Conceito de pH e pOH | Brasil Escola
Summary
TLDRIn this educational chemistry lesson, the instructor explains the concepts of pH and pOH, highlighting how these scales measure the acidity or basicity of a substance. The teacher walks through the chemical foundation, referencing the auto-ionization of water and the equilibrium constant, K_w. The formulas for calculating pH and pOH are discussed, as well as their relationship: pH + pOH = 14. The lesson emphasizes the importance of context when interpreting pH values and provides real-life examples such as lemon juice (acidic) and ammonia (basic). The video encourages viewers to engage with the content for better understanding and application of these principles.
Takeaways
- 😀 pH and pOH are two concepts used to measure the acidic or basic nature of a solution.
- 😀 pH stands for 'potential hydrogen' and measures the concentration of H3O+ ions in a solution.
- 😀 pOH stands for 'potential hydroxyl' and measures the concentration of OH- ions in a solution.
- 😀 Both pH and pOH are calculated using logarithmic scales.
- 😀 pH and pOH are inversely related, meaning pH + pOH = 14 at 25°C.
- 😀 The concentration of H3O+ and OH- in pure water is 1 x 10^-7 M, which leads to a pH and pOH of 7 (neutral).
- 😀 A solution with pH less than 7 is acidic, and a solution with pH greater than 7 is basic.
- 😀 pH is used to measure acidity, while pOH is used to measure basicity.
- 😀 The relationship between pH and pOH is important for understanding the balance of acids and bases in solutions.
- 😀 Everyday examples include lemon juice (acidic), ammonia (basic), and saliva (neutral).
Q & A
What is the main topic of the lesson?
-The main topic of the lesson is the concept of pH (potential hydrogen ion concentration) and pOH (potential hydroxyl ion concentration), with a focus on how these values are calculated and their significance in measuring acidic and basic properties of a substance.
What is the relationship between pH and pOH?
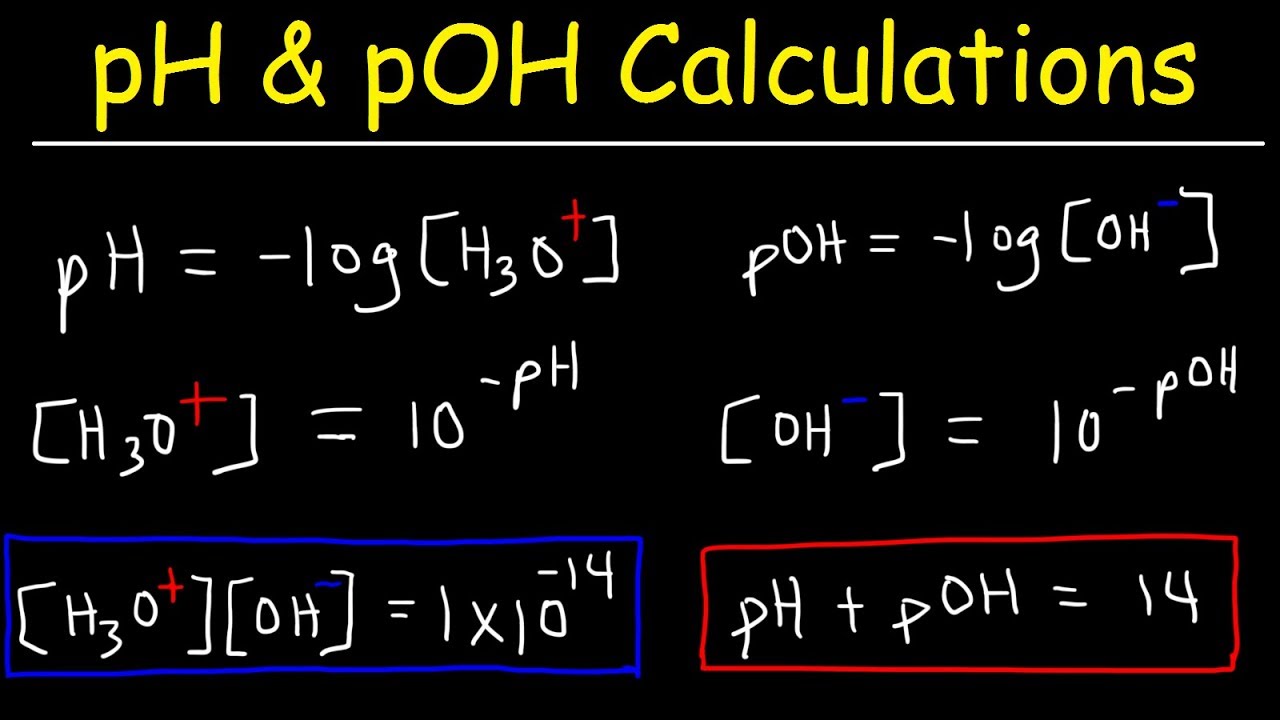
-pH and pOH are related by the equation pH + pOH = 14. This relationship comes from the ionization of water, where the concentrations of hydrogen ions (H+) and hydroxyl ions (OH-) are equal, leading to the sum of pH and pOH always being 14.
How is pH calculated?
-pH is calculated as the negative logarithm of the hydrogen ion concentration, represented by the formula pH = -log[H+]. This measures the acidity of a solution.
How is pOH calculated?
-pOH is calculated as the negative logarithm of the hydroxyl ion concentration, represented by the formula pOH = -log[OH-]. This measures the basicity of a solution.
What is the significance of the value 7 in pH and pOH scales?
-In both pH and pOH scales, a value of 7 represents neutrality. A pH of 7 indicates a neutral solution, while a pOH of 7 also indicates a neutral solution.
What happens when pH is less than 7 or greater than 7?
-When pH is less than 7, the solution is acidic, and when pH is greater than 7, the solution is basic. Similarly, for pOH, a value less than 7 indicates basicity, and a value greater than 7 indicates acidity.
What is the ionization constant (Kw) of water?
-The ionization constant (Kw) of water at 25°C is 1 × 10^-14. This constant represents the product of the concentrations of hydrogen ions [H+] and hydroxyl ions [OH-] in pure water.
How can you calculate pH or pOH from the other?
-To calculate pH from pOH, subtract the pOH value from 14. Similarly, to calculate pOH from pH, subtract the pH value from 14.
What are some common examples of substances with different pH levels?
-Common acidic substances include lemon juice and pineapple juice, while examples of basic substances are ammonia and bleach (sodium hydroxide). Neutral substances include saliva and blood.
Why is it important to differentiate between pH and pOH values?
-It's important to differentiate between pH and pOH because each value measures different aspects: pH measures acidity (H+ concentration), and pOH measures basicity (OH- concentration). Both are essential for understanding the chemical nature of substances.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

Pengantar Oseanografi - Acidity, Alkalinity dan Dissolve Gases

Introduction to pH | Biology foundations | High school biology | Khan Academy
pH, pOH, H3O+, OH-, Kw, Ka, Kb, pKa, and pKb Basic Calculations -Acids and Bases Chemistry Problems

ESCALAS TERMOMÉTRICAS: COMO MEDIR A TEMPERATURA DE UM CORPO | Resumo de Física para o Enem
pH and pOH: Crash Course Chemistry #30

05. KHT - Ilmu Tanah Hutan - pH Tanah
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
