Photosynthesis Steps and Pathways
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the process of photosynthesis, detailing the two main steps: the light reaction and the dark reaction (Calvin cycle). In the light reaction, light energy is captured, water is split to produce ATP and NADPH, and oxygen is released. The dark reaction utilizes these energy molecules to convert carbon dioxide into glucose. The video also touches on variations like C4 and CAM pathways, highlighting how different plants adapt their photosynthesis to conserve water. This informative overview provides insight into the essential role of photosynthesis in plant life.
Takeaways
- 🌞 Photosynthesis occurs in two main stages: light reactions and dark reactions (Calvin cycle).
- 💡 The light reactions take place in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts, capturing light energy.
- 💧 Water is split during the light reactions, producing oxygen as a byproduct and releasing electrons.
- 🔋 The light reactions generate energy molecules ATP and NADPH, essential for the dark reactions.
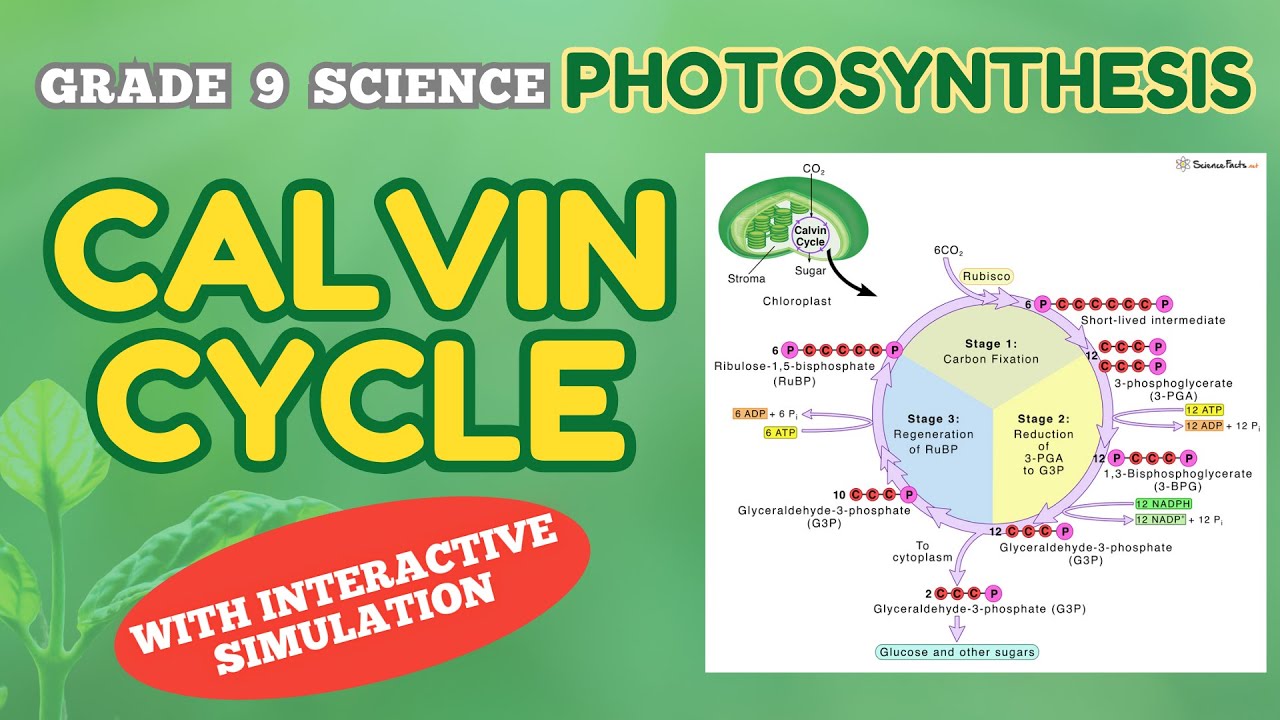
- 🌿 The dark reactions (Calvin cycle) occur in the stroma, where CO2 is converted into glucose.
- 🔄 It takes six turns of the Calvin cycle to produce one glucose molecule (C6H12O6).
- 🌍 C4 plants, like corn, adapt by creating a four-carbon compound to minimize water loss during the day.
- 🌵 CAM plants, such as cacti, open their stomata at night to conserve water and take in CO2.
- ⚗️ NADP+ and ADP produced in the dark reactions can be recycled back to the light reactions.
- 👩🏫 Understanding these processes highlights the efficiency and adaptability of plants in various environments.
Q & A
What are the two main steps of photosynthesis?
-The two main steps of photosynthesis are the light reaction and the dark reaction (Calvin cycle).
Where do the light reactions occur in the chloroplast?
-The light reactions occur in the thylakoid membranes of the chloroplast.
What is produced as a byproduct of the light reaction?
-Oxygen (O₂) is produced as a byproduct of the light reaction when water is split.
What are the main products generated during the light reaction?
-The main products of the light reaction are ATP and NADPH, which are energy carriers.
What is the function of the electron transport chain in photosynthesis?
-The electron transport chain transfers excited electrons from photosystems, facilitating the production of NADPH and ATP while moving hydrogen ions into the thylakoid space.
How does the Calvin cycle utilize carbon dioxide?
-The Calvin cycle utilizes six carbon dioxide molecules to synthesize glucose, using ATP and NADPH produced in the light reactions.
What does the term 'dark reaction' imply, and is it always dark?
-'Dark reaction' implies that these reactions do not require light directly, but they can still occur in the presence of light.
How many turns of the Calvin cycle are needed to produce one molecule of glucose?
-It takes six turns of the Calvin cycle to produce one molecule of glucose.
What adaptations do C4 plants have for photosynthesis?
-C4 plants, like corn, produce a four-carbon compound that allows them to partially close their stomata during the day to minimize water loss.
How do CAM plants adapt to conserve water?
-CAM plants, such as cacti, open their stomata at night to collect CO₂ and close them during the day, allowing them to conserve water in hot environments.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

Reaksi Gelap Fotosintesis ( Fiksasi CO2 / Siklus Calvin)

Calvin cycle | Dark reaction | C3 Cycle | Photosynthesis | Home Revise
PHOTOSYNTHESIS: CALVIN CYCLE || Grade 9 Science _ BIOLOGY

GENERAL BIOLOGY I - Photosynthesis | Light-dependent Reactions and Light-independent Reactions

Apakah hubungan Fotosintesis dengan Reaksi Terang dan Reaksi Gelap?

Reaksi Gelap Fotosintesis Learn
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
