What is Mitosis & Meiosis? | Complete | Animated Explanation
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the processes of mitosis and meiosis, two types of cell division. Mitosis results in two identical daughter cells, crucial for growth, repair, and asexual reproduction. The video details the stages of mitosis, from interphase through cytokinesis. Meiosis, on the other hand, produces four genetically diverse gametes with half the chromosome number, essential for sexual reproduction. The video covers the distinct phases of meiosis, including crossover and genetic variation. Both processes are vital for life, with mitosis focusing on cellular duplication and meiosis ensuring genetic diversity in offspring.
Takeaways
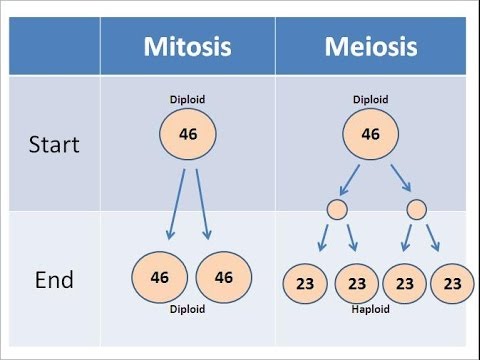
- 😀 Mitosis is the process of cell division where one cell duplicates into two identical daughter cells with the same genetic code.
- 😀 Mitosis consists of two main stages: Karyokinesis (nuclear division) and Cytokinesis (cytoplasmic division).
- 😀 The cell prepares for division during Interphase, which includes protein synthesis, DNA duplication, and enzyme activation.
- 😀 Mitosis involves four main phases: Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, and Telophase.
- 😀 Prophase sees the chromosomes condense, the nuclear envelope disintegrate, and the mitotic spindle begin to form.
- 😀 In Metaphase, chromosomes align at the cell's center, and microtubules connect to their centromeres.
- 😀 Anaphase is the phase where sister chromatids are pulled apart to opposite sides of the cell.
- 😀 Telophase marks the end of mitosis, with the nuclear envelope reforming and the cell preparing to split into two.
- 😀 Mitosis is crucial for growth, tissue repair, and the regeneration of lost or damaged body parts.
- 😀 Meiosis is a process of cell division that reduces chromosome numbers by half, forming four genetically unique haploid cells (sperm and eggs).
- 😀 Meiosis includes two divisions: Meiosis 1, which separates homologous chromosomes, and Meiosis 2, which separates sister chromatids.
Q & A
What is the difference between mitosis and meiosis?
-Mitosis is a process where a single cell divides to produce two identical daughter cells, while meiosis is a two-step division process that results in four daughter cells, each with half the genetic material of the parent cell, typically seen in the formation of gametes (sperm and eggs).
What are the phases of mitosis?
-Mitosis is divided into four main phases: Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, and Telophase, followed by Cytokinesis, which divides the cytoplasm and completes the cell division.
What is the significance of mitosis?
-Mitosis is crucial for growth, development, tissue repair, and the replacement of damaged cells in multicellular organisms. It also ensures that daughter cells have identical genetic material, maintaining consistency in cellular function.
How does genetic variation occur during meiosis?
-Genetic variation in meiosis arises from processes like homologous recombination (crossover), where homologous chromosomes exchange genetic material, creating new combinations of alleles in the gametes.
What happens during prophase 1 of meiosis?
-During prophase 1, homologous chromosomes pair up and undergo homologous recombination (crossing over), exchanging segments of DNA, which enhances genetic diversity. This phase is also marked by the disappearance of the nuclear envelope and the formation of spindle fibers.
What is the role of the centromere in mitosis and meiosis?
-The centromere is the region where two sister chromatids are joined together. During both mitosis and meiosis, the centromere plays a key role in chromosome alignment and separation by anchoring the chromosomes to spindle fibers for proper segregation.
What is the result of mitosis in terms of chromosome number?
-Mitosis results in two daughter cells, each with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell. The chromosome number remains constant, maintaining genetic consistency across cells.
How does meiosis contribute to sexual reproduction?
-Meiosis contributes to sexual reproduction by producing haploid gametes (sperm and eggs), each containing half the number of chromosomes of the parent cell. When fertilization occurs, the diploid chromosome number is restored in the zygote.
What happens during metaphase 1 in meiosis?
-During metaphase 1 of meiosis, homologous chromosome pairs align along the metaphase plate. This alignment is critical for the separation of the chromosome pairs during the subsequent stages of meiosis.
Why is cytokinesis important after mitosis and meiosis?
-Cytokinesis is the process that divides the cytoplasm and other cell contents, resulting in the formation of two separate cells after mitosis or four cells after meiosis. It ensures that each daughter cell has the necessary components to function independently.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenant5.0 / 5 (0 votes)