Cell Division: Meiosis vs. Mitosis
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the processes of mitosis and meiosis, which are essential types of cell division. Mitosis involves one division, resulting in two genetically identical diploid cells, crucial for growth and repair. Meiosis, on the other hand, consists of two divisions, creating four genetically unique haploid gametes, which are necessary for sexual reproduction. The video highlights key stages in both processes, such as prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase, and explains how mechanisms like crossing over and independent assortment contribute to genetic diversity.
Takeaways
- 😀 Mitosis is a type of cell division that plays crucial roles in embryonic development, tissue growth, and cell repair.
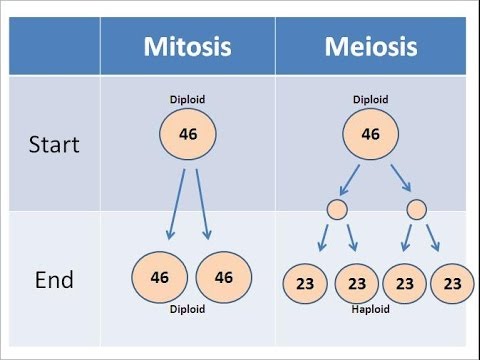
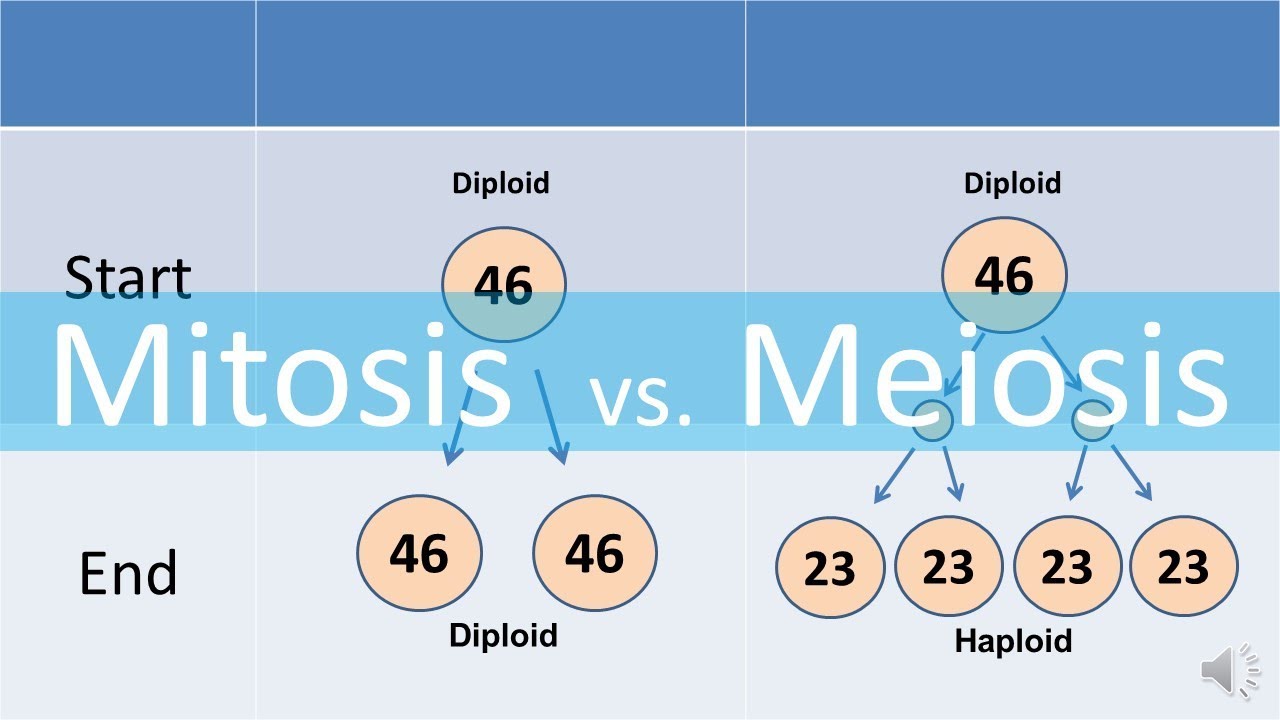
- 😀 Mitosis results in two daughter cells with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell, making them diploid.
- 😀 In mitosis, DNA replication is followed by prophase, during which chromatin condenses into chromosomes.
- 😀 During metaphase in mitosis, spindle fibers align chromosomes in the center of the cell.
- 😀 In anaphase of mitosis, each chromosome splits into two identical chromatids, which are pulled to opposite ends of the cell.
- 😀 Telophase marks the reforming of nuclear envelopes around chromosomes as the cell finishes dividing.
- 😀 Meiosis is a two-stage cell division process that creates gametes (sperm and eggs) with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
- 😀 Meiosis results in four haploid daughter cells, each with 23 unpaired chromosomes.
- 😀 In meiosis 1, crossing over occurs, where chromatids exchange DNA sections, creating new gene combinations.
- 😀 Independent assortment during meiosis 1 randomly arranges chromosome pairs, increasing genetic diversity.
- 😀 Meiosis 2 is similar to mitosis, but the resulting daughter cells are haploid and contain unique sets of chromosomes, ensuring genetic variability.
Q & A
What is the primary purpose of mitosis?
-The primary purpose of mitosis is to promote tissue growth, replace damaged or dying cells, and support embryonic development.
How do the daughter cells produced in mitosis compare to the parental cell?
-The daughter cells produced in mitosis contain the same number of chromosomes as the parental cell and are genetically identical to it.
What is the significance of the term 'diploid' in relation to mitosis?
-'Diploid' refers to the fact that the daughter cells in mitosis contain 23 pairs of chromosomes, one from the mother and one from the father, making them genetically similar to the parent cell.
What key events happen during prophase in mitosis?
-During prophase, chromatin condenses into chromosomes, each consisting of two identical sister chromatids, the nuclear envelope dissolves, and spindle fibers begin to grow from the centrioles.
What is the main difference between mitosis and meiosis in terms of cell division?
-Mitosis involves one division, producing two genetically identical daughter cells, while meiosis involves two divisions, producing four daughter cells with half the chromosome number of the original cell.
What are gametes, and how are they related to meiosis?
-Gametes are reproductive cells, namely eggs and sperm, produced by meiosis. Meiosis reduces the chromosome number by half to ensure that when gametes combine during fertilization, the resulting zygote has the correct number of chromosomes.
How does crossing over during prophase 1 of meiosis contribute to genetic diversity?
-Crossing over involves chromatids exchanging corresponding sections of DNA, leading to new combinations of genes and contributing to genetic variability among offspring.
What role does independent assortment play in meiosis?
-Independent assortment occurs during metaphase 1 when homologous chromosome pairs line up randomly. This random arrangement of chromosomes ensures genetic variation in the resulting gametes.
What happens during anaphase 1 of meiosis?
-During anaphase 1, homologous chromosome pairs separate and move to opposite ends of the cell, reducing the chromosome number by half.
How does meiosis contribute to human genetic variability?
-Meiosis produces gametes with unique sets of chromosomes due to crossing over and independent assortment. When fertilization occurs, the genetic material from two parents combines, resulting in genetic diversity.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)