Metode PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction)
Summary
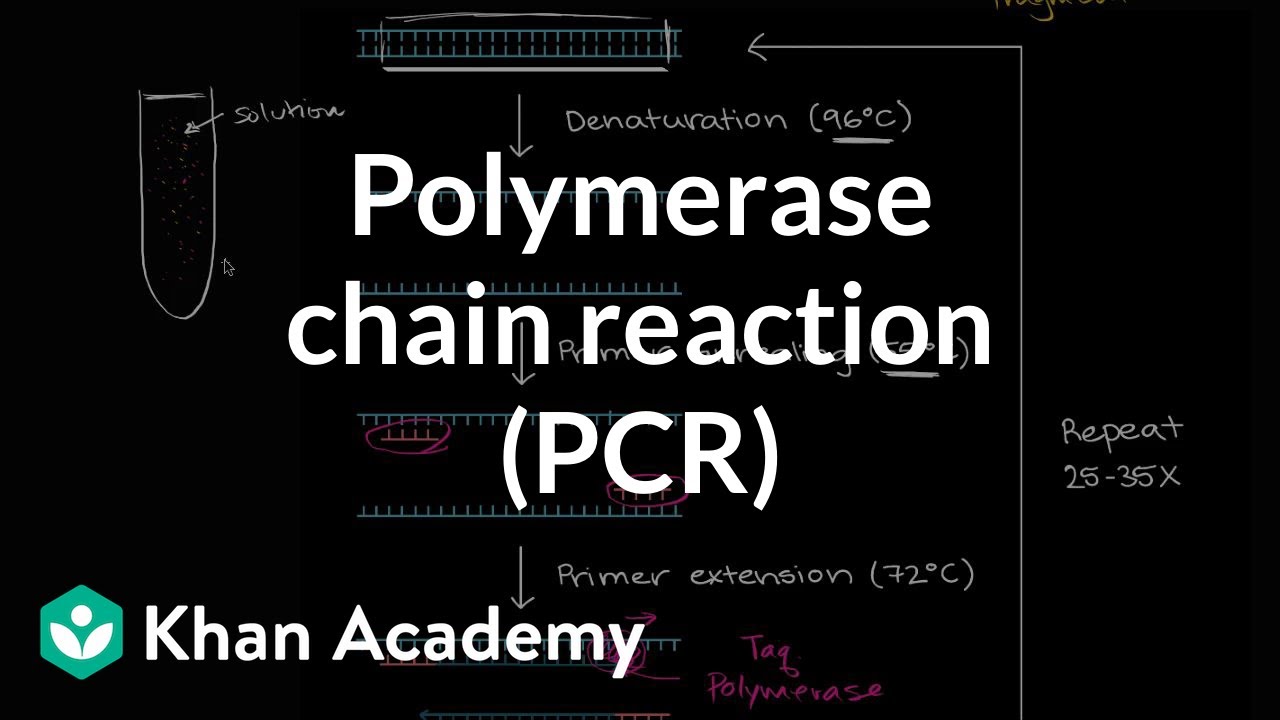
TLDRThis lecture introduces the Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR), a vital in vitro technique for DNA amplification, akin to natural DNA replication. Key components include template DNA, primers, Taq polymerase, and nucleotides, all crucial for the PCR process. The procedure consists of three main phases: denaturation, annealing, and extension, with each cycle doubling the DNA copies. The results can be visualized through gel electrophoresis. The lecture emphasizes PCR's significance in various fields such as molecular biology, genetics, and forensic science, making it an essential tool for researchers and practitioners.
Takeaways
- 😀 The script introduces the Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) as an in vitro technique for DNA replication, similar to natural DNA replication in the body.
- 🧬 PCR requires several components including template DNA, primers, nucleotides, and enzymes such as Taq polymerase.
- 🔥 The three main stages of PCR are denaturation, annealing, and extension, which involve specific temperature settings.
- 🔬 Denaturation occurs at approximately 94-95°C, breaking hydrogen bonds in the DNA to separate the strands.
- 📏 During annealing, the temperature is lowered (40-55°C) to allow primers to attach to the single-stranded DNA templates.
- 🔄 Extension involves the synthesis of new DNA strands by Taq polymerase at a temperature of around 72°C.
- 🔁 PCR typically involves 25-35 cycles, exponentially increasing the amount of DNA with each cycle, calculated as 2^n, where n is the cycle number.
- 💡 The Taq polymerase enzyme is heat-stable, allowing it to function effectively during the high temperatures of PCR.
- ⚗️ The PCR process is often visualized and analyzed through agarose gel electrophoresis to separate and identify the amplified DNA.
- 🌟 The script concludes with an emphasis on understanding PCR, its applications, and how it facilitates DNA analysis in molecular biology.
Q & A
What is PCR and what does it stand for?
-PCR stands for Polymerase Chain Reaction. It is an in vitro technique used for amplifying DNA, mimicking the natural process of DNA replication.
What are the main stages of the PCR process?
-The main stages of PCR include denaturation, annealing, and extension. Each stage involves specific temperature settings and reactions that lead to DNA amplification.
What occurs during the denaturation stage?
-During denaturation, the DNA double helix is heated to about 94-95 degrees Celsius, causing the hydrogen bonds between the strands to break and resulting in single-stranded DNA.
What is the purpose of primers in PCR?
-Primers are short sequences of nucleotides that bind to the template DNA during the annealing stage. They provide a starting point for the DNA polymerase to synthesize new DNA strands.
How does the temperature affect the PCR process?
-Temperature plays a crucial role in PCR: high temperatures (around 94-95°C) are used for denaturation, lower temperatures (40-55°C) are used for annealing, and around 72°C is used for extension.
What is the role of DNA polymerase in PCR?
-DNA polymerase synthesizes new DNA strands by adding nucleotides to the growing chain during the extension phase. Taq polymerase is commonly used because it can withstand high temperatures.
How many cycles are typically conducted in a PCR process?
-Typically, 25 to 35 cycles are conducted in a PCR process, allowing for exponential amplification of the target DNA.
What is the significance of MgCl2 in PCR?
-MgCl2 is a cofactor that is essential for the activity of DNA polymerase. It helps stabilize the DNA and is crucial for the overall efficiency of the PCR reaction.
What is gel electrophoresis and how is it used in PCR?
-Gel electrophoresis is a technique used to separate and visualize DNA fragments after PCR. It involves applying an electric current to a gel matrix, allowing the DNA to migrate based on size.
What are some advanced types of PCR mentioned in the transcript?
-Advanced types of PCR mentioned include real-time PCR and digital PCR, which offer more precise quantification and analysis of DNA.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)