Funções orgânicas oxigenadas - Brasil Escola
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, Professor Choven introduces organic oxygenated functions in chemistry, covering various types including alcohols, phenols, ethers, aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, salts of carboxylic acids, acid anhydrides, and esters. The professor explains key concepts such as functional groups, nomenclature, and how to identify each type of compound based on its structure. The lesson is aimed at simplifying the identification of these functions through easy-to-remember guidelines and nomenclature rules, making it an essential resource for students studying organic chemistry.
Takeaways
- 😀 Organic functions consist of substances with similar chemical properties, defined by their functional groups.
- 😀 The functional group is the atom or group of atoms that defines an organic function.
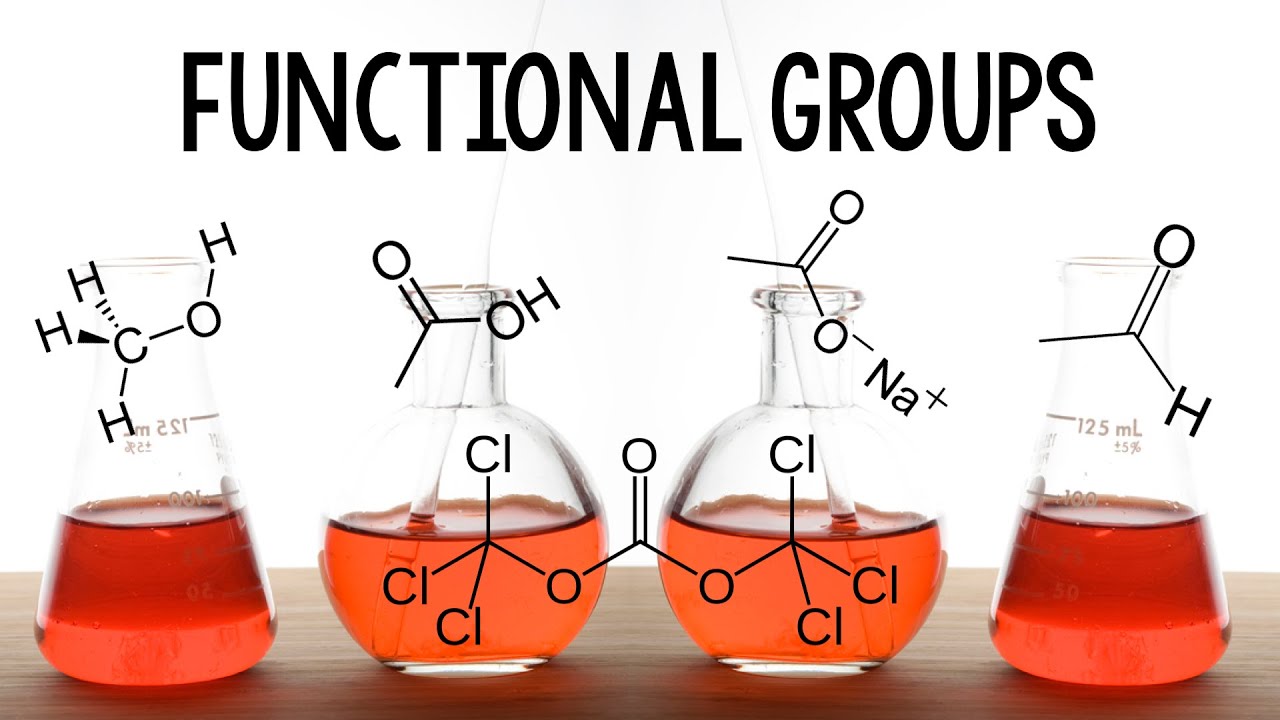
- 😀 Organic oxygenated functions include alcohols, phenols, enols, ethers, aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, carboxylic acid salts, carboxylic acid anhydrides, and esters.
- 😀 Alcohols have a hydroxyl group (-OH) attached to a saturated carbon, with the suffix '-ol'.
- 😀 Phenols have a hydroxyl group attached to an aromatic ring, also with the '-ol' suffix.
- 😀 Enols feature a hydroxyl group attached to a carbon that has a double bond, and they also use the '-ol' suffix.
- 😀 Ethers are characterized by an oxygen atom connecting two carbon atoms, and are named with the '-oxy' suffix for the smaller part of the ether.
- 😀 Aldehydes have a carbonyl group (C=O) at the end of the carbon chain, with the suffix '-al'.
- 😀 Ketones feature a carbonyl group between two carbon atoms and use the '-one' suffix for naming.
- 😀 Carboxylic acids have a carboxyl group (-COOH) and are named with the suffix '-oic acid'.
Q & A
What defines an organic functional group?
-An organic functional group is defined by an atom or a group of atoms that characterizes a specific organic function. This determines the chemical properties of the compound.
What are the main oxygenated organic functions mentioned in the script?
-The main oxygenated organic functions discussed are alcohols, phenols, enols, ethers, aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, carboxylate salts, acid anhydrides, and esters.
How is an alcohol defined in terms of its functional group?
-An alcohol is defined by the presence of a hydroxyl group (-OH) attached to a saturated carbon atom.
What is the functional group of a phenol?
-A phenol has a hydroxyl group (-OH) attached to an aromatic ring, typically a benzene ring.
What distinguishes an enol from other alcohols?
-An enol is characterized by a hydroxyl group (-OH) attached to a carbon atom that also has a double bond. This is what differentiates it from a typical alcohol.
How do you identify an ether's structure?
-An ether is identified by an oxygen atom connected between two carbon atoms. The oxygen bridges the two carbon chains.
What defines an aldehyde in terms of its functional group?
-An aldehyde is defined by the presence of a carbonyl group (C=O) at the end of a carbon chain, usually with a hydrogen atom attached to the carbonyl carbon (C=O-H).
What is the structural characteristic of a ketone?
-A ketone contains a carbonyl group (C=O) attached to two carbon atoms. Unlike aldehydes, the carbonyl group is not at the end of the chain.
How is a carboxylic acid identified in its structure?
-A carboxylic acid is identified by the presence of a carboxyl group (-COOH), which is a combination of a carbonyl group (C=O) and a hydroxyl group (-OH).
What differentiates a carboxylate salt from a carboxylic acid?
-A carboxylate salt is similar to a carboxylic acid but with the hydrogen of the carboxyl group replaced by a metal ion. This forms a salt and gives the compound a different structure.
What is the key structural feature of an ester?
-An ester has a structure where a carboxyl group (-COOH) has been modified by replacing the hydrogen of the carboxyl group with an alkyl or aryl group, resulting in the ester group (-COO-).
What is the general rule for identifying the sufix of aldehydes and ketones?
-The suffix for aldehydes is 'al' (as in formaldehyde), and for ketones, it’s 'one' (as in acetone).
What are the key suffixes used for naming functional groups in this lesson?
-The key suffixes include 'ol' for alcohols, phenols, and enols, 'oxo' for aldehydes, 'one' for ketones, 'oic' for carboxylic acids, 'ato' for salts of carboxylic acids and anhydrides, and 'oate' for esters.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)