Dinamika Litosfer: Tenaga Endogen
Summary
TLDRThis educational video covers the dynamics of the Earth's lithosphere, focusing on internal forces that shape the planet. It explains Earth's three main layers: the crust, mantle, and core, their structures, and differences between oceanic and continental crusts. The video delves into tectonic movements like epirogenic and orogenic forces, the volcanic process, and various types of volcanic eruptions. It also highlights seismic activity, types of earthquakes, and how seismic waves propagate. Throughout, viewers gain insights into geological processes that continually reshape Earth's surface, from earthquakes to volcanic events, providing a comprehensive look at Earth's internal dynamics.
Takeaways
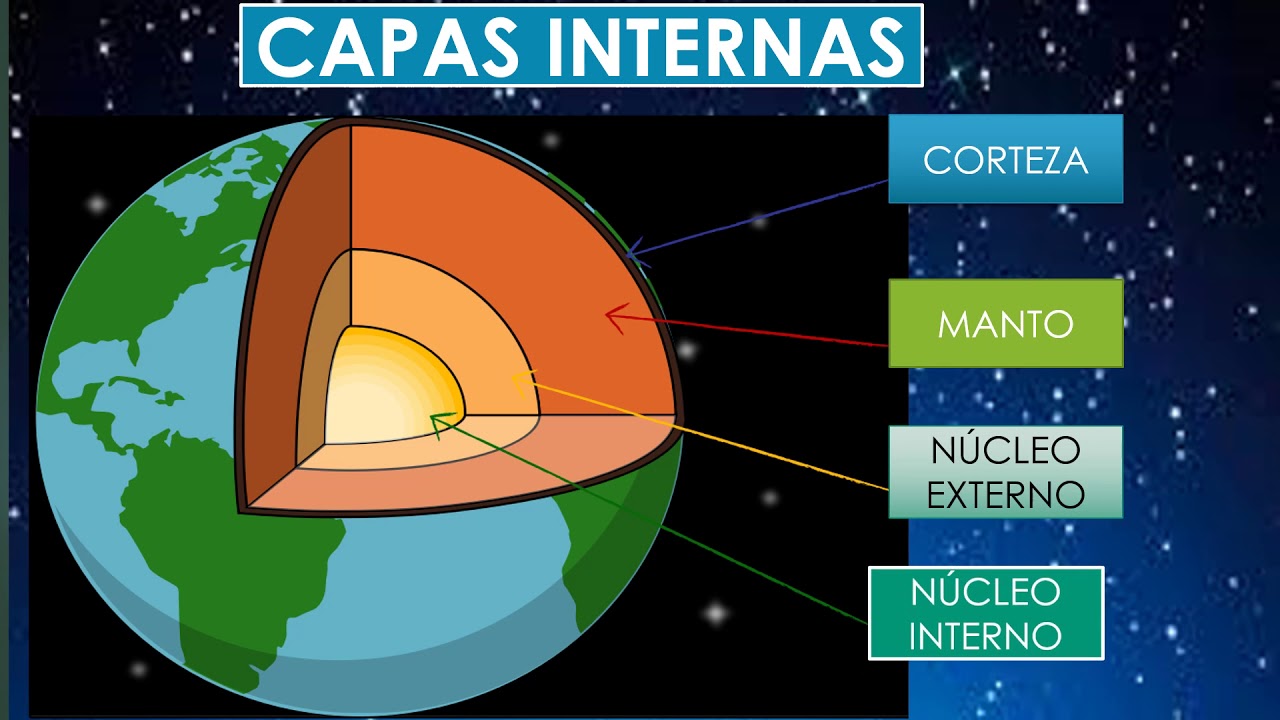
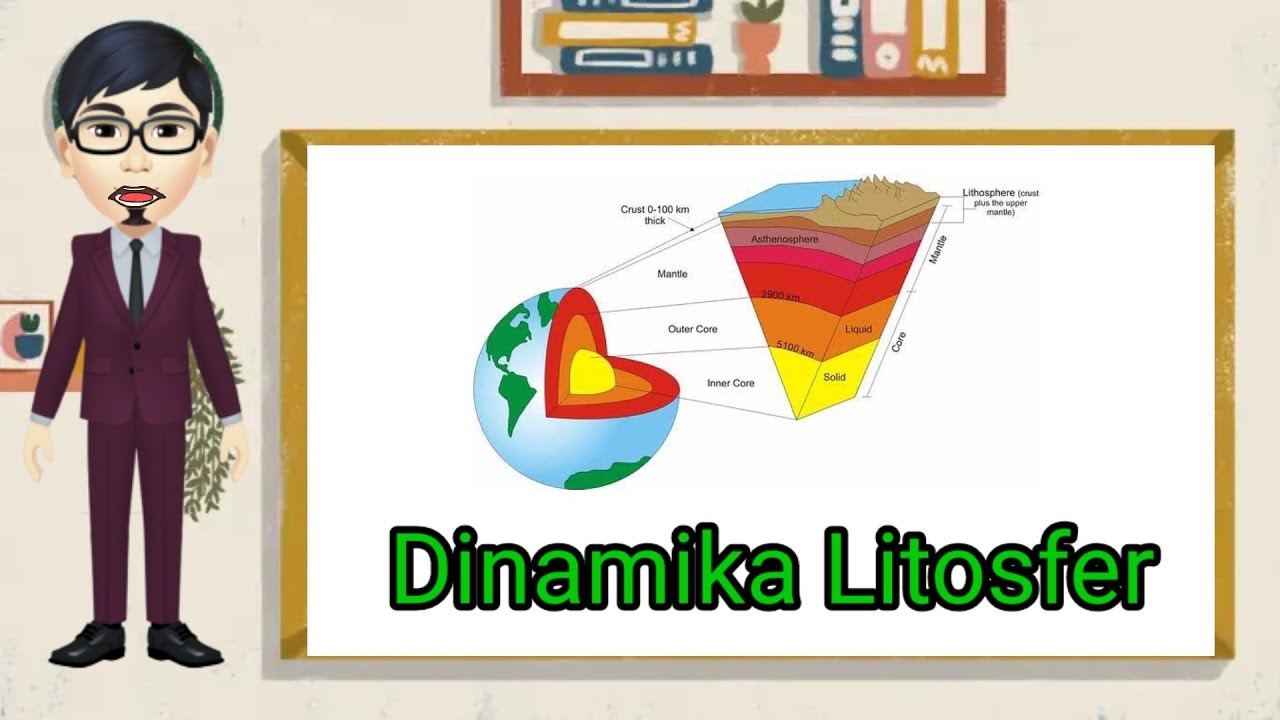
- 😀 The Earth is divided into three main layers: the crust, the mantle, and the core.
- 😀 The Earth's crust is the thinnest layer, ranging from 5 to 70 km thick and consists of oceanic and continental crusts.
- 😀 The mantle lies beneath the crust, extending down to 2,900 km and is the source of magma for volcanic activity.
- 😀 The core is composed of molten iron and nickel, with the outer core being liquid and the inner core solid.
- 😀 Continental crust is thicker, ranging from 35 to 70 km, and is older with a lower density compared to oceanic crust.
- 😀 Tectonic movements can cause folding, faulting, and the formation of surface reliefs, classified into epirogenetic and orogenetic movements.
- 😀 Epirogenetic movements are slow, large-scale movements that raise or lower continents, while orogenetic movements occur faster and affect smaller regions.
- 😀 Volcanic processes involve the movement of magma and include intrusions (underground) and extrusions (surface eruptions).
- 😀 Intrusions of magma can form various geological structures such as batholiths, laccoliths, and dikes.
- 😀 Volcanic eruptions can be effusive (lava flows) or explosive (releasing gas, ash, and volcanic bombs), each producing different volcanic landforms.
- 😀 Earthquakes are caused by sudden energy release within the Earth, often linked to tectonic plate movements and occur along faults or plate boundaries.
Q & A
What are the three main layers of the Earth?
-The Earth is divided into three main layers: the crust, the mantle, and the core.
What are the differences between oceanic and continental crust?
-The continental crust is thicker (35-70 km) and older (up to 1 billion years), while the oceanic crust is thinner (7-10 km) and younger (less than 200 million years). The continental crust is also less dense compared to the oceanic crust.
What is the astenosphere, and why is it important?
-The astenosphere is part of the upper mantle, extending to a depth of 2,900 km. It is important because it serves as the source of magma for volcanic activity.
How are tectonic movements classified?
-Tectonic movements are classified into two types: epirogenetic (slow vertical movements over large areas) and orogenetic (rapid movements over smaller areas that cause folding and faulting).
What is the difference between positive and negative epirogenetic movements?
-Positive epirogenetic movements involve the sinking of land, causing the sea level to appear to rise, while negative epirogenetic movements involve the rising of land, causing the sea level to appear to fall.
What are the two types of volcanic eruptions?
-The two types of volcanic eruptions are effusive eruptions, which involve the slow outflow of lava, and explosive eruptions, which release gas and solid materials like ash and rocks.
What are the different types of volcanic material?
-Volcanic materials include solid materials like bombs (large rocks), lapilli (small rocks), and ash, as well as liquid lava, lahar (hot or cold mudflows), and gas emissions such as sulfur dioxide and steam.
What are the three main types of volcanoes?
-The three main types of volcanoes are shield volcanoes, which have gentle slopes and form from fluid lava; stratovolcanoes, which are steeper and formed from explosive eruptions; and calderas, which are large volcanic craters formed by eruptions that collapse the volcano's structure.
What is the difference between seismic waves?
-Seismic waves include primary waves (P-waves), which are longitudinal and the fastest; secondary waves (S-waves), which are transverse and slower; and surface waves, which cause the most damage as they travel along the Earth's surface.
What are the four types of earthquakes based on their causes?
-The four types of earthquakes are tectonic (caused by plate movement), volcanic (caused by volcanic activity), collapse (due to rock or cave collapses), and impact (caused by meteorite impacts).
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Dinamika Litosfer dan Dampaknya Terhadap Kehidupan

BAB 6 STRUKTUR BUMI DAN PERKEMBANGANNYA BAGIAN 1 - IPA Kelas 8 Kurikulum Merdeka
VIDEO DE LAS CAPAS EXTERNAS E INTERNAS DE LA TIERRA. AUTORA VICTORIA GUAMÁN.

Struktur Bumi dan Perkembangannya

Geo X. 19. Dinamika Litosfer dan Dampaknya Bagi Kehidupan Manusia.
Mapel Geografi Kelas X " Dinamika Litosfer "
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)