrants 2, 3, and 4, you can find the reference angle (the angle between the terminal side and the x-axis) and adjust the signs of sine and cosine accordingly based on the quadrant.
What are the common angles on the unit circle that you need to memorize?
-The most common angles to memorize are 30°, 45°, and 60°, as well as the values for 0°, 90°, 180°, and 270°. These help you evaluate sine and cosine for many other angles.
What is the value of sine at 60 degrees?
-At 60 degrees, the sine value is √3 / 2. This is the y-coordinate of the point corresponding to 60° on the unit circle.
How does the reference angle help in evaluating trigonometric functions?
-The reference angle is the acute angle formed between the terminal side of the angle and the x-axis. It helps you determine the sine and cosine values in other quadrants by adjusting the sign based on the quadrant where the angle lies.
What is the sine and cosine of 180°?
-At 180°, the cosine value is -1 (x-coordinate) and the sine value is 0 (y-coordinate). The point on the unit circle for 180° is (-1, 0).
What are the sine and cosine values for 315°?
-At 315°, the sine value is -√2 / 2 (since y is negative in quadrant 4), and the cosine value is √2 / 2 (since x is positive in quadrant 4).
How do you evaluate trigonometric functions for angles like π/3 or 2π/3?
-For angles in radians like π/3, you can convert the angle to degrees (π/3 = 60°). Once you have the degree measure, use the unit circle to find the sine and cosine values. For π/3 (60°), sine is √3 / 2 and cosine is 1/2. For 2π/3 (120°), sine is √3 / 2 and cosine is -1/2.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenant5.0 / 5 (0 votes)