Hydrocarbon Derivatives
Summary
TLDRIn this episode of Organic Chemistry Made Easy, the focus is on hydrocarbon derivatives and seven key functional groups: alcohols, aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, esters, amines, and ethers. Each group is explained with its structure, naming rules, and examples. Alcohols are classified based on their carbon bonding, aldehydes and ketones contain carbonyl groups, carboxylic acids feature a carboxyl group, and esters are derived from acids. Amines and ethers are also explored, with practical applications like acetone as a nail polish remover and ethanol in alcoholic drinks. The episode provides clear insights into these functional groups for easy understanding.
Takeaways
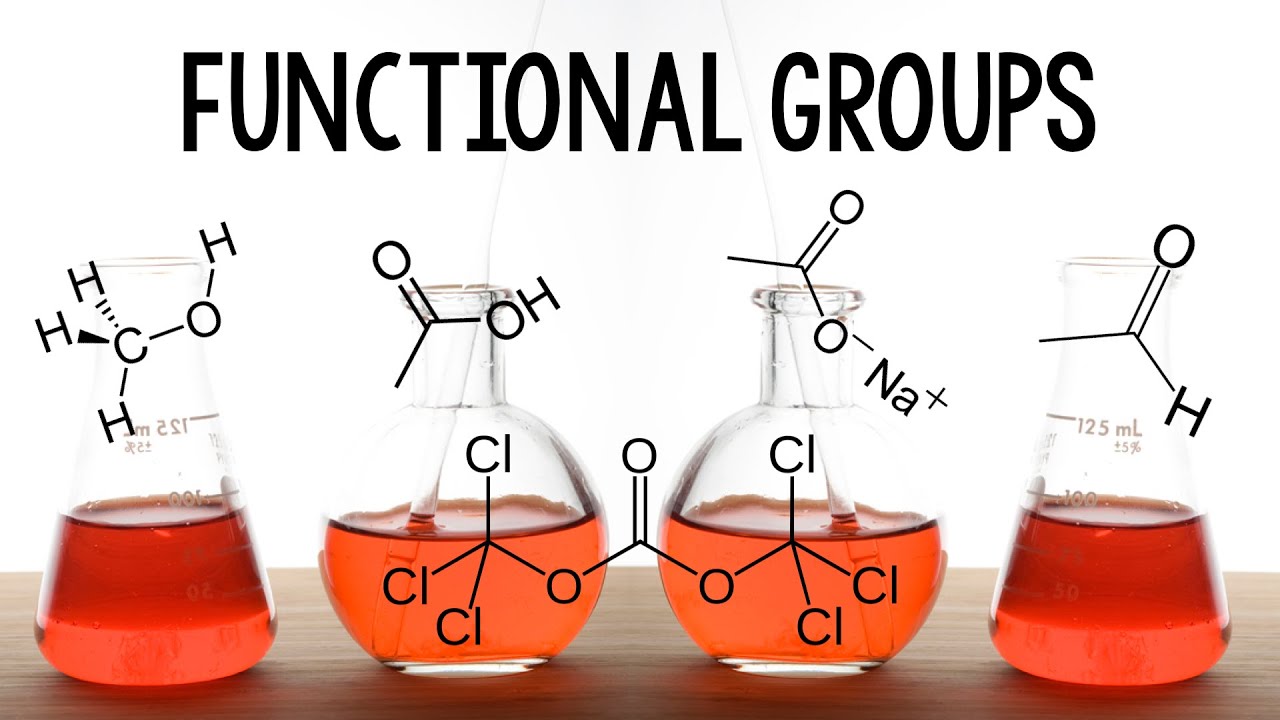
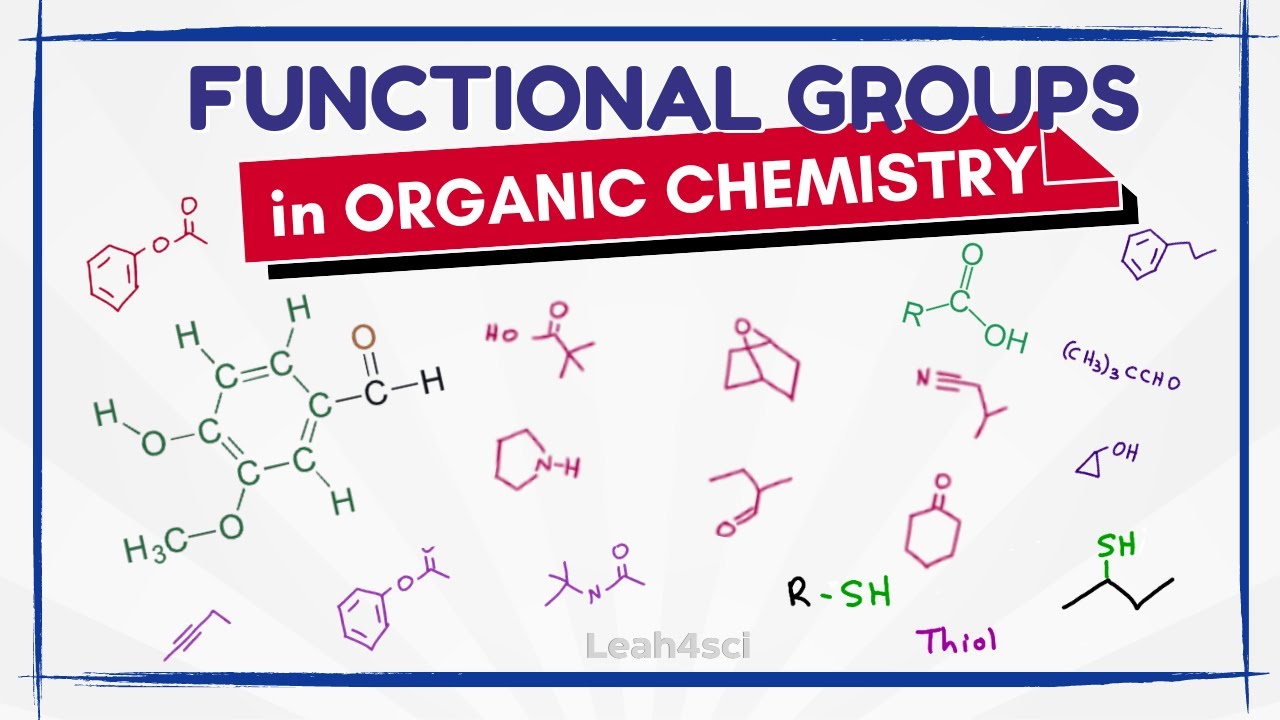
- 😀 Hydrocarbons are compounds made up of carbon and hydrogen atoms, while hydrocarbon derivatives contain other elements like oxygen, nitrogen, or halogens.
- 😀 Functional groups are specific groups of atoms attached to the carbon backbone of hydrocarbon derivatives, influencing their chemical properties.
- 😀 Alcohols contain a hydroxyl group (-OH) and are classified as primary, secondary, or tertiary based on the number of carbons attached to the carbon bearing the -OH group.
- 😀 To name alcohols, the base name of the hydrocarbon is taken and its ending is changed to '-ol' (e.g., ethanol, isopropanol).
- 😀 Aldehydes contain a carbonyl group (C=O) at the end of the carbon chain, while ketones have the carbonyl group in the middle of the chain.
- 😀 Aldehydes are formed from primary alcohols, and ketones are formed from secondary alcohols.
- 😀 Carboxylic acids contain a carboxyl group (C=O and -OH) and are named by adding 'acid' to the base name (e.g., acetic acid, formic acid).
- 😀 Esters are formed when a carboxylic acid reacts with an alcohol, releasing water, and they have a fruity scent.
- 😀 Amines contain an amine group (-NH2) and are named by adding 'amine' to the base name (e.g., methylamine, ethylamine).
- 😀 Ethers contain an oxygen atom connected to two alkyl groups and are named by listing the alkyl groups alphabetically followed by 'ether' (e.g., ethyl methyl ether).
Q & A
What are hydrocarbon derivatives?
-Hydrocarbon derivatives are compounds made up of carbon and hydrogen atoms, but they also contain at least one element other than carbon or hydrogen, such as oxygen, nitrogen, or halogens. These elements are typically attached as part of a functional group.
What are functional groups?
-Functional groups are specific groups of atoms that are attached to hydrocarbons, and they define the chemical properties and reactivity of a compound. Examples include hydroxyl groups, carbonyl groups, and amino groups.
How do you name alcohols?
-To name alcohols, you take the base name of the hydrocarbon chain and change its ending to 'ol.' For example, ethane becomes ethanol when a hydroxyl (OH) group is attached to one of the carbons.
What are the different types of alcohols, and how are they classified?
-Alcohols are classified as primary, secondary, or tertiary based on the number of carbon atoms attached to the carbon bearing the hydroxyl group. A primary alcohol has one carbon attached to the hydroxyl-bearing carbon, a secondary alcohol has two, and a tertiary alcohol has three.
What is the difference between aldehydes and ketones?
-Both aldehydes and ketones contain a carbonyl group (C=O), but in aldehydes, the carbonyl group is at the end of the carbon chain, while in ketones, it is found in the middle or center of the chain.
How do you name aldehydes and ketones?
-To name aldehydes, the base chain name is modified by changing the ending to 'al.' For ketones, the base chain name changes to 'one.' For example, propanal for an aldehyde and propanone (or acetone) for a ketone.
What is the process of turning alcohols into aldehydes or ketones?
-Primary alcohols are oxidized to form aldehydes, while secondary alcohols are oxidized to form ketones. This occurs through the removal of hydrogen atoms from the alcohol.
What are carboxylic acids and how are they named?
-Carboxylic acids contain a carboxyl group (-COOH), which consists of a carbonyl group bonded to a hydroxyl group. They are named by replacing the 'e' in the base hydrocarbon name with 'oic acid,' such as methanoic acid (formic acid) or ethanoic acid (acetic acid).
How are esters formed and named?
-Esters are formed when a carboxylic acid reacts with an alcohol, releasing water. To name an ester, the alkyl group from the alcohol is named first, followed by the acid part, which is modified to end in 'ate.' For example, methyl ethanoate.
What are the characteristics of ethers, and how are they named?
-Ethers contain an oxygen atom bonded to two alkyl groups. They are named by listing the alkyl groups alphabetically, followed by the word 'ether.' For example, methyl ethyl ether.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenant5.0 / 5 (0 votes)