Contoh Perhitungan Rangka Batang dengan Metode Potongan | Analisa Struktur Rangka Batang
Summary
TLDRThis tutorial explains how to analyze a truss structure under various loads. The process involves calculating the forces acting on the individual members using principles like equilibrium and moment calculations. It covers how to approach the problem using methods like Sigma moments and horizontal/vertical force analysis. The script guides the user through calculating forces in specific members, including diagonal and horizontal components, and provides insights into the geometry involved. The focus is on applying these principles to determine the forces in select truss members (HC, BC, and HG) by using appropriate cutting techniques and ensuring all components balance in terms of forces and moments.
Takeaways
- 😀 The problem involves analyzing a frame structure with forces acting at specific points (B, C, D) and a horizontal force at point H.
- 😀 The goal is to calculate the forces in three specific members: HC (diagonal), BC (horizontal), and HJ (diagonal).
- 😀 Reactions at the supports have already been calculated, with horizontal and vertical reactions at points P and Q.
- 😀 A cut (section) is made through the three members to determine the forces in them.
- 😀 The analysis begins with calculating the moment (∑M = 0) about a point where the forces meet, typically at support points.
- 😀 Horizontal and vertical forces are balanced using the principle of static equilibrium (∑F = 0).
- 😀 When calculating moments, the distances from the forces to the pivot point (moment arms) are critical.
- 😀 Geometry plays a vital role in resolving forces, particularly in the diagonal members HC and HJ, where trigonometric ratios help break them down into horizontal and vertical components.
- 😀 The force in the diagonal member HC is found to be 75 kN after solving the equilibrium equations.
- 😀 The force in the horizontal member BC is calculated to be approximately 82.5 kN.
- 😀 The process involves both calculating moments and resolving the forces using geometry and equilibrium equations to find the unknown forces in the frame.
Q & A
What is the main focus of the example problem in the transcript?
-The main focus of the example problem is to analyze the internal forces in specific members of a truss structure, particularly in members HC, BC, and HG, using static equilibrium principles and the method of sections.
How are the reactions at the supports determined in this example?
-The reactions at the supports are first calculated using equilibrium equations for the truss, considering both horizontal and vertical forces. The reaction forces are given as 30 N horizontally and 50 N vertically at specific points.
What method is used to find the forces in the truss members HC, BC, and HG?
-The method used is the 'method of sections,' which involves making a cut through the truss that passes through the members HC, BC, and HG, and then applying the equilibrium equations to solve for the unknown forces.
What is the significance of choosing the right point for moment calculations?
-Choosing the right point for moment calculations is crucial because it helps eliminate forces that pass through the point of rotation, simplifying the calculations. For example, moments are taken around point C to eliminate forces acting through it.
How are the directions of forces assigned in this analysis?
-Forces are assumed to be 'tension' (pulling away from the joint) and are considered positive when acting in a counterclockwise direction. If the force direction is reversed, the sign is adjusted accordingly.
Why are both horizontal and vertical force equilibrium equations used in this problem?
-Both horizontal and vertical force equilibrium equations are used to ensure that the truss is in a state of static equilibrium. The sum of all horizontal forces and the sum of all vertical forces must both equal zero for the structure to remain stable.
How is the moment arm related to force calculations in the method of sections?
-The moment arm is the perpendicular distance from the line of action of a force to the point about which the moment is being calculated. It is used to determine the rotational effect of a force around a given point, and it is multiplied by the force to calculate the moment.
How is the force in member HC calculated in this example?
-The force in member HC is calculated by applying the moment equation around point C, using the distances from point C to the lines of action of the forces and solving for the unknown force in HC.
What role do geometric relationships play in solving for forces like HC?
-Geometric relationships are used to determine the components of forces acting along diagonal members like HC. For example, Pythagoras' theorem is applied to find the length of the diagonal and its components in both horizontal and vertical directions.
How are the final forces in members BC, HC, and HG determined?
-The final forces in members BC, HC, and HG are determined by solving the system of equations derived from the equilibrium conditions. These involve solving for unknown forces using both horizontal and vertical force equilibrium and moment equations.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

Metode Elemen Hingga #1 Analisa Rangka Batang Sederhana dengan SAP2000
SA21: Virtual Work Method (Trusses)
SAP 2000 - Analisa Struktur Baja (SNI)
SA04: Truss Analysis: Method of Joints
Contoh Perhitungan Nilai Umum K Batang Tekan Struktur Baja | Lightboard
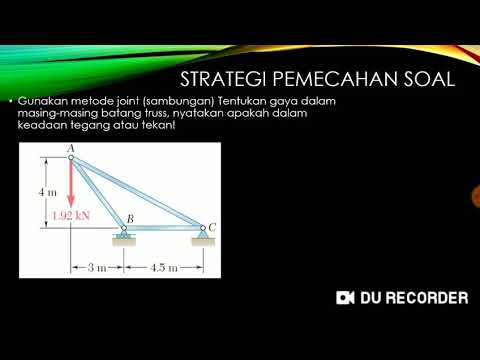
Pembahasan Soal Analisis Struktur Truss dengan metode joint/sambungan
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
