FISIKA Kelas 12 - Rangkaian Arus Searah | GIA Academy
Summary
TLDRThis video from Akademi YouTube channel explains the basics of direct current (DC) circuits, covering essential topics like battery recharging, the definition of direct current, Ohm's Law, Kirchhoff's Laws, and series and parallel circuits. It also includes practical examples and calculations to enhance understanding, such as determining electric current, resistance, and voltage using various formulas and tools like ammeters and voltmeters. The video aims to make viewers comfortable with fundamental electrical concepts and problem-solving techniques in DC circuits.
Takeaways
- 📱 Smartphones are commonly used communication tools, and their batteries need recharging over time.
- 🔋 Smartphone batteries are examples of secondary cells, which can be recharged multiple times.
- ⚡ When recharging a smartphone, electrical energy is converted into chemical energy.
- 🔄 Direct current (DC) is the flow of positive charges from high to low potential in one direction.
- 🔌 The current in a circuit is defined by the equation I = Q/t, where I is the current, Q is the charge, and t is the time.
- 📏 Ammeters measure current and are connected in series, while voltmeters measure voltage and are connected in parallel.
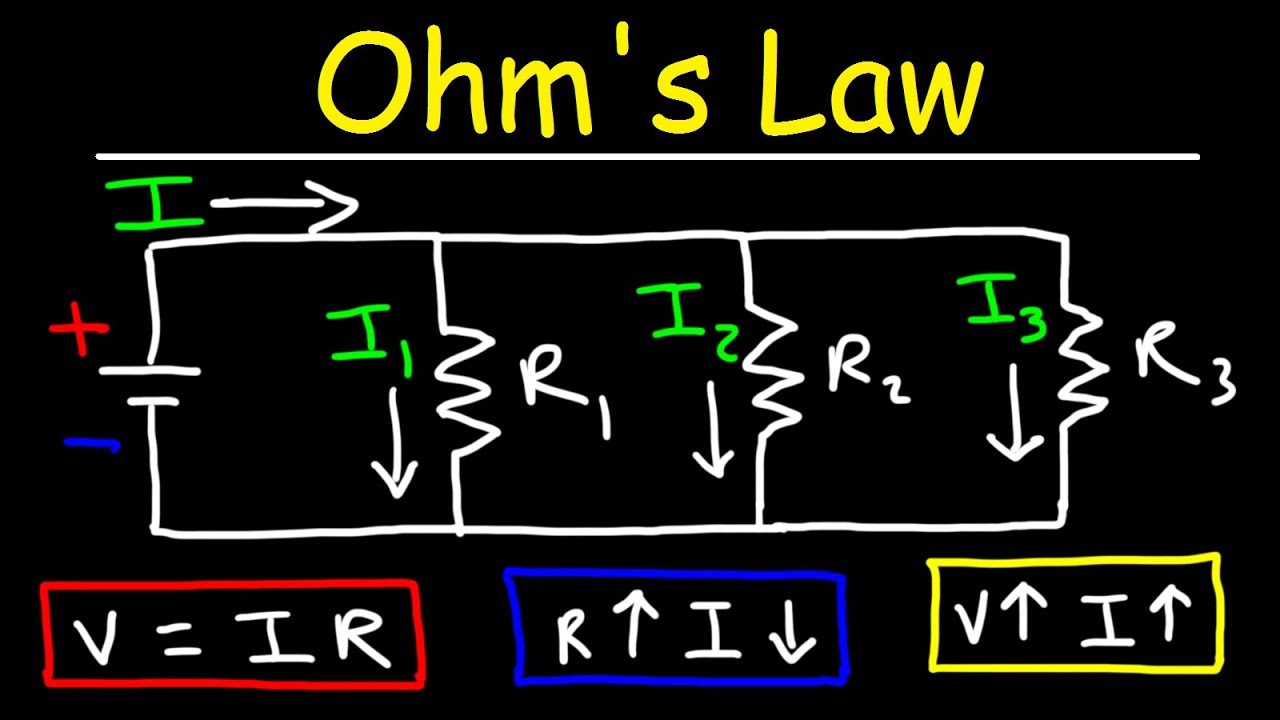
- 📉 Ohm's Law states that the current through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage across the two points and inversely proportional to the resistance (I = V/R).
- 🧮 Resistance in a wire is affected by its length, material, and cross-sectional area, and can be calculated using R = ρL/A.
- 🌡️ Resistance also varies with temperature, and the temperature coefficient of resistance is used to calculate this change.
- 🔄 Kirchhoff's laws describe the conservation of current and energy in electrical circuits: the sum of currents entering a junction equals the sum of currents leaving, and the sum of voltage drops equals the sum of voltage sources in a closed loop.
Q & A
What is a secondary element in the context of smartphone batteries?
-A secondary element refers to a battery that can be recharged, such as those used in smartphones.
What happens to the energy stored in a smartphone battery when it is used continuously?
-The energy stored in the battery decreases and eventually gets depleted.
What type of current flows in one direction only, and what is its abbreviation?
-Direct current, abbreviated as DC, flows in one direction only.
What is Ohm's Law and its formula?
-Ohm's Law states that the current through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage across the two points and inversely proportional to the resistance. The formula is I = V / R.
What factors affect the resistance of a wire conductor?
-The resistance of a wire conductor is affected by its length, the material (resistivity), and the cross-sectional area.
What is Kirchhoff's First Law?
-Kirchhoff's First Law states that the total current entering a junction equals the total current leaving the junction, expressed as ΣI_in = ΣI_out.
What does Kirchhoff's Second Law state?
-Kirchhoff's Second Law states that in any closed circuit, the sum of the electromotive forces is equal to the sum of the potential drops, expressed as ΣE - ΣIR = 0.
How is the equivalent resistance calculated in a series circuit?
-The equivalent resistance in a series circuit is the sum of all individual resistances, R_total = R1 + R2 + ... + Rn.
How is the equivalent resistance calculated in a parallel circuit?
-The equivalent resistance in a parallel circuit is calculated using the formula 1/R_total = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + ... + 1/Rn.
What is the difference between electromotive force (emf) and terminal voltage?
-Electromotive force (emf) is the potential difference when no current is flowing, while terminal voltage is the potential difference when the circuit is closed and current is flowing.
How can you determine the total current in a series circuit with identical resistors?
-The total current can be determined by dividing the total voltage by the sum of the resistances. For identical resistors, I = V_total / (n * R), where n is the number of resistors.
What is the formula for resistance affected by temperature change?
-The formula is R_T = R_0 (1 + αΔT), where R_T is the resistance at temperature T, R_0 is the initial resistance, α is the temperature coefficient of resistance, and ΔT is the change in temperature.
In a closed circuit, how is the current direction determined in relation to the voltage source?
-In a closed circuit, current flows from the positive terminal to the negative terminal of the voltage source.
What happens to the brightness of lamps in a parallel circuit if one lamp is removed?
-If one lamp in a parallel circuit is removed, the voltage across the remaining lamps increases, causing them to become brighter.
What is the relationship between voltage (V), current (I), and resistance (R) as shown in a V-I graph?
-The relationship is linear, indicating that as the voltage increases, the current also increases proportionally if the resistance remains constant.
How can the total emf of batteries connected in series be calculated?
-The total emf of batteries connected in series is the sum of the individual emfs, E_total = E1 + E2 + ... + En.
How do you calculate the current in a closed single-loop circuit using Kirchhoff's Second Law?
-The current is calculated using I = (E1 + E2) / (R1 + R2), where E1 and E2 are the emfs, and R1 and R2 are the resistances in the loop.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
Ohm's Law

ФИЗИКА ЗА 5 МИНУТ - ЭЛЕКТРОДИНАМИКА

Arus, Tegangan, dan Hambatan | Rangkaian DC | Part 1 | Fisika Dasar

Electrical Engineering: Basic Concepts (4 of 7) Electric Current: DC vs AC

RANGKAIAN ARUS SEARAH : Kuat Arus Listrik, Hukum Ohm - Materi Fisika SMA Kelas 12, TKA SMA | Part 1

Series & Parallel Circuits EXPLAINED with Kirchhoff's Circuit Laws // HSC Physics
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)