Operasi Pasar Terbuka
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the speaker discusses the concept of open market operations, a key tool of monetary policy used by central banks. The main focus is on how the central bank buys and sells government securities to control the money supply. During a recession, the central bank buys securities to increase money supply, encouraging investment and consumption to boost the economy. Conversely, during high inflation, the central bank sells securities to reduce the money supply, which helps lower inflation and strengthens the currency. The speaker explains these processes in simple terms and their effects on economic stability.
Takeaways
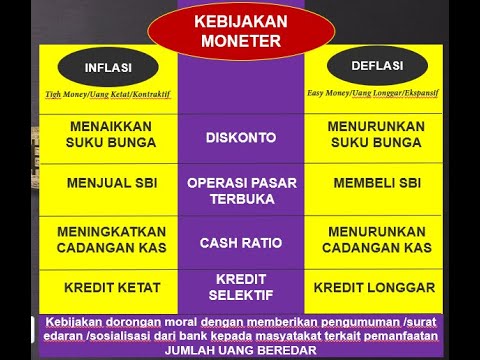
- 😀 Open market operations (OMO) are a tool of monetary policy used by the central bank to influence the money supply.
- 😀 OMO involves buying and selling government securities like Bank Indonesia certificates (SBI) or bonds.
- 😀 The primary goal of OMO is to control the money supply and stabilize the economy, including managing inflation and currency value.
- 😀 During a recession, the government buys securities to increase the money supply, encouraging investment and consumption.
- 😀 By increasing the money supply in a recession, the central bank helps boost economic activity and combat economic downturns.
- 😀 During high inflation, the government sells securities to reduce the money supply, controlling inflation and strengthening the currency.
- 😀 Selling securities decreases liquidity in the market, which helps reduce inflation and stabilize the economy.
- 😀 The central bank's actions during recession and inflation are essentially the opposite: buying securities in a recession and selling them during inflation.
- 😀 Open market operations play a crucial role in stabilizing the currency (the rupiah) by adjusting the amount of money in circulation.
- 😀 By manipulating the money supply, the central bank influences both investment and consumer spending, which are key drivers of economic growth.
- 😀 OMO is a fundamental tool that helps the central bank manage the economy by either stimulating it during recession or cooling it during inflation.
Q & A
What is Open Market Operations (OMO) in macroeconomics?
-Open Market Operations (OMO) refer to the actions taken by a central bank, such as buying and selling government securities, to control the money supply in the economy.
Why does the central bank conduct Open Market Operations?
-The central bank conducts OMO to influence the money supply, aiming to stabilize prices and manage economic conditions such as inflation and recessions.
How does Open Market Operations impact money supply during a recession?
-During a recession, the central bank increases the money supply by buying government securities from banks and the public. This action injects money into the economy, encouraging spending and investment, which can stimulate economic growth.
What happens to the economy when the central bank buys securities during a recession?
-When the central bank buys securities, money flows into the economy, increasing the cash available to businesses and individuals. This leads to increased investments, higher consumption, and ultimately, economic recovery.
What is the effect of increasing the money supply on inflation and the economy?
-Increasing the money supply typically lowers interest rates, boosting demand and investment. This can lead to higher consumption and economic growth, but if overdone, it may also risk increasing inflation.
What does the central bank do during periods of high inflation?
-During high inflation, the central bank reduces the money supply by selling government securities. This action removes money from circulation, cooling down the economy and helping to control inflation.
How does selling government securities reduce inflation?
-When the central bank sells government securities, money flows out of the economy as buyers pay for the securities. This reduces the amount of money in circulation, leading to decreased demand and helping to lower inflation.
What are the outcomes when the central bank sells securities to combat inflation?
-Selling securities decreases the money supply, which reduces inflationary pressures, strengthens the currency (Rupiah in this case), and restores economic stability.
How does Open Market Operations help stabilize the value of a currency like the Rupiah?
-OMO helps stabilize the Rupiah by adjusting the money supply. By controlling inflation and balancing the economy, the central bank can ensure that the currency maintains its value, avoiding excessive fluctuations.
What is the ultimate goal of Open Market Operations?
-The ultimate goal of Open Market Operations is to maintain economic stability by managing inflation, stabilizing the currency, and ensuring sustainable economic growth.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

Kebijakan Moneter, Kebijakan Untuk Mengatur Jumlah uang beredar, Mengatasi Inflasi

Monetary Policy explained
KEBIJAKAN MONETER

Bank Sentral (Bank Indonesia): Bahas Soal SMA Kelas X

What's all the Yellen About? Monetary Policy and the Federal Reserve: Crash Course Economics #10

KELOMPOK 2 || PERAN UANG DAN KEBIJAKAN MONETER
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
