#1 #Kelas10 #Geografi #smstr2 | Lapisan Bumi dan Karakteristiknya
Summary
TLDRThis educational video delves into the Earth's lithosphere, explaining its structure and dynamics. The lithosphere, a layer made up of rocks, includes both continental and oceanic crusts. The video covers how tectonic movements cause changes in the Earth's surface, creating geological formations like mountains, valleys, and faults. It also introduces the concepts of folding and faulting due to tectonic forces. The video aims to help viewers understand the importance of the lithosphere and tectonic processes in shaping the planet's landscape.
Takeaways
- 😀 The Earth's surface features such as mountains, valleys, and waterfalls are the result of dynamic processes in the lithosphere.
- 😀 Lithosphere comes from the Greek words 'lithos' meaning stone and 'sphaira' meaning layer, referring to the Earth's outer layer made of rock.
- 😀 The lithosphere includes both the Earth's crust and the upper mantle. There are two types of crust: continental and oceanic.
- 😀 The continental crust is characterized by landmasses, while the oceanic crust is covered by seawater.
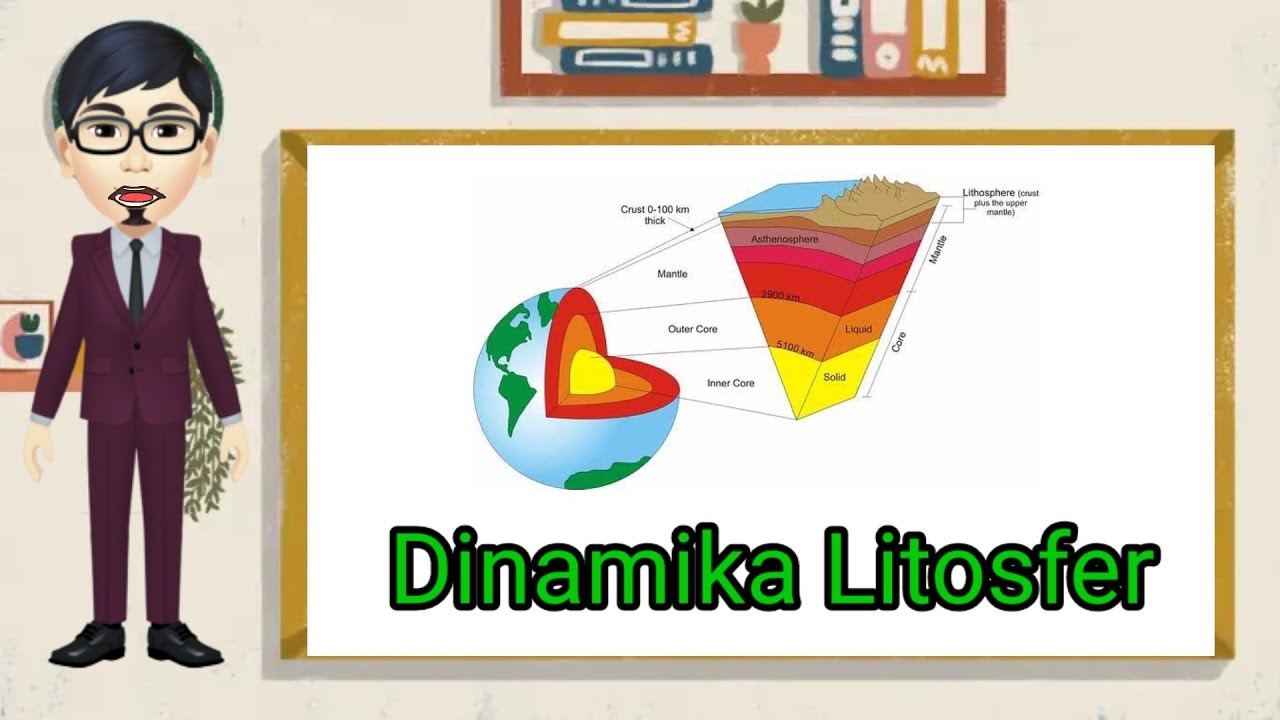
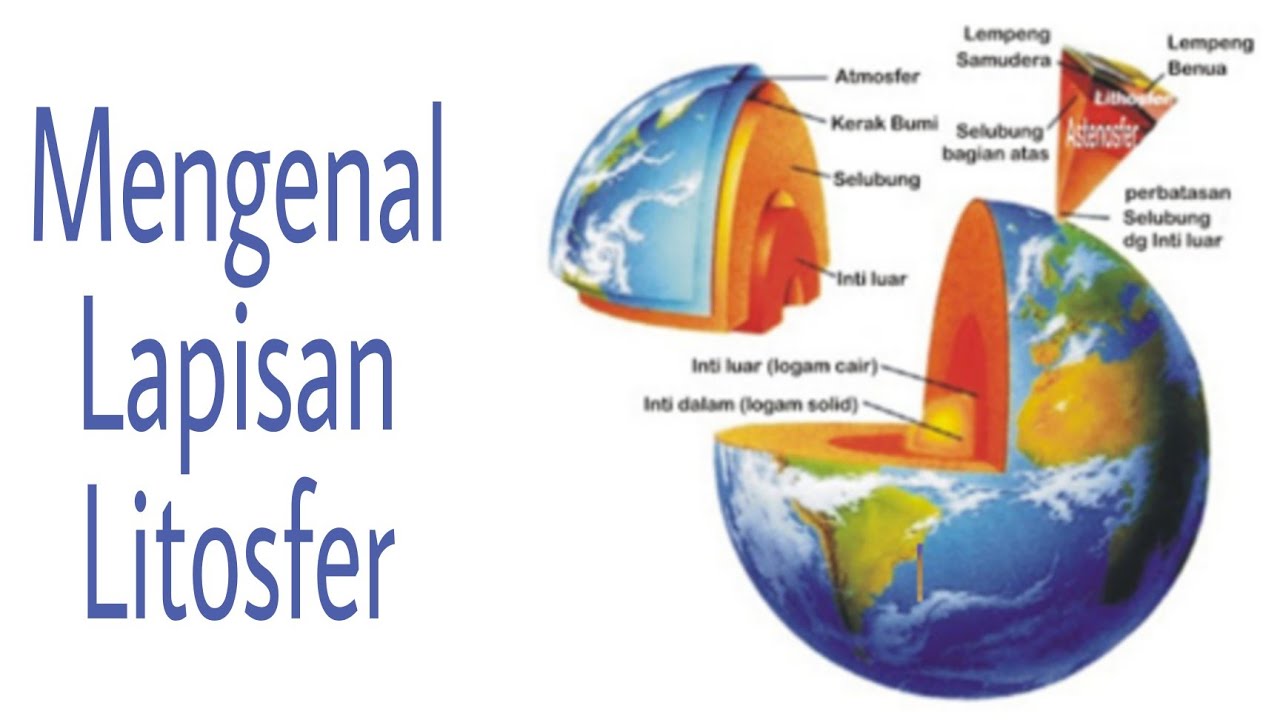
- 😀 The Earth's layers consist of the lithosphere (outer layer), the mantle (middle layer), and the core (inner layer).
- 😀 The lithosphere has two distinct layers: the sial layer, which consists of silicon and aluminum, and the sima layer, made of silicon and magnesium.
- 😀 The mantle, also called the intermediary layer, sits beneath the lithosphere, while the core consists of iron and nickel.
- 😀 Tectonism refers to the horizontal or vertical movement of Earth's layers, leading to phenomena like folds and faults.
- 😀 Folds, which are wave-like formations in the Earth's crust, can be categorized into upright, sloping, and overturned types.
- 😀 Faults, which occur due to tectonic forces, can be classified into upward (thrust) and downward (graben) faults. An example of a fault in Indonesia is the Semangko fault in Sumatra.
- 😀 Tectonism results from both endogenic (internal) and exogenic (external) forces, shaping the Earth's surface and creating various landforms.
Q & A
What is the Lithosphere?
-The lithosphere is the outer layer of the Earth, consisting of rock formations. It includes the Earth's crust and the upper part of the mantle.
Why are there mountains, valleys, and waterfalls on Earth?
-These natural formations exist due to the dynamic movements of the lithosphere, which undergoes tectonic processes such as folding, faulting, and other geological changes.
What does the term 'Lithosphere' originate from?
-The word 'lithosphere' comes from Greek, with 'lithos' meaning stone or rock, and 'sphaira' meaning layer or sphere.
What are the two types of Earth's crust?
-The Earth's crust is divided into two types: the continental crust, which forms landmasses, and the oceanic crust, which is covered by water.
What is the structure of the Earth's layers?
-The Earth has three main layers: the lithosphere (outer layer), the asthenosphere (mantle), and the inner core (core), which is made of nickel and iron.
What are the two types of lithosphere layers?
-The lithosphere consists of two layers: the 'sial' layer, which is made of silicon and aluminum, and the 'sima' layer, composed of silicon and magnesium.
What is tectonism?
-Tectonism refers to the horizontal or vertical movements of Earth's layers, leading to changes in the Earth's structure, including the formation of folds and faults.
How do folds and faults affect the Earth's surface?
-Folds and faults, formed by tectonic movements, cause changes in the Earth's surface, such as the creation of mountains, valleys, and other landforms.
What are the types of folds?
-Folds are classified into several types, including upright, inclined, overturned, and recumbent folds, depending on the direction and angle of the layers.
What is a fault, and can you give an example in Indonesia?
-A fault is a crack or fracture in the Earth's crust caused by tectonic forces. An example in Indonesia is the Semangko Fault, located on Sumatra Island.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenant5.0 / 5 (0 votes)