GENERAL BIOLOGY I - Photosynthesis | Light-dependent Reactions and Light-independent Reactions
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the essential biological process of photosynthesis, highlighting its two main stages: light-dependent reactions and light-independent reactions (Calvin cycle). It explains how plants convert sunlight into chemical energy stored in glucose, detailing the role of chlorophyll, the splitting of water, and the production of ATP and NADPH. The Calvin cycle utilizes these energy carriers to fix carbon dioxide into glucose, demonstrating the fundamental process that fuels life on Earth. Through this intricate dance of light and chemistry, photosynthesis sustains not only plants but all organisms that rely on them for oxygen and food.
Takeaways
- 😀 Photosynthesis is a vital biological process that converts sunlight into chemical energy stored in glucose.
- 🌱 It occurs in the chloroplasts of plant cells, primarily within the leaves.
- ☀️ The process consists of two main stages: light dependent reactions and light independent reactions (Calvin Cycle).
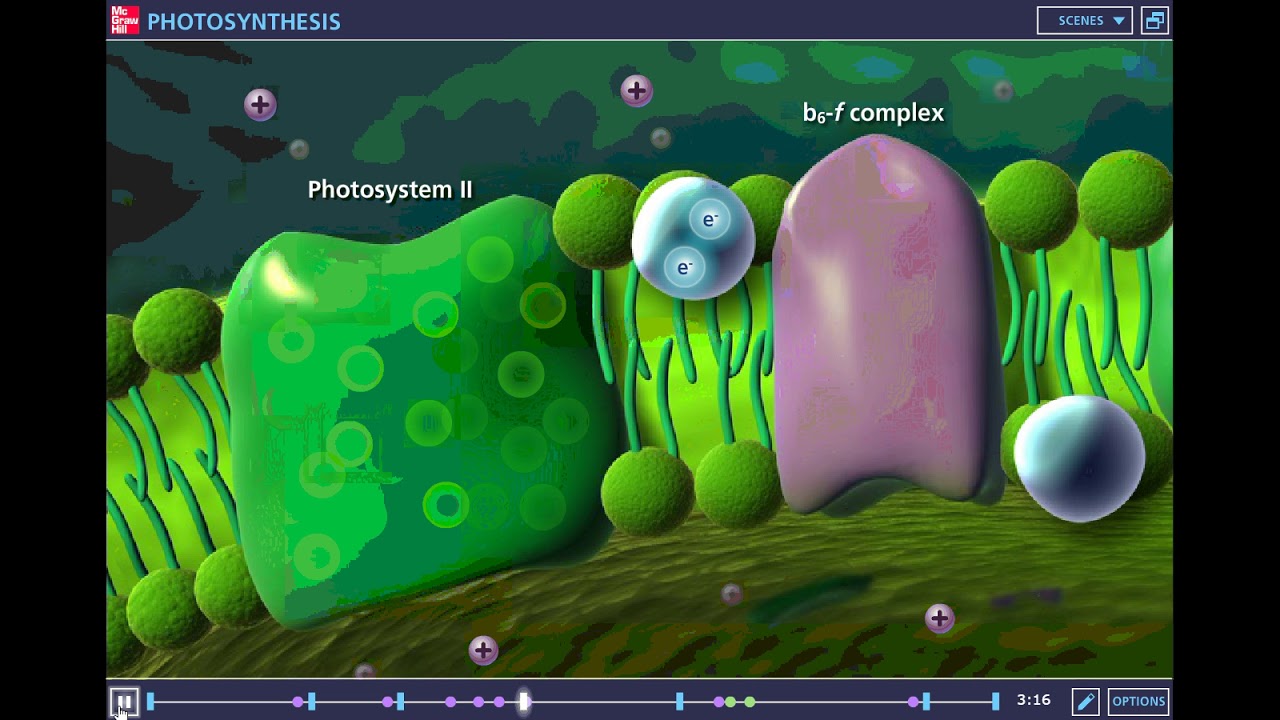
- ⚡ The light dependent reactions take place in the thylakoid membranes and require sunlight to generate ATP and NADPH.
- 💧 Water molecules are split during the light dependent reactions, producing oxygen as a byproduct.
- 🔋 High-energy electrons produced in photosystem II are transferred through an electron transport chain, creating a proton gradient that powers ATP synthesis.
- 🔄 The Calvin Cycle occurs in the stroma of chloroplasts, using ATP and NADPH to convert carbon dioxide into glucose.
- 🔬 The enzyme rubisco captures carbon dioxide and initiates the Calvin Cycle, producing glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (G3P).
- 🌾 Two molecules of G3P are required to form one glucose molecule, emphasizing the cycle's efficiency.
- 🍬 Glucose produced is essential for plant growth and serves as a starting molecule for synthesizing starch and cellulose.
Q & A
What is photosynthesis?
-Photosynthesis is a biological process that allows plants, algae, and some bacteria to convert light energy from the sun into chemical energy stored in glucose.
What are the two main stages of photosynthesis?
-The two main stages of photosynthesis are the light-dependent reactions and the light-independent reactions (Calvin cycle).
Where does photosynthesis occur in plant cells?
-Photosynthesis occurs in the chloroplasts of plant cells, primarily within the leaves.
What is the role of Photosystem II in the light-dependent reactions?
-Photosystem II absorbs light energy, which excites electrons and initiates the process of photolysis, splitting water molecules and releasing oxygen.
How do light-dependent reactions generate ATP?
-Light-dependent reactions create a proton gradient by pumping hydrogen ions into the thylakoid space, which powers ATP synthase to convert ADP into ATP.
What is photolysis, and what are its products?
-Photolysis is the process of splitting water molecules using light energy, resulting in oxygen, protons, and electrons.
What happens to the electrons after they pass through the electron transport chain?
-After passing through the electron transport chain, the electrons are re-energized in Photosystem I and used to reduce NADP+ to NADPH.
What occurs during the Calvin cycle?
-During the Calvin cycle, ATP and NADPH from the light-dependent reactions are used to fix carbon dioxide into glucose through carbon fixation, reduction, and regeneration phases.
What is the role of the enzyme RuBisCO in photosynthesis?
-RuBisCO captures carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and attaches it to ribulose bisphosphate, facilitating the first step of the Calvin cycle.
How many turns of the Calvin cycle are needed to produce one molecule of glucose?
-The Calvin cycle must turn six times to produce one molecule of glucose.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)