Animation of Router working while Forwarding Packets in Networks
Summary
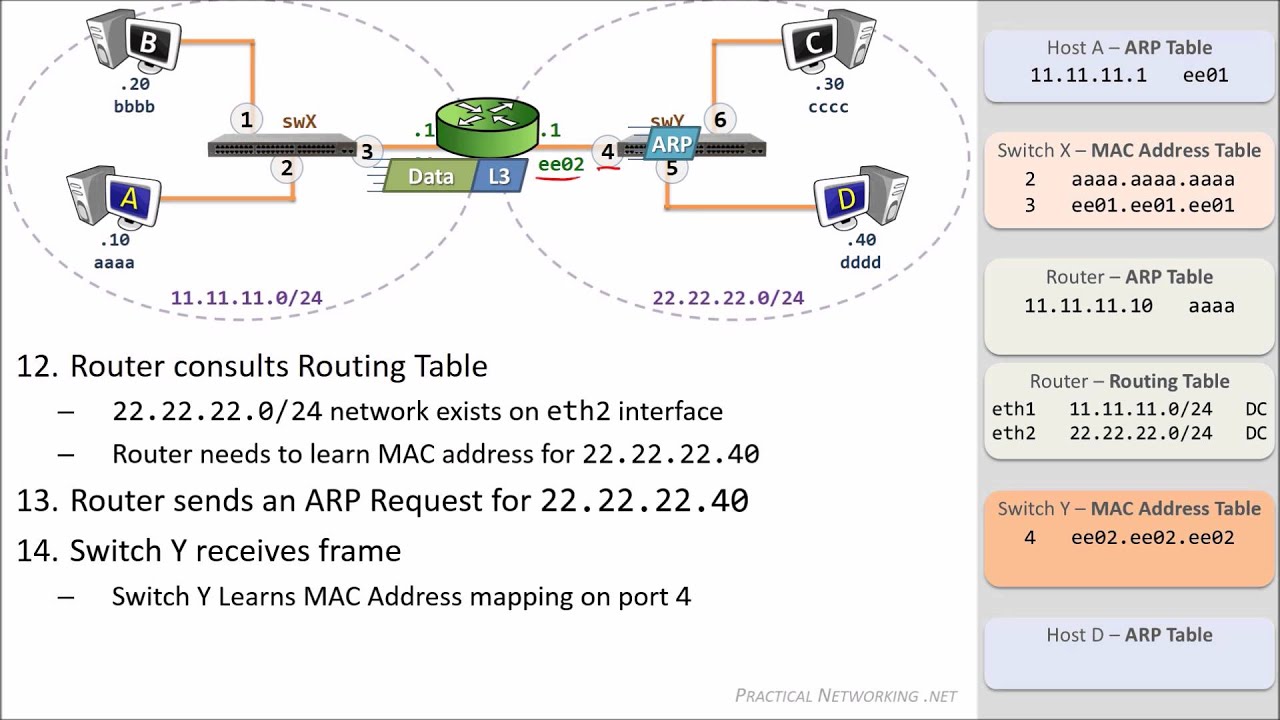
TLDRThis video explains the operation of a router in a data transmission scenario between two computers. It outlines how Computer 1 sends data to Computer 2 by creating a packet with the appropriate source and destination IP addresses. The data frame is directed to the router's interface, where the router checks its routing table to determine the best route. Upon finding that Computer 2's network is connected to its eth1 interface, the router creates a new frame with the correct MAC addresses and forwards it to Computer 2, successfully completing the data transmission process.
Takeaways
- 📦 Data transmission begins with Computer 1 sending data to Computer 2.
- 🔍 The packet header is filled with the source and destination IP addresses.
- 📡 A data frame is created for transmission to the router's eth0 interface.
- 🔗 The destination MAC address in the frame header is set to the router's eth0 MAC address.
- 🖥️ The source MAC address is filled with Computer 1's MAC address.
- 🚀 The frame is sent from Computer 1 to the router.
- 📖 The router reads the destination IP address upon receiving the frame.
- 🗺️ The router consults its routing table to find the destination network.
- 🔄 The router identifies that the destination network is connected to its eth1 interface.
- 📤 A new frame is created with Computer 2's MAC address as the destination and forwarded out of the eth1 interface.
Q & A
What is the initial action taken by Computer 1 when it wants to send data to Computer 2?
-Computer 1 fills in the packet header with the destination IP address of Computer 2 and its own source IP address.
What is created after the packet header is filled in?
-A frame is created, which includes the MAC addresses for delivery.
What MAC address is used as the destination in the frame header?
-The MAC address of the router's eth0 interface is used as the destination MAC address in the frame header.
How does Computer 1 identify its own MAC address in the frame?
-Computer 1 fills in its own MAC address as the source MAC address in the frame.
What does the router do upon receiving the frame from Computer 1?
-The router reads the destination IP address and consults its routing table to determine the next hop.
What does the router determine about the destination network?
-The router determines that the destination network (172.31.0.0) is directly connected to its eth1 interface.
What happens after the router identifies the destination network?
-The router creates a new frame using Computer 2's MAC address as the destination and the MAC address of its eth1 interface as the source.
Which interface does the router use to forward the frame to Computer 2?
-The router forwards the new frame out through its eth1 interface.
What is the result of this data transmission process?
-Computer 2 successfully receives the frame sent by Computer 1.
Why is it important for the router to consult its routing table?
-Consulting the routing table allows the router to determine the best path to the destination network.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

Cómo conectar dos PCs con un cable ethernet cruzado (crossover), para compartir carpetas y archivos

18. CAMBRIDGE IGCSE (0478-0984) 2.1 Data transmission methods

Uji Kompetensi Keahlian TKJ Paket 4 - Cara Sharing File Menggunakan Kabel UTP (Peer to Peer)
Packet Traveling - How Packets Move Through a Network

Bab 3 Aktivitas Belajar 3 3

What is USB and What Does it Stand for? Explained Simply for Beginners by The Tech Academy
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
