R-2R Ladder Digital to Analog Converter & Advantage।Voltage Switched Network in Digital Electronic
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the R-2-R ladder digital-to-analog converter (DAC) is explained in detail, highlighting its use of two resistor values, R and 2R, to convert digital inputs into corresponding analog voltages. The script walks through the working principles, including resistor calculations for parallel and series arrangements, as well as the voltage divider rule. The output voltage is calculated using a summing amplifier formula, with a breakdown of how each digital bit influences the output. The video also emphasizes the advantages of the R-2-R ladder DAC, including its simplicity, accuracy, expandability, and stable performance.
Takeaways
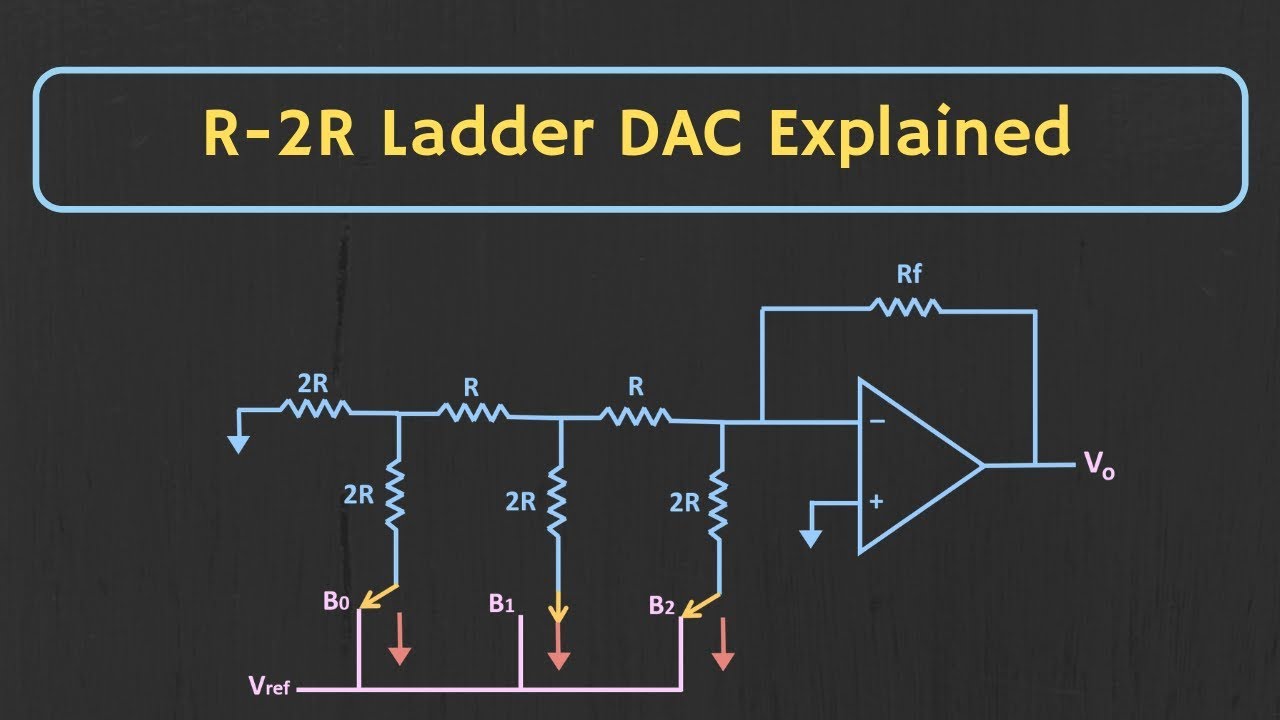
- 😀 The R-2R ladder DAC is a resistive network that uses only two resistor values: R and 2R.
- 😀 The circuit is referred to as a scaling circuit, where the Most Significant Bit (MSB) is on the right and the Least Significant Bit (LSB) is on the left.
- 😀 The DAC operates by using a summing amplifier to combine input voltages and produce an output voltage.
- 😀 The R-2R resistors are connected in series and parallel to achieve the desired resistance values for each input bit.
- 😀 The voltage divider formula is applied to calculate the output voltage, which depends on the resistor values and the input voltage.
- 😀 For an input 'A=1, B=0, C=0, D=0', the output voltage is calculated as 'V_output = V_input / 2'.
- 😀 The DAC can handle various digital input codes, adjusting the output voltage accordingly, such as 'V_output = V_input / 4' for input 'A=0, B=1, C=0, D=0'.
- 😀 The output voltage is a weighted sum of the inputs, with each bit contributing to the final value based on its position (MSB to LSB).
- 😀 The general formula for the output of the R-2R ladder DAC is 'V_output = A/2 + B/4 + C/8 + D/16'.
- 😀 The R-2R ladder DAC has advantages such as requiring only two resistor values, being scalable by adding more bits, and maintaining stable node voltages with changing binary inputs.
Q & A
What is an R to R ladder digital-to-analog converter?
-An R to R ladder digital-to-analog converter is a resistive network that converts a digital input signal into an analog output signal. It uses only two values for resistors, R and 2R, in a ladder-like configuration.
Why is the R to R ladder called so?
-The R to R ladder is named for its use of resistors with values of R and 2R, forming a ladder-like structure where the resistors are arranged in a specific way to achieve the conversion from digital to analog.
What is the role of the summing amplifier in the R to R ladder DAC?
-The summing amplifier in the R to R ladder DAC adds together the weighted voltages from the digital inputs, creating the output voltage. It uses a formula to combine the voltages from different digital inputs to produce a final analog output.
What happens when the digital input is AB CD = 100?
-When the digital input is AB CD = 100, the resulting output voltage is V/2. This is calculated using the voltage divider formula, where resistors and the input voltage divide according to their configuration.
How does the voltage divider affect the output voltage in the R to R ladder DAC?
-The voltage divider determines the proportion of input voltage that appears across each resistor. In the R to R ladder DAC, as the input values change, the voltage divider formula is applied to find the output voltage based on the resistor values.
What is the formula used to calculate the output voltage in the R to R ladder DAC?
-The formula for calculating the output voltage in the R to R ladder DAC is V_output = (A/2) + (B/4) + (C/8) + (D/16), where A, B, C, and D are the digital input bits and the denominators correspond to the weighted resistors in the ladder.
What are the advantages of using the R to R ladder DAC?
-Advantages of the R to R ladder DAC include its simplicity (using only two types of resistors), scalability (additional sections can be added to handle more bits), and its ability to maintain constant voltage nodes even with changing binary inputs.
How does the R to R ladder DAC handle binary inputs like 0001?
-For binary inputs like 0001, the output voltage is calculated as v/16. Each bit in the input affects the output voltage according to its place value, and as more bits are added, the voltage contribution becomes smaller, following the binary weight.
How do you calculate the output for inputs like 0010, 0100, or 1000?
-For inputs like 0010, 0100, or 1000, the output voltage is divided by powers of 2. For example, when the input is 0100, the output is v/4. Each combination of inputs modifies the output voltage according to its binary weight.
What is the relationship between the input bits and the output voltage in an R to R ladder DAC?
-The relationship is that each digital input bit corresponds to a fraction of the total voltage, based on its binary position. For example, the most significant bit (MSB) contributes the largest portion of the output, while the least significant bit (LSB) contributes the smallest portion.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)