Dualisme Gelombang Partikel • Part 1: Radiasi Benda Hitam, Pergeseran Wien, dan Teori Kuantum Planck
Summary
TLDRThis video delves into quantum physics, covering topics such as black body radiation, Wien's displacement law, and Planck's quantum theory. It explains key concepts like Stefan-Boltzmann's law, the relationship between temperature and radiation intensity, and how energy is emitted in discrete quantities (quantized energy). Additionally, the script includes a detailed example of solving a physics problem involving radiation from a black body. The explanation emphasizes the dual wave-particle nature of light and the significance of Planck's constant in understanding photon energy, offering an accessible breakdown of complex physics principles.
Takeaways
- 😀 Radiation from black bodies is governed by Stefan-Boltzmann's law, which states that energy emitted is proportional to the fourth power of the temperature and the surface area of the black body.
- 😀 The emission of radiation from a surface depends on its emissivity, which ranges from 0 to 1, with 1 representing a perfect black body.
- 😀 Wien's Displacement Law explains that as the temperature of a black body increases, the wavelength at which the maximum radiation intensity occurs decreases.
- 😀 Planck's theory of quantum mechanics introduced the concept that energy emitted by a black body is quantized, existing in discrete multiples of a base value.
- 😀 Light exhibits both wave-like and particle-like properties, a phenomenon known as wave-particle duality, where light can behave as both a wave and a particle (photon).
- 😀 A photon is a particle of light that carries discrete energy values based on its frequency, described by the formula E = h * f, where h is Planck's constant.
- 😀 The intensity of radiation from a surface can be calculated by dividing the emitted power by the surface area, and the formula is related to the Stefan-Boltzmann law.
- 😀 The temperature of a black body can be directly related to the wavelength at which maximum radiation intensity occurs using Wien's Displacement Law: λ_max = C / T.
- 😀 In problems involving radiation from objects, the Stefan-Boltzmann law can be used to calculate the rate of radiation, intensity, and energy emitted by a surface.
- 😀 The formula for energy emitted by a body over time involves multiplying the power (calculated using Stefan-Boltzmann's law) by the time duration, allowing for practical calculations of radiated energy.
Q & A
What is the Stefan-Boltzmann law?
-The Stefan-Boltzmann law states that the energy radiated by a black body surface per unit time is proportional to the fourth power of its absolute temperature and the surface area of the object. The formula is P = εσA T^4, where P is the power, ε is the emissivity, σ is the Stefan-Boltzmann constant, A is the surface area, and T is the temperature in Kelvin.
What is the significance of the emissivity (ε) in the Stefan-Boltzmann law?
-Emissivity (ε) represents the efficiency of an object in emitting radiation compared to a perfect black body. Its value ranges between 0 and 1, where 1 indicates a perfect black body that emits the maximum possible radiation.
How do you calculate the intensity of radiation emitted by a body?
-Intensity (I) of radiation is calculated by dividing the power (P) by the surface area (A). In mathematical terms, I = P/A, which simplifies to I = εσT^4 when using the Stefan-Boltzmann law.
What does Wien's Displacement Law describe?
-Wien's Displacement Law states that as the temperature of a black body increases, the wavelength of maximum intensity radiation decreases. In other words, the peak wavelength of radiation shifts to shorter wavelengths as the temperature rises.
What is the formula for Wien's Displacement Law?
-The formula for Wien's Displacement Law is λ_max = b / T, where λ_max is the wavelength at which the intensity is maximum, T is the temperature in Kelvin, and b is a constant (approximately 2.898 x 10^-3 m·K).
What does Planck's Quantum Theory explain about energy?
-Planck's Quantum Theory proposes that energy is emitted or absorbed in discrete packets, called quanta. The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to its frequency, as described by the formula E = hf, where E is energy, h is Planck's constant, and f is the frequency of the radiation.
What is dualism in wave-particle theory?
-Wave-particle dualism refers to the concept that light (and other electromagnetic radiation) exhibits both wave-like and particle-like properties. It can behave as a continuous wave with frequency and wavelength, but also exhibit discrete energy levels in the form of particles known as photons.
What is a photon in the context of quantum mechanics?
-A photon is a quantum of electromagnetic radiation, essentially a particle of light. It carries energy in discrete amounts, proportional to the frequency of the radiation, as described by the formula E = hf.
How is the energy of a photon related to its wavelength?
-The energy of a photon is inversely proportional to its wavelength. This relationship can be expressed as E = hc / λ, where E is the energy, h is Planck's constant, c is the speed of light, and λ is the wavelength of the photon.
In the example provided, how do you calculate the power radiated by a black body?
-In the example, the power radiated by a black body is calculated using the Stefan-Boltzmann law. The given values for temperature, emissivity, and the surface area of the object are used in the formula P = εσA T^4 to find the power.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

Blackbody Radiation: the Laws of Stefan, Wien, and Planck!

Understanding Thermal Radiation

This math trick revolutionized physics
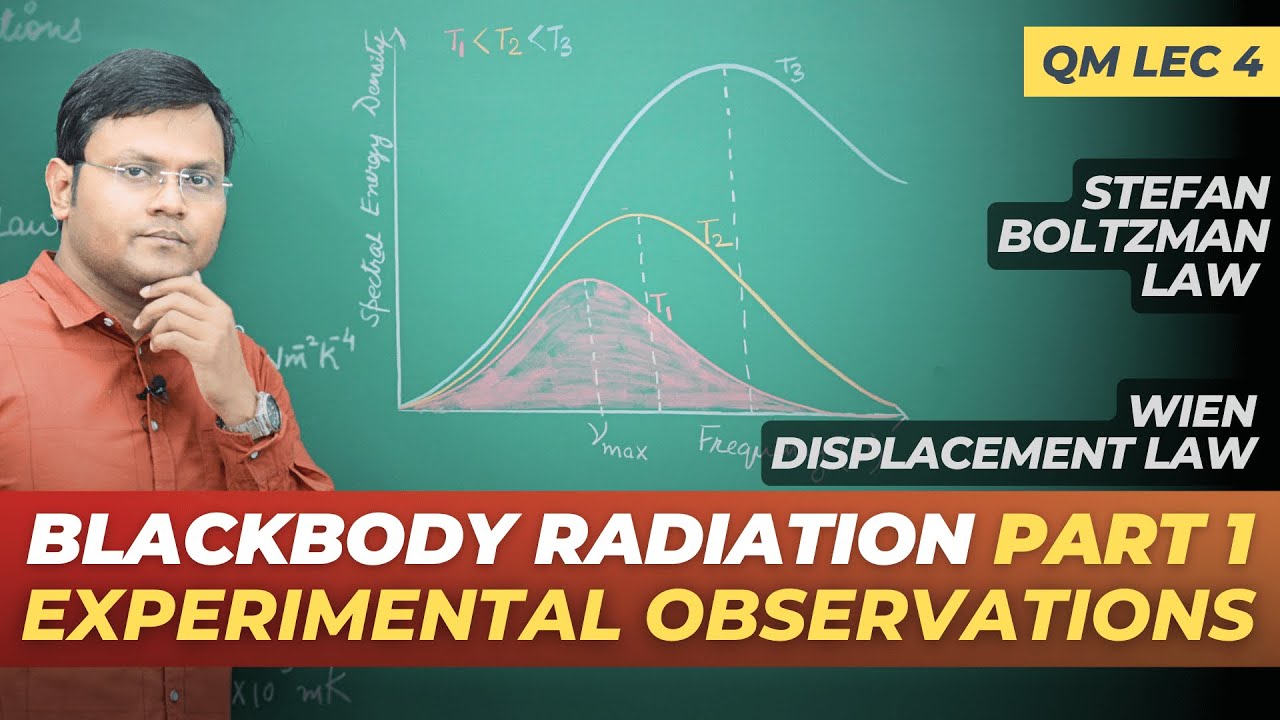
Blackbody Radiation Part 1 - Experimental Observations: Stefan Law, Wiens Displacement Law

AULA EXTREMAMENTE COMPLETA: Max Planck│ Quantização da Energia │ Modelos Atômicos

MATERI FISIKA SMA KELAS 12 | GEJALA KUANTUM | RADIASI BENDA HITAM DAN PERGESERAN WIEN
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
