Reaksi Gelap Fotosintesis ( Fiksasi CO2 / Siklus Calvin)
Summary
TLDRIn this video, Widyaningsih explains the dark reaction of photosynthesis, focusing on the Calvin cycle, where carbon dioxide (CO2) is fixed into glucose. The process occurs in the chloroplast stroma and doesn’t require sunlight. Key stages include CO2 binding with ribulose diphosphate (RuBP), the conversion of phosphoglyceric acid (PGA) into phosphoglyceraldehyde (PGAL), and the formation of glucose using energy from ATP and NADPH produced during the light reaction. The video also highlights the key differences between the dark and light reactions, emphasizing the CO2 fixation mechanism and the role of enzymes in the Calvin cycle.
Takeaways
- 😀 The dark reaction of photosynthesis, also known as CO2 fixation, occurs in the chloroplast stroma and does not require sunlight.
- 😀 The Kelvin cycle is responsible for binding CO2 into glucose (C6H12O6), and involves ribulose diphosphate (RuBP) as the starting molecule.
- 😀 ATP and NADPH, produced during the light reaction of photosynthesis, are used in the dark reaction to convert phosphoglyceric acid (PGA) into phosphoglyceraldehyde (PGAL).
- 😀 The primary outcome of the dark reaction is the production of glucose or carbohydrates, which is essential for the plant’s energy needs.
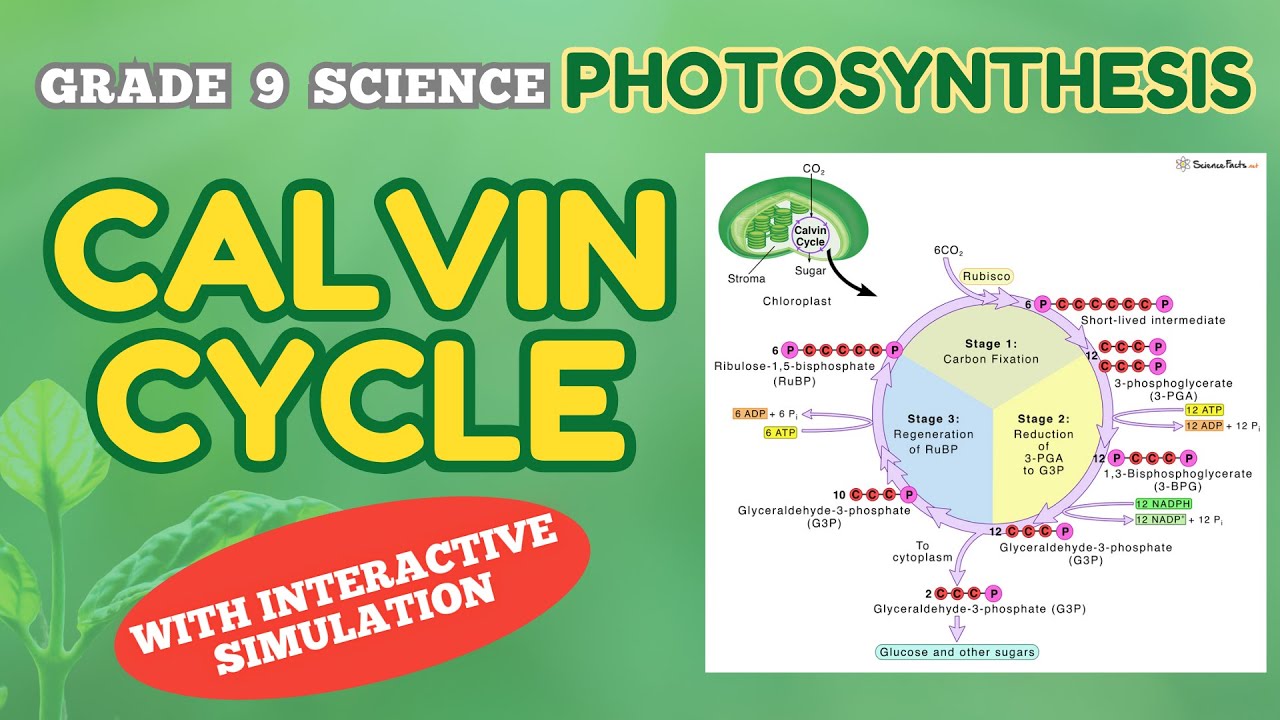
- 😀 The CO2 fixation process begins with the binding of 6 CO2 molecules to 6 RuBP molecules, forming 12 phosphoglyceric acid (PGA) molecules.
- 😀 The Kelvin cycle uses ATP and NADPH to convert PGA into phosphoglyceraldehyde (PGAL), which eventually forms glucose.
- 😀 In the final stages of the Kelvin cycle, 10 PGAL molecules are converted back into RuBP, completing the cycle.
- 😀 The dark reaction is not dependent on light, which is why it is termed as such, though it still requires the energy from the light reaction (ATP and NADPH).
- 😀 A key distinction between the light and dark reactions is that the light reaction involves electron flow, photolysis, and light capture by chlorophyll, while the dark reaction involves CO2 fixation and carbohydrate synthesis.
- 😀 The process of photosynthesis overall combines the light and dark reactions, with the end result being the production of glucose (C6H12O6) from CO2 and H2O.
Q & A
What is the dark reaction of photosynthesis?
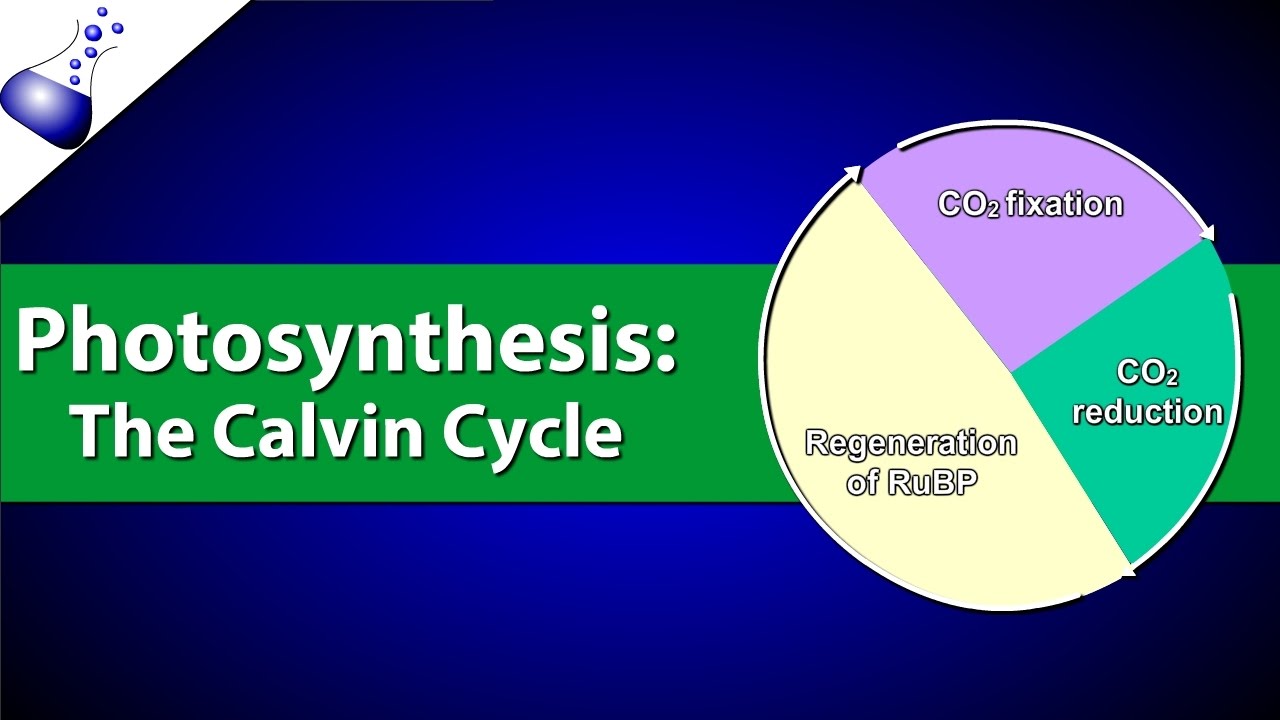
-The dark reaction of photosynthesis is a process that does not require sunlight. It involves the fixation of CO2 into glucose, which is also known as the Calvin cycle, occurring in the chloroplast stroma.
Why is the dark reaction called the 'dark reaction'?
-It is called the 'dark reaction' because it does not require sunlight to take place. Instead, it uses the products from the light reaction, such as ATP and NADPH, to fix CO2 into glucose.
Where does the dark reaction occur in the cell?
-The dark reaction occurs in the stroma, the fluid inside the chloroplasts, where CO2 is fixed into carbohydrates through the Calvin cycle.
What is the first step in the Calvin cycle?
-The first step of the Calvin cycle involves the binding of 6 molecules of CO2 with 6 molecules of ribulose diphosphate (RuBP), resulting in the formation of phosphoglyceric acid (PGA).
What role do ATP and NADPH play in the Calvin cycle?
-ATP and NADPH, produced in the light reaction, provide the energy needed to convert phosphoglyceric acid (PGA) into phosphoglyceraldehyde (PGAL), a sugar molecule, in the Calvin cycle.
What happens to the 10 molecules of PGAL in the Calvin cycle?
-The 10 molecules of PGAL are used to regenerate RuBP (ribulose diphosphate), which allows the cycle to continue. Only 2 molecules of PGAL are used to form glucose or carbohydrates.
What is the end product of the dark reaction?
-The end product of the dark reaction is glucose (C6H12O6), a carbohydrate that is formed from the fixation of CO2 during the Calvin cycle.
What is the relationship between the light reaction and the dark reaction?
-The light reaction and dark reaction are interconnected. The light reaction captures sunlight to produce ATP and NADPH, which are then used in the dark reaction (Calvin cycle) to fix CO2 into glucose.
Which processes occur during the light reaction of photosynthesis?
-The light reaction involves the capture of light energy by chlorophyll, the flow of electrons through the photosystems, and the breakdown of water molecules (photolysis), which produces ATP and NADPH.
What is CO2 fixation in the context of photosynthesis?
-CO2 fixation refers to the process in which carbon dioxide (CO2) is bound to RuBP (ribulose diphosphate) in the dark reaction, ultimately leading to the production of glucose through the Calvin cycle.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)