operasi bisnis week #12 master schedule
Summary
TLDRThe video covers the Master Schedule (MPS), a vital tool for balancing production and demand over time, with a focus on its integration with Material Requirements Planning (MRP). It highlights key concepts like demand forecasting, production capacity, and inventory levels. The video explains how to calculate net requirements by factoring in forecasted demand, current inventory, and scheduled receipts. Additionally, it addresses challenges such as managing production capacity and adjusting schedules to avoid stockouts and overproduction. Practical exercises and real-world examples are provided to deepen understanding.
Takeaways
- 😀 Master Schedule (MPS) is a tool used for planning production and operations, balancing supply and demand over a specific period.
- 😀 The key components of Master Schedule include demand forecast, production capacity, and inventory levels.
- 😀 A well-managed Master Schedule helps businesses avoid overproduction and stock-outs, ensuring efficient operations.
- 😀 Gross requirement is based on forecasted market demand, and net requirement is calculated by subtracting inventory and scheduled receipts.
- 😀 Scheduled receipts refer to items that are ordered and scheduled to arrive during the planning period, contributing to inventory.
- 😀 Net requirements are calculated by subtracting inventory and scheduled receipts from gross requirements, ensuring sufficient supply for production.
- 😀 A critical challenge in Master Scheduling is when demand exceeds production capacity, requiring careful adjustment of the schedule.
- 😀 Adjustments to the Master Schedule may be necessary to accommodate production constraints, delays, or other unforeseen factors.
- 😀 Real-life examples demonstrate how high market demand might not always match available production capacity, leading to missed orders or backlogs.
- 😀 The workflow of Master Scheduling includes three primary steps: analyzing input data (demand, inventory, receipts), calculating requirements, and adjusting schedules as needed.
- 😀 The ultimate goal of a Master Schedule is to provide a clear MPS (Master Production Schedule) that feeds into Material Requirement Planning (MRP) to ensure material availability for production.
Q & A
What is the primary purpose of a Master Schedule (MPS)?
-The primary purpose of a Master Schedule (MPS) is to plan production and operations by balancing supply and demand over a specific time period. It helps businesses operate efficiently and avoid overproduction or stockouts.
How does a Master Schedule relate to Material Requirements Planning (MRP)?
-A Master Schedule (MPS) determines the number of units to produce, and based on this, Material Requirements Planning (MRP) is used to calculate the materials and components required to meet production goals.
What are the main components that affect the calculation of a Master Schedule?
-The main components include demand forecasting (market demand), production capacity (available resources), and inventory levels (existing stock). These components are crucial for determining the production plan.
What is the difference between gross and net requirements in the context of MPS?
-Gross requirements represent the total forecasted demand for a product, while net requirements are the actual units needed to be produced, after accounting for inventory and scheduled receipts (incoming materials).
What is a 'Scheduled Receipt' and how does it impact net requirements?
-A Scheduled Receipt refers to materials or products that have been ordered and are expected to arrive in the future. It reduces the net requirement for the week in which it is scheduled to arrive.
Can you explain the formula for calculating net requirements?
-Net requirement is calculated as: Net Requirement = Gross Requirement - Inventory - Scheduled Receipts. This helps determine the actual amount of production needed to meet demand.
How does production capacity affect the Master Schedule?
-Production capacity limits how much can be produced in a given time period. If market demand exceeds the production capacity, adjustments must be made to either increase capacity or defer some orders.
What happens when market demand exceeds production capacity in the Master Schedule?
-When demand exceeds production capacity, the company can only produce up to the maximum capacity, and the remaining demand might need to be deferred or directed to competitors, leading to potential lost sales.
Why is it important to manage inventory levels in a Master Schedule?
-Managing inventory levels is essential to prevent stockouts (where production cannot meet demand) or overstocking (leading to excessive costs or waste). Proper inventory management ensures that production runs smoothly without excess material or shortages.
What is the role of capacity analysis in the Master Schedule process?
-Capacity analysis helps to identify whether the available production resources (like labor, machines, etc.) are sufficient to meet the forecasted demand. If there is a shortfall in capacity, adjustments to the schedule or production strategy are necessary.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

Memahami Perencanaan Kebutuhan Material untuk proses produksi ...

Planejamento e Controle da Produção # 15 – Implantação do MRP

Explicación MRP

What is the Material Requirement planning (MRP)? | MRP Process

SAP PP Training for Beginners: A Complete Guide | Proexcellency
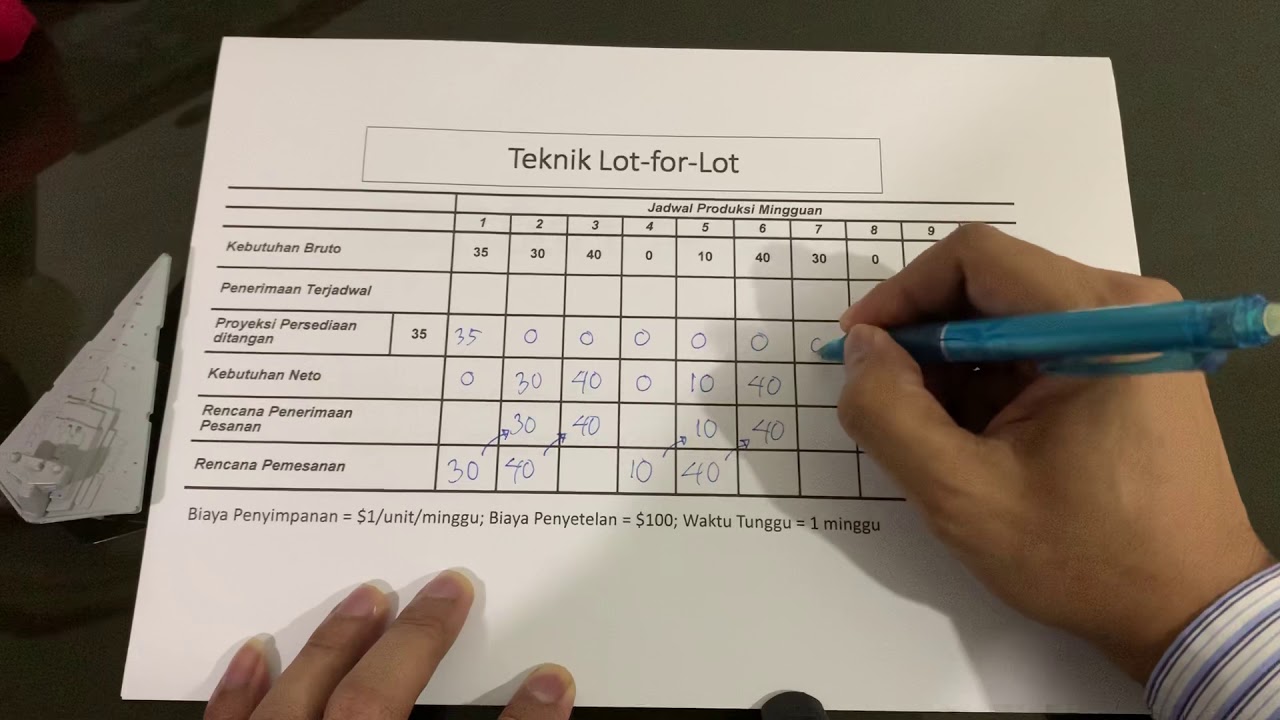
Teknik Lot for Lot pada Lot Sizing (Penentuan Ukuran Lot) dalam Sistem MRP
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
