Voltage Current and Resistance
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the fundamental concepts of voltage, current, and resistance in electrical circuits. It covers definitions, units, and relationships between the three, such as Ohm's Law. Key examples are provided to illustrate how voltage, current, and resistance interact, using analogies like water flow in pipes. The video also explores practical applications and calculations, demonstrating how to use Ohm's Law to solve for voltage, current, or resistance. Clear visuals and simple explanations help viewers understand the principles governing electricity, making complex ideas accessible to all.
Takeaways
- ⚡ Voltage is the electric potential energy difference per unit charge, measured in volts (V), with 1 V = 1 joule per coulomb.
- 🔋 Higher voltage means electrons carry more energy; e.g., a 10 V battery delivers more energy per charge than a 5 V battery.
- 💡 Current represents the flow of electric charge, measured in amperes (A), where 1 A = 1 coulomb per second.
- 💧 Current can be visualized as water flow: more electrons flowing = higher current, fewer electrons = lower current.
- 🛑 Resistance is the opposition to current flow, measured in ohms (Ω), and devices like resistors provide resistance in circuits.
- 📏 Longer wires have more resistance; thinner wires also have more resistance than thicker ones.
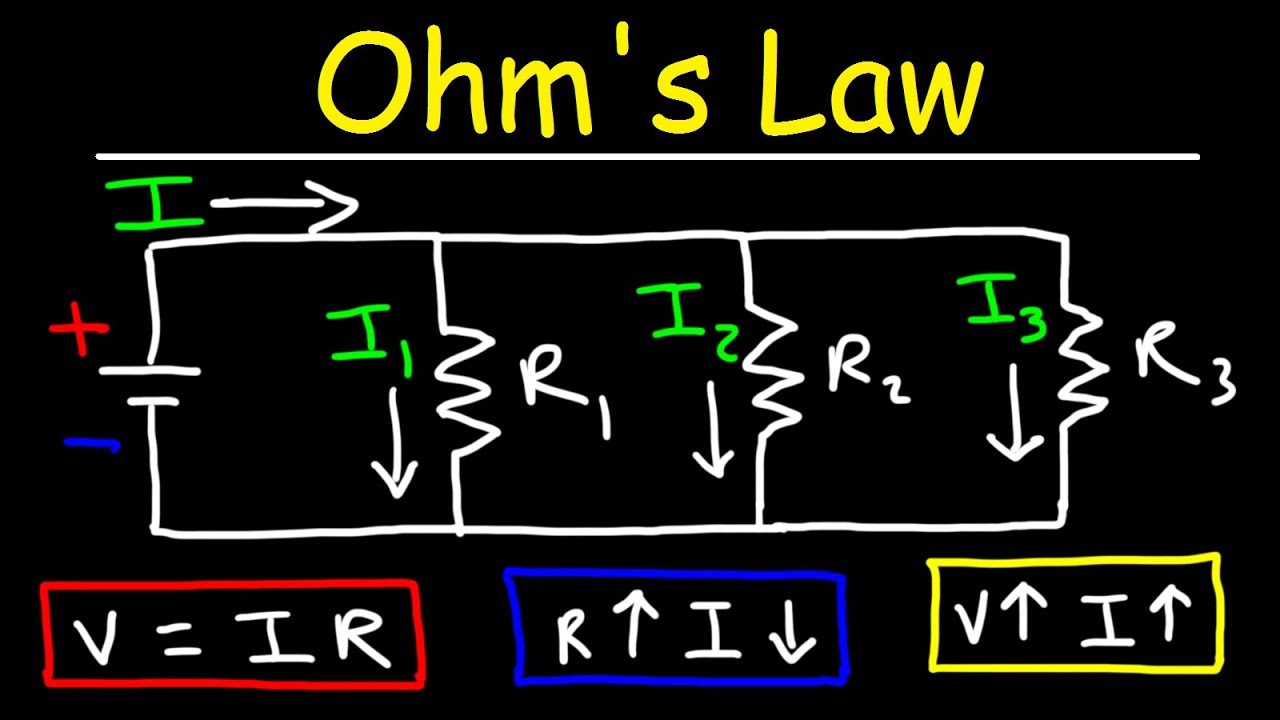
- 🔀 Resistance and current are inversely related: increasing resistance decreases current, and decreasing resistance increases current.
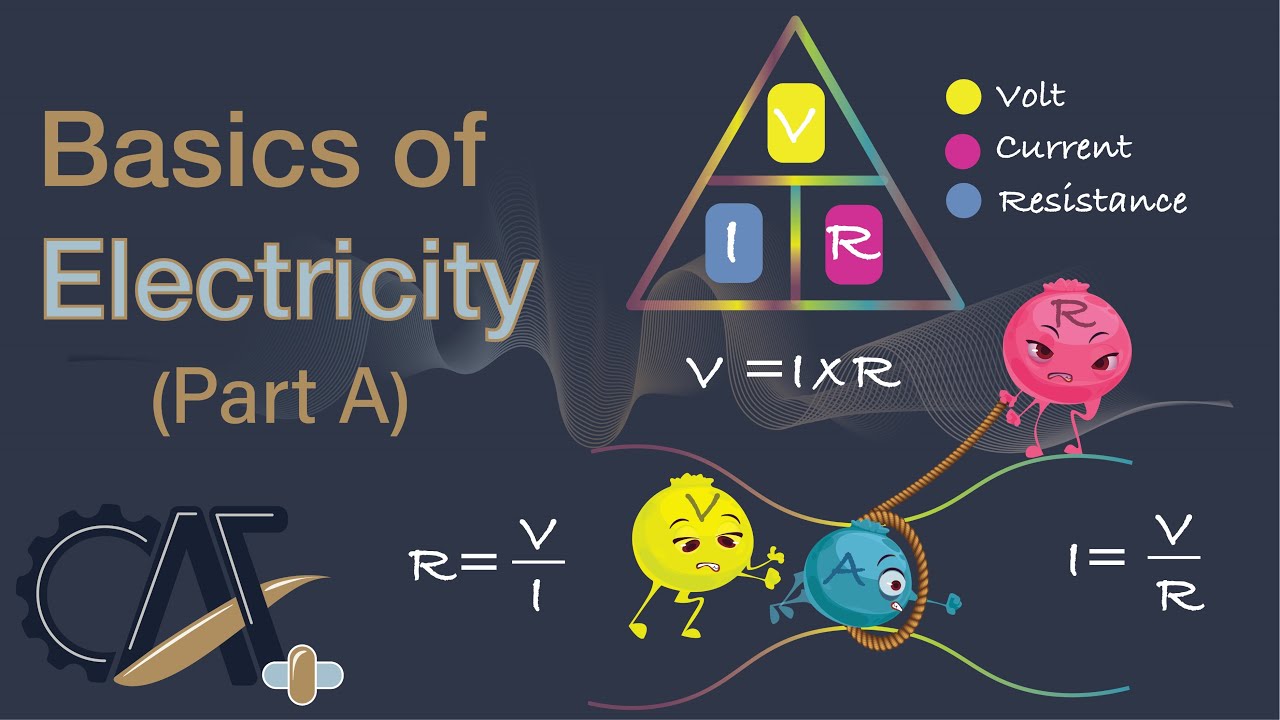
- 📐 Ohm’s Law relates voltage, current, and resistance: V = I × R, with derived forms I = V / R and R = V / I.
- 🔌 Current flows from high potential to low potential (conventional current), while electrons flow from low potential to high potential.
- 📊 Voltage across a component is the difference between electric potentials of its two ends; polarity affects the sign of the measured voltage.
- 🧮 Always use consistent units in calculations: volts for voltage, amps for current, and ohms for resistance.
- 🔧 Example calculations demonstrate how to find current, voltage, or resistance using Ohm’s Law with real-world components like batteries, light bulbs, and hairdryers.
- 🛣️ Analogies like water flow in pipes and cars on highways help visualize how voltage, current, and resistance interact.
Q & A
What is voltage, and how is it related to electric potential energy?
-Voltage is the electric potential energy difference per unit charge. It is measured in volts, where 1 volt equals 1 joule of electric potential energy per 1 coulomb of charge. Higher voltage means more energy per electron, as seen in batteries with different voltages.
How does voltage impact the energy of electrons in a circuit?
-The voltage determines how much energy each electron carries. For example, a 5-volt battery means each coulomb of charge carries 5 joules of energy. Higher voltage batteries, like a 10-volt battery, deliver more energy per coulomb.
What is electric current, and how is it measured?
-Electric current is the flow of electrons through a conductor and is measured in amperes (amps). One ampere equals one coulomb of charge flowing per second. The symbol for current is 'I'.
How can the flow of current be compared to water flow?
-The flow of current is similar to water flowing through pipes. If a large amount of water flows quickly, the current is high. If a small amount of water flows slowly, the current is low.
What is resistance, and how does it affect the flow of current?
-Resistance is a measure of how much a material resists the flow of electric current. It is measured in ohms (Ω). As resistance increases, current decreases. Think of resistance like a narrow road where fewer cars (electrons) can pass through.
What factors influence the resistance of a wire?
-The resistance of a wire is influenced by its length and thickness. Longer wires have more resistance, and thinner wires have more resistance than thicker wires because electrons have a greater distance to travel and face more obstacles in thin wires.
How are resistance and current related?
-Resistance and current are inversely related. If you increase the resistance, the current decreases. If you decrease the resistance, the current increases, assuming the voltage remains constant.
What is Ohm's Law, and how can it be applied in circuits?
-Ohm's Law states that voltage (V) is equal to the current (I) multiplied by the resistance (R), or V = IR. It can be used to calculate any one of these three variables if the other two are known.
How does increasing the voltage in a circuit affect the current?
-Increasing the voltage in a circuit, with resistance held constant, causes the current to increase. This is because a higher voltage forces electrons to move with greater energy, increasing the flow of current.
How does the direction of conventional current differ from electron flow?
-Conventional current flows from a region of high electric potential to low electric potential, while electrons, being negatively charged, actually flow in the opposite direction—from low potential to high potential.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenant5.0 / 5 (0 votes)