belajar las Tig/Argon pada media besi||teknik dasar
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the host provides practical insights into TIG (argon) welding, demonstrating techniques using a Daiden 200 TIG welding machine. The focus is on adjusting settings like amperage (ranging from 70 to 110 amps) and choosing the right materials for welding iron. Various wire types (argon welding wire, clothesline wire, and stainless wire) are tested to highlight differences in welding results. Key tips include the importance of tungsten tip shape, maintaining the correct distance during welding, and balancing theory with hands-on practice. The video emphasizes learning through practice while sharing real-world welding challenges and solutions.
Takeaways
- 😀 The tungsten tip should always be pointed to maintain a focused arc during TIG welding.
- 😀 The ideal distance between the tungsten tip and the workpiece is approximately 2-3 mm for optimal results.
- 😀 Using clean materials is important for welding, as it affects the overall quality of the weld.
- 😀 Amperage adjustments play a crucial role in the quality of the weld, with 110A being ideal for 6mm thick iron.
- 😀 Lower amperages, such as 70A, make it difficult to melt the material and result in weaker welds.
- 😀 Using the right type of welding wire (e.g., specific argon welding wire for steel or iron) ensures better control and weld quality.
- 😀 Welding with a blunt tungsten tip produces a larger arc, making it harder to control the weld pool.
- 😀 Ordinary wire (e.g., clothesline wire) can be used for welding, but it may cause difficulty due to contaminants like zinc.
- 😀 The speed and rhythm of welding should match the material's melting rate to avoid under-penetration or weak welds.
- 😀 Practical experience is key to mastering TIG welding, and beginners should balance theoretical knowledge with hands-on practice.
- 😀 The welding process is an ongoing learning experience, and even experienced welders must continue to refine their techniques and address mistakes.
Q & A
What is the significance of using a pointed tungsten tip in TIG welding?
-A pointed tungsten tip is crucial in TIG welding because it helps focus the arc at a specific point, providing a stable and precise weld. It allows for better control over the welding process, especially when working with thin materials.
Why should the tungsten tip distance be adjusted to 2-3 mm from the material during welding?
-Maintaining a distance of 2-3 mm from the material ensures a stable arc, providing a consistent heat input to the joint. It prevents the tungsten from touching the workpiece, which can lead to contamination or unstable arcs.
What happens if you use a blunt tungsten tip instead of a pointed one in TIG welding?
-Using a blunt tungsten tip results in a larger, less focused arc, making it harder to control the groove and heat distribution. This often leads to inconsistent penetration, burnt sides, and poor weld quality.
Can regular iron welding be done with TIG welding, and what materials should be used for the filler wire?
-Yes, regular iron can be welded using TIG welding. It is recommended to use a filler wire specifically for iron or steel, such as argon welding wire designed for this purpose. Using ordinary wire or unsuitable materials like galvanized wire can lead to issues like poor control and inconsistent welds.
How does the amperage setting affect the weld when using TIG welding on iron?
-The amperage setting directly influences the melt rate and penetration of the weld. Higher amperages, like 110A, result in smoother, more controlled welds, while lower amperages, such as 70A, may struggle to melt the material properly, leading to weak welds with poor penetration.
What issues arise when using a 70 ampere setting for welding 6 mm thick iron?
-At 70 amperes, the weld often struggles with penetration, making it difficult to achieve a strong bond. The heat generated by the arc is insufficient to properly melt the material, resulting in a weak weld with poor fusion.
What are the effects of using galvanized wire in TIG welding?
-Using galvanized wire, which contains zinc, can cause excessive sparks and smoke during welding. This results in an unstable arc, and the zinc can also contaminate the weld, leading to issues with the quality and strength of the joint.
How should the filler wire be handled during TIG welding to ensure a stable weld?
-The filler wire should be held steadily and fed into the welding pool in a controlled manner. It should be placed in the center of the welding line, and the movement should be consistent to maintain proper penetration and avoid defects.
What is the ideal welding wire for beginners in TIG welding?
-For beginners, it is recommended to use a welding wire designed specifically for the material being welded, such as argon welding wire for steel or iron. This helps maintain stability and control during the welding process, especially when learning the technique.
What can be learned from the comparison of welding with different amperage settings (110A, 90A, and 70A)?
-Comparing different amperage settings helps understand the impact on weld quality. Higher amperages like 110A produce smoother and more consistent welds, while lower amperages like 70A result in poor fusion and weaker joints. This highlights the importance of selecting the right amperage for the material and thickness.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

Tutorial Dasar Penggunaan Mesin Las TIG Untuk Pemula - Daesung TIG 200

Yuk Belajar Las Tig Argon Khusus Pemula dengan Mesin Las Tig Argon dari Daiden

What is TIG Welding? (GTAW)

Learning how to TIG weld made easy
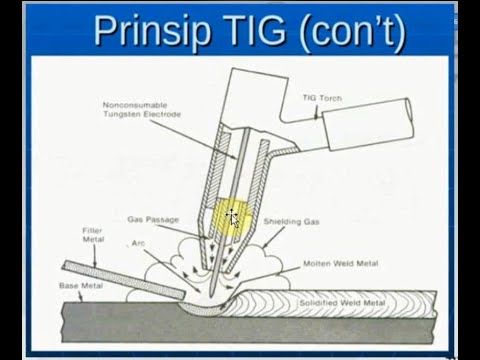
Prinsip Kerja dan Komponen Las TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas)

Plasma Arc Welding | Manufacturing Processes
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
