Desain Primer untuk PCR (Designing Primer for PCR)
Summary
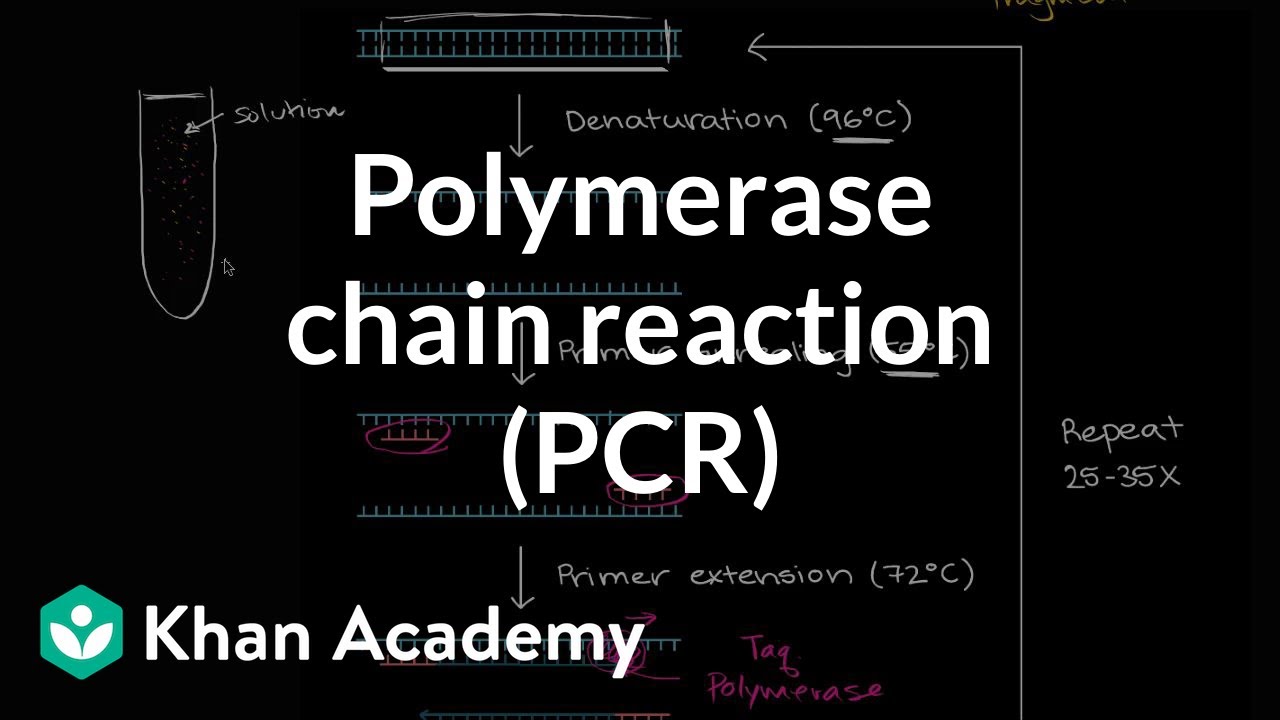
TLDRThis video explains the process of designing primers for PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction), a vital technique in molecular biology. It covers the essential components of PCR, including DNA template, polymerase, primers, and dNTPs. Key factors in primer design—such as DNA target sequence, melting temperature (Tm), and GC content—are discussed in detail. The video walks viewers through the manual method of primer design, including step-by-step calculations, and introduces tools like NCBI for online primer design. The importance of primer optimization and testing for PCR success is also highlighted.
Takeaways
- 😀 The design of primers is a critical step in the PCR process, involving components like DNA template, polymerase, primers, and dNTPs.
- 😀 Three key factors in primer design: DNA sequence, melting temperature (TM), and GC content.
- 😀 The DNA sequence needs to be examined for the start codon (beginning of translation) and the stop codon (end of translation).
- 😀 Melting temperature (TM) indicates the temperature at which the forward and reverse primers will separate. The optimal range is 55°C to 65°C.
- 😀 GC content in primers should be between 40% and 60% for stable and strong binding.
- 😀 Primer lengths for DNA barcoding typically range from 18-25 nucleotides, with a few exceptions allowing up to 30 nucleotides.
- 😀 Manual primer design involves calculating TM, GC content, and carefully selecting the forward and reverse primers based on the target sequence.
- 😀 Online tools like NCBI can be used to design primers efficiently by inputting DNA sequences and evaluating potential primer sequences.
- 😀 Primer TM should be as close as possible for both forward and reverse primers to ensure effective PCR reactions.
- 😀 Optimizing primers involves adjusting the annealing temperature based on the calculated TM to ensure accurate binding during PCR.
- 😀 GC content and complementarity between primers should be checked to avoid self-binding and other issues that could affect PCR efficiency.
Q & A
What are the main components required for a PCR reaction?
-The main components required for a PCR reaction are DNA template, Taq polymerase, primers (both forward and reverse), and dNTPs (deoxynucleotide triphosphates).
Why is the primer important in PCR?
-The primer is important in PCR because it binds to the target DNA sequence, allowing the DNA polymerase to extend the sequence and replicate the target region.
What are the three key factors to consider when designing primers?
-The three key factors to consider when designing primers are: 1) the DNA target sequence, 2) the melting temperature (Tm), and 3) the GC content (percentage of guanine and cytosine bases).
What is the role of the start and stop codons in primer design?
-The start and stop codons define the boundaries of the gene or region of interest in the DNA sequence. The primer must bind near these codons to accurately amplify the target region.
How is melting temperature (Tm) calculated for primers?
-The melting temperature (Tm) is calculated using the formula: Tm = 2 × (number of A or T) + 4 × (number of G or C). This gives the temperature at which the primer will separate from the DNA strand.
What is the optimal range for the melting temperature (Tm) of primers in PCR?
-The optimal melting temperature (Tm) for primers in PCR is typically between 55°C and 65°C.
Why is it important for the GC content of primers to be between 40% and 60%?
-GC content between 40% and 60% ensures that the primer forms strong bonds with the DNA template. G and C bases form three hydrogen bonds, which provide stronger binding compared to the two bonds formed by A and T bases.
What is the typical length of a primer used in DNA barcoding PCR?
-Primers used in DNA barcoding PCR are typically between 18 and 25 bases long, although they can range from 15 to 30 bases.
How can primers be designed using NCBI's online tools?
-Primers can be designed using NCBI's online tools by inputting the DNA sequence of interest, selecting the target region, and letting the tool suggest primer pairs based on the sequence provided.
What is the significance of the complementary nature of the forward and reverse primers?
-The forward and reverse primers are complementary to the DNA strands at opposite ends of the target region. They bind to the template DNA and enable the amplification of the target sequence during PCR. The primers' complementary nature ensures accurate binding and efficient amplification.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)